B Cells
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to B Cells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to learn about B cells, which are an essential part of our immune system. Can anyone tell me what they might think B cells do?

Do they help us fight off infections?

Exactly! B cells produce antibodies that bind to pathogens, neutralizing them. Think of them as the 'soldiers' of our immune system. They're part of the adaptive immune response, which means they have a specific target.

So what's the difference between B cells and other immune cells?

Great question! While some immune cells respond quickly to infections, B cells can remember specific pathogens due to some of them becoming memory B cells. So they can respond much quicker the next time we encounter the same pathogen.

Why do we need to remember these pathogens?

In summary, if we encounter the same pathogen again, memory B cells help us mount a faster and stronger immune response. This concept is central to how vaccines work! Any other questions about B cells?
Antibody Functionality
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what B cells are, let's talk about the antibodies they produce. What do you think antibodies do?

They must help to fight off germs, right?

Yes! Antibodies bind to antigens on pathogens. This binding can neutralize the pathogen directly or mark it for attack by other immune cells.

How do the antibodies recognize the pathogens?

Antibodies are very specific; they have unique structures that fit with specific antigens, like a key fits into a lock. If a pathogen mutates, the antibodies might not work as well.

That sounds like why we need new vaccines sometimes!

Exactly! When we get new strains, our B cells might need to learn to recognize the new types of antigens, which is why some vaccines are updated annually. Let's summarize: B cells create antibodies specifically designed for pathogens, and they also form memory cells for future responses.
Memory B Cells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now focus on memory B cells. Can someone explain what they think memory B cells do?

Are they the cells that help remember previous infections?

Exactly! Memory B cells remain in the body long after the initial infection is cleared. This allows our body to respond rapidly to future infections by the same pathogen.

How do vaccines take advantage of memory B cells?

Great insight! Vaccines expose the immune system to a harmless form of an antigen, which helps generate memory B cells without causing disease. So if the body encounters the real pathogen later, it can respond quickly.

Just like when we get chickenpox once and we don’t get it again!

Exactly! This memory response is very efficient and crucial for long-term immunity. To summarize: Memory B cells are vital for protecting us from future infections.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
B cells are a type of lymphocyte in the adaptive immune system responsible for producing antibodies that target and neutralize pathogens. They play a vital role in the body's ability to remember and respond to previously encountered pathogens.
Detailed
B Cells
B cells, a fundamental component of the adaptive immune system, play a crucial role in the body's defense against pathogens. These lymphocytes are primarily responsible for producing antibodies, which specifically bind to antigens on pathogens, neutralizing their harmful effects.
Key Functions and Characteristics
- Antibody Production: B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibodies that target specific antigens.
- Memory B Cells: After an initial immune response, some B cells form memory cells that enable a faster and more effective response upon subsequent exposure to the same antigen.
- Involvement in Humoral Immunity: They are integral to the humoral immune response, providing a specific line of defense in the body's immune arsenal.
Understanding the functionality of B cells is vital for developing vaccines and immunotherapies, as these strategies often aim to enhance B cell responses to protect against infections.
Youtube Videos

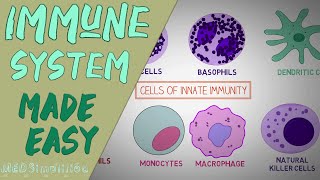



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to B Cells
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
B Cells: Produce antibodies that bind to antigens on pathogens, neutralizing them.
Detailed Explanation
B cells are a type of white blood cell that plays a critical role in the immune system. They are part of the adaptive immune response, meaning they specifically target and remember pathogens. When activated, B cells produce antibodies. These antibodies are special proteins that can attach to specific parts (antigens) on pathogens like bacteria and viruses. By binding to these antigens, antibodies can neutralize the threat and mark the pathogen for destruction by other immune cells.
Examples & Analogies
Think of B cells as smart soldiers in an army. When they encounter an enemy (the pathogen), they create special weapons (antibodies) that can attach to the enemy and either disable it or signal other soldiers to come help attack.
Function of Antibodies
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
B Cells produce antibodies that specifically recognize and bind to antigens.
Detailed Explanation
Antibodies produced by B cells are highly specific; each type of antibody can recognize a unique antigen. When an antibody binds to its corresponding antigen, it can neutralize the pathogen directly by blocking its ability to infect cells, or it can tag the pathogen for destruction by other immune cells—a process called opsonization. Antibodies also play a role in activating other immune system components that help to eliminate pathogens from the body.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a custom lock and key system. Each key is like an antibody and can only unlock a specific lock (the antigen on a pathogen). When the right key (antibody) is used on the lock (antigen), it either keeps the door closed (neutralizing the pathogen) or signals security (other immune cells) to take action against any potential intruders.
Memory B Cells
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
B Cells also form memory cells that provide long-lasting immunity.
Detailed Explanation
After a B cell has been activated and produced antibodies against a pathogen, some of these B cells become memory B cells. These cells 'remember' the specific antigens associated with the pathogen, so if the same pathogen invades the body again in the future, the memory B cells can quickly respond by producing the corresponding antibodies much faster than the first time. This is how vaccinations offer long-lasting protection against diseases.
Examples & Analogies
Think of memory B cells as having a photo album of past vacations. If you see a familiar place (a repeat infection), you can quickly recall the experiences (immune response) because of those stored memories, making it easier to respond effectively.
Key Concepts
-
B Cells: Immune cells responsible for producing antibodies.
-
Antibodies: Proteins that target pathogens for neutralization.
-
Memory B Cells: Cells that provide long-lasting immunity by remembering prior pathogens.
Examples & Applications
When a person is vaccinated against influenza, their B cells produce antibodies specific for the flu virus, aiding in faster recovery if infected again.
In a case of primary immunodeficiency, individuals may demonstrate difficulties in generating adequate B cell responses, leading to recurrent infections.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
B cells go on patrol, producing antibodies to control!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a kingdom called Immunity, B cells fought brave battles against invading pathogens with their magical weapons—the antibodies—to protect their realm forever!
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym B.A.M.: B cells Attack Microbes (with antibodies)!
Acronyms
B.A.S.E.
cells And Specificity for pathogens' Entry.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- B Cells
A type of lymphocyte that plays a significant role in the adaptive immune system by producing antibodies.
- Antibodies
Proteins produced by B cells that specifically recognize and bind to antigens on pathogens.
- Memory B Cells
Long-lived cells formed after an infection that help recognize and respond more rapidly to subsequent encounters with the same pathogen.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
