Passive Immunity
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Passive Immunity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore passive immunity. Can anyone tell me what they understand about it?

Isn't it about receiving antibodies from someone else?

That's correct! Passive immunity is when antibodies are transferred from one individual to another. This can provide quick, temporary protection.

So, it's like getting a shortcut to immunity?

Great analogy! It really is. While it offers immediate protection, how long do you think this immunity lasts?

Isn't it a matter of weeks or months?

Exactly! It tends to last for a few weeks to months. Now let's discuss some sources of passive immunity.
Sources of Passive Immunity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone name some sources of passive immunity?

I know maternal antibodies are a source!

Excellent! Maternal antibodies can be transmitted through the placenta or through breast milk. This provides newborns with essential protection against infections.

What about antibody therapies?

Yes! Antibody therapies, such as intravenous immunoglobulin, are another important source of passive immunity, especially for people with weak immune systems. Why do you think it's important to have these options?

It helps sick people get better more quickly!

Exactly! Passive immunity can save lives by providing immediate protection.
Comparing Active vs. Passive Immunity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's compare passive immunity with active immunity. What are some of the major differences?

I think active immunity takes longer because the body has to make antibodies.

Correct! Active immunity is the result of the body's immune response to an infection or a vaccine, and it takes time to develop. Passive immunity provides immediate protection.

But isn't one better than the other?

Not exactly. They serve different purposes. Passive immunity is useful for immediate defense, while active immunity provides long-term protection and memory. Can you think of a situation where each would be useful?

Maybe passive for newborns and active for vaccinations?

Exactly! You've made great connections there.
Real-World Applications of Passive Immunity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's discuss real-world applications of passive immunity. How is it used in healthcare?

Vaccines?

Good try, but vaccines stimulate active immunity. Passive immunity involves direct transfer of antibodies. It’s often used with treatments for infectious diseases or in rare cases of severe allergies.

Like when someone gets a shot for rabies?

Exactly! After potential exposure to rabies, passive immunity is essential for effective treatment. This quick intervention can be lifesaving. Why do you think it’s crucial to act fast in such cases?

Because the disease can be deadly?

That's right! Passive immunity plays a vital role in preventing infections when time is of the essence.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Passive immunity is a type of immunity that occurs when antibodies are transferred from one individual to another, such as from mother to child through breast milk or from an injection of antibody-containing serum. It offers immediate but temporary protection against infections.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Passive immunity is characterized by the acquisition of antibodies from an external source rather than producing them through the host's immune response. This type of immunity is particularly significant during early life, where maternal antibodies provide newborns with essential defense against infections.
Key Points:
- Definition: Passive immunity involves the transfer of antibodies from one individual to another.
- Examples:
- Maternal antibodies transferred through the placenta during pregnancy or through breast milk.
- Antibody therapies, such as immunoglobulin treatments, used for immediate protection against certain diseases.
- Duration: The protection provided by passive immunity is temporary, lasting only a few weeks to months, depending on the source and type of antibodies involved.
- Contrast with Active Immunity: Unlike active immunity, where the body produces its own antibodies following exposure to an antigen, passive immunity does not involve immune memory, rendering it a swift but short-term solution against infections.
Youtube Videos

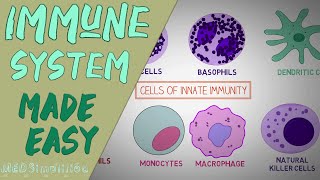

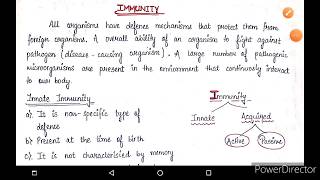


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Passive Immunity
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Passive Immunity: The transfer of antibodies from another source (e.g., maternal antibodies or antibody therapies).
Detailed Explanation
Passive immunity refers to the process where an individual receives antibodies from another source rather than producing them on their own. This can occur naturally, for example, when a mother passes antibodies to her baby through the placenta during pregnancy or through breast milk after birth. Alternatively, it can happen artificially, for instance, through antibody therapies where pre-formed antibodies are administered to treat certain infections or conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of passive immunity like borrowing an umbrella. When it rains, you might not have your own umbrella to keep you dry, but if a friend lends you theirs, you can stay dry until the rain stops. Similarly, passive immunity gives someone immediate protection by using antibodies that someone else has already produced.
Natural Passive Immunity
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Natural passive immunity develops when antibodies are transferred from mother to child.
Detailed Explanation
Natural passive immunity occurs specifically when a mother transfers her antibodies to her child. This transfer can happen during pregnancy through the placenta, where antibodies cross over to protect the fetus from infections. After birth, breastfeeding continues to provide passive immunity, as breast milk is rich in antibodies that help safeguard the infant during its early life when its immune system is still developing.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a mother hen keeping her chicks warm under her wings. Just like the hen protects her chicks from the cold, a mother provides her baby with antibodies to protect them from diseases. The protection is immediate, just like how the chicks feel safe right away.
Artificial Passive Immunity
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Artificial passive immunity can be achieved through the administration of antibodies prepared in advance.
Detailed Explanation
Artificial passive immunity involves giving a person antibodies from another source, usually through medical treatment. This is often done with immune globulin injections, which contain antibodies specific to infectious agents. For example, after exposure to tetanus toxin, a patient may receive tetanus immunoglobulin to quickly provide protection while their own immune system starts to respond to the infection.
Examples & Analogies
Consider it like getting a ride home from a friend when your car breaks down. Your friend is providing you with a quick solution while you sort out your own vehicle. Similarly, artificial passive immunity gives a person rapid protection from illness while their immune system begins to build its defenses.
Duration and Limitations of Passive Immunity
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The effects of passive immunity are temporary, as the body does not produce its own antibodies.
Detailed Explanation
One key characteristic of passive immunity is that it is not permanent. The antibodies received from another source gradually break down over time, and the body does not generate a memory or long-lasting immunity from this transfer. As a result, while passive immunity provides immediate protection, it does not create a lasting immune response. For example, maternal antibodies can protect an infant for several months, but after that period, the infant’s immune system must start producing its own antibodies through vaccinations or exposure to pathogens.
Examples & Analogies
Think of passive immunity as a rented apartment. While you can live there temporarily and enjoy the benefits, it is not your permanent home. Eventually, you need to find your own place (or in the case of immunity, develop your own antibodies) to ensure long-term security and protection.
Key Concepts
-
Passive Immunity: Transfer of antibodies providing immediate, temporary protection.
-
Maternal Antibodies: Vital for newborn immunity, offering protective factors during early life.
-
Antibody Therapy: Utilizes pre-made antibodies to provide quick defense against certain diseases.
Examples & Applications
Maternal antibodies transferred to a baby during pregnancy.
Rabies post-exposure prophylaxis using immunoglobulin injections.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For a baby’s safety, antibodies flow, from mother’s love, protection to show!
Stories
In a village, a mother shares her strength, protecting her child with love at length, through her breast, antibodies flow, giving the baby a shield from foe.
Memory Tools
MAB - Maternal Antibodies Boost (Aids in remembering passive immunity source).
Acronyms
PAT - Passive Antibody Transfer (to help recall passive immunity).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Passive Immunity
Immunity that results from the transfer of antibodies from one individual to another.
- Maternal Antibodies
Antibodies transferred from a mother to her child, providing protection against infections.
- Antibody Therapy
Medical treatment that utilizes antibodies to boost immune response or provide immediate immunity.
- Active Immunity
Immunity that develops as a response to exposure to an antigen, through infection or vaccination.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
