Immunodeficiencies
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Immunodeficiencies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll be discussing immunodeficiencies. Can anyone tell me what the immune system does?

Isn't it supposed to protect the body from infections and diseases?

Exactly! Now, when we talk about immunodeficiencies, we're discussing conditions where this protective ability is weakened. Can you think of why someone might have a weak immune system?

Maybe because of some genetic disorder?

Or if they got infected by a virus like HIV!

Great points! We have congenital immunodeficiencies which are genetic and acquired ones, like those caused by infections. Let's remember: 'C' for Congenital and 'A' for Acquired to recall these types!

That's a good way to remember it!

At the end of our session, we'll revisit these definitions to ensure they're clear.
Congenital Immunodeficiencies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive deeper into congenital immunodeficiencies. Can someone explain what that means?

Those are immunodeficiencies that a person is born with, right?

Exactly! A classic example is Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, or SCID. How might this affect a child?

They would struggle to fight off infections since both T and B cells are affected.

Right! No functioning immune cells mean higher vulnerability. Remember 'SCID' as 'Severe Compromised Immune Defense' to enhance recall.

That makes sense!
Acquired Immunodeficiencies: HIV/AIDS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we have acquired immunodeficiencies, such as those caused by HIV/AIDS. What do you know about this?

HIV is a virus that targets T cells, right?

Correct! It specifically attacks the CD4 T cells. Why is this significant?

Because it weakens the immune system and makes it harder to fight off infections?

Exactly right! You can remember this by associating 'HIV' with 'Highly Impairing Virus' for easy recall. What are some opportunistic infections associated with this?

Things like pneumonia and certain types of cancers, right?

Yes! Very well summarized. This is why awareness and prevention are vital.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses various immunodeficiencies, their causes—including congenital factors and infections like HIV/AIDS— and the implications for the affected individuals. Understanding these conditions is crucial for both diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Detailed
Immunodeficiencies
Immunodeficiencies are significant conditions that result in reduced efficacy of the immune system, which can be either acquired or congenital. Congenital immunodeficiencies are genetic disorders present at birth, while acquired immunodeficiencies may arise from infections, medications, malnutrition, or diseases.
Types of Immunodeficiencies
- Congenital Immunodeficiencies: These are genetic disorders where the immune system's development is impaired, leading to increased susceptibility to infections from a young age. Examples include Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) and X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia.
- Acquired Immunodeficiencies: Such as those seen in HIV/AIDS, where the virus attacks and destroys CD4 T cells, drastically impairing the body's immune response. This leads to opportunistic infections, which are infections that occur more frequently and are more severe in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Understanding these disorders is crucial for developing effective treatments and support mechanisms for affected individuals, highlighting the importance of immunology in both medical research and clinical practice.
Youtube Videos

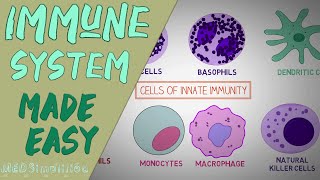



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Immunodeficiencies
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Conditions where the immune system is weakened or absent, such as in HIV/AIDS or congenital immunodeficiencies.
Detailed Explanation
Immunodeficiencies are medical conditions that compromise the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections and diseases. This weakness can either be due to an external factor, such as an infection like HIV/AIDS, or be present at birth due to congenital immunodeficiencies, which are genetic disorders that affect the immune system's ability to function properly.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the immune system as a security team guarding a building. If the team is fully staffed and well-trained (a healthy immune system), they can effectively prevent intruders (pathogens) from entering and causing harm. However, if some team members are missing or not functioning correctly (as in immunodeficiencies), intruders can easily break in, leading to potential problems and damage to the building (the body).
HIV/AIDS as an Immunodeficiency Example
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Such as in HIV/AIDS.
Detailed Explanation
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that specifically attacks the immune system, particularly the CD4+ T cells, which are critical for coordinating the immune response. As the virus progresses, the individual's immune system weakens considerably, leading to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), where the body becomes highly susceptible to opportunistic infections and certain cancers due to its inability to fight off these threats.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine someone who has a very small and outdated fire department (the immune system) to protect a large city. If a new fire starts (an infection), the small department struggles to respond quickly and effectively, leading to disastrous consequences. This is similar to what happens in individuals with HIV/AIDS; the immune system's inability to respond properly allows infections to take hold and spread.
Congenital Immunodeficiencies
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Such as congenital immunodeficiencies.
Detailed Explanation
Congenital immunodeficiencies are inherited disorders that are present at birth and affect how the immune system functions. These conditions can manifest in various ways, from mild to severe, and can include issues such as the absence of certain immune cells or the malfunctioning of immune pathways. Patients with congenital immunodeficiencies often experience frequent infections and may need medical interventions like immunoglobulin therapy or stem cell transplants to manage their condition.
Examples & Analogies
Think of born-with congenital immunodeficiency like having a factory that produces security alarms but is missing critical parts from the start. Because the factory (the body) can't build effective alarms (the immune response), it leads to repeated security breaches (infections) throughout the life of the factory owner (the individual).
Key Concepts
-
Immunodeficiency: A condition affecting the immune system's function.
-
Congenital Immunodeficiency: Immunodeficiency from genetic factors present at birth.
-
Acquired Immunodeficiency: Immunodeficiency developed later due to factors like infections.
Examples & Applications
A child with SCID who suffers frequent infections due to low immune response.
An adult with HIV who develops opportunistic infections like pneumonia.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When your immune system can't fight, infections will take flight.
Stories
Meet Johnny, born with no defenses, he fights infections but faces tense suspense. His friends must help, with treatments new, to fight those germs that come to view!
Memory Tools
VIP: Very Important Proficiency - for remembering who is vulnerable - immunodeficient individuals.
Acronyms
'C' for Congenital and 'A' for Acquired to remember types of immunodeficiencies.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Immunodeficiency
A condition where the immune system's ability to fight infectious disease is compromised or entirely absent.
- Congenital Immunodeficiency
A type of immunodeficiency present at birth due to genetic defects affecting the immune system.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency
A type of immunodeficiency that develops over time, often due to infections, medications, malnutrition, or diseases.
- HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus, a virus that attacks the immune system, leading to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
