Flow Cytometry
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Flow Cytometry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we’re going to discuss flow cytometry. Can anyone tell me what they think it is?

Is it a way to analyze cells?

Exactly! Flow cytometry is a technique that allows us to analyze individual cells in a fluid. It helps researchers and clinicians examine the physical and chemical properties of cells.

What kind of properties can we analyze?

Good question! We can analyze cell size, granularity, and the expression of specific proteins using fluorescent markers.

How does it use these fluorescent markers?

Cells are tagged with fluorescent antibodies that are specific to certain cell types. This allows us to separate and count different cells based on their characteristics.

Why is that important in immunology?

It is crucial for understanding immune responses and monitoring diseases such as cancers. We’ll cover more applications in a bit!

In summary, flow cytometry is an amazing tool that provides detailed information about cells in a quick and efficient manner.
Applications of Flow Cytometry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve into how flow cytometry is applied in research and medicine. Can anyone suggest a field where it is used?

Is it used in cancer research?

Absolutely! It’s widely used to analyze cancerous cells and monitor treatment responses.

What about in the study of immune responses?

Great point! Flow cytometry helps assess immune cell populations, which is vital for developing vaccines or understanding autoimmune diseases.

Can it be used for diagnostics?

Yes, it’s a key technique in diagnosing hematological disorders by identifying and characterizing different leukocyte populations.

Are there any limitations to using flow cytometry?

Good question! Some limitations include the requirement for specific antibodies and the need for highly skilled personnel for accurate interpretation.

In summary, flow cytometry is a versatile technique with wide-ranging applications in research and diagnostics.
Technical Aspects of Flow Cytometry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s get into the technical workings of flow cytometry. Can anyone describe the basic process?

Do we start with preparing the cells?

Correct! First, cells are suspended in a fluid solution. They are then passed through a laser beam one by one.

And the lasers detect the fluorescent tags?

Yes! The lasers excite the fluorescent markers, and detectors capture the emitted light, allowing us to quantify and analyze each cell.

How do we ensure accurate results?

Calibration with standard controls is key, along with using proper panel designs for the antibodies.

What about data analysis afterward?

Data analysis requires specialized software that helps visualize and interpret the results effectively.

To sum it up, understanding these technical aspects is crucial for leveraging flow cytometry in research.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
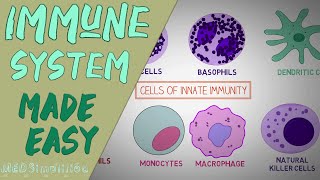
Flow cytometry provides a sophisticated method for analyzing various parameters of cells, including size, granularity, and protein expression. It is widely used in both research and clinical settings to assess immune cell populations and responses.
Detailed
Flow cytometry is an advanced technology utilized primarily to measure the physical and chemical characteristics of cells and particles suspended in a fluid. The process involves labeling cells with fluorescent antibodies that bind to specific cell surface markers, allowing for the identification and quantification of different cell types within a heterogeneous population. This technology can analyze thousands of cells per second, producing data that can be used to assess cell viability, characterizing immune responses, and analyzing cellular functions. Its application ranges from immunology research, where it helps to understand immune cell populations and their functions, to clinical diagnostics, where it assists in identifying and monitoring diseases such as leukemia and lymphoma.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Flow Cytometry
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Flow cytometry is a technique used to analyze the physical and chemical properties of cells, often used to assess immune cell populations.
Detailed Explanation
Flow cytometry is a method that allows researchers to measure and analyze the characteristics of cells as they flow in a liquid stream through a laser. This technique can identify different types of cells based on their size, granularity, and the presence of specific markers on their surface. It's particularly valuable in immunology for analyzing immune cells because it helps scientists understand the makeup and function of these cells in various diseases and treatments.
Examples & Analogies
Think of flow cytometry like a highly specialized sorting machine at a recycling plant. Just as the machine sorts materials like paper, plastic, and metal based on their characteristics, flow cytometry sorts and analyzes cells based on their unique features, helping scientists understand how cells work and what role they play in the immune system.
Applications of Flow Cytometry in Immunology
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Flow cytometry is often used to assess immune cell populations.
Detailed Explanation
In immunology, flow cytometry is crucial for studying different types of immune cells, such as lymphocytes (B cells, T cells) and their activation states. By tagging cells with fluorescent markers that attach to specific proteins, scientists can quantify how many of each type of cell are present in a sample and analyze their activation or function. This helps in understanding diseases such as infections, cancers, and autoimmune disorders, and can guide treatment decisions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're a teacher in a classroom with a variety of students (immune cells), each with different academic strengths (functions). With flow cytometry, you can quickly assess the class by looking at test scores (fluorescent markers) to understand how many students excel in math versus literature (different immune cell types). This insight helps you tailor your teaching approach to better support each student's needs, paralleling how flow cytometry aids in understanding and treating diseases.
How Flow Cytometry Works
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Flow cytometry works by passing cells through a laser and using detectors to measure different characteristics.
Detailed Explanation
In flow cytometry, a sample containing cells is injected into a flow chamber where they are aligned so that they pass one by one through a laser beam. As each cell passes through the laser, it scatters light and may emit fluorescence if tagged with fluorescent dyes. Detectors capture this information, allowing the system to analyze various parameters, such as cell size, internal complexity, and expression of surface markers, which are crucial for distinguishing different cell types.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a traffic light monitoring system. As each car (cell) passes under the traffic light (laser), sensors detect how fast it's going (size) and what color it is (specific markers). Just like this system helps monitor traffic flow and identify vehicle types, flow cytometry enables scientists to monitor cell populations and identify unique characteristics rapidly.
Key Concepts
-
Flow Cytometry: A technique for analyzing physical and chemical properties of cells.
-
Fluorescent Markers: Specific dyes that help identify proteins on cell surfaces.
-
Immune Cell Analysis: Assessing the characteristics of immune cells to understand health.
Examples & Applications
Flow cytometry can be used to differentiate between various types of leukocytes in a blood sample.
Researchers utilize flow cytometry to evaluate the effectiveness of cancer treatments by assessing cell surface markers.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Flow cytometry is nifty and bright, it analyzes cells in a flash of light!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a lab, scientists sought to understand cells. With flow cytometry, they could see each cell's colors and sizes dance under the laser lights.
Memory Tools
For FLOW: 'Fast Laser Output for Watching cells!'
Acronyms
FLUORO for Fluorescent Labels Used in Observing Responses in Organisms.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Flow Cytometry
A technique used to analyze the physical and chemical properties of cells in a fluid as they pass through a laser.
- Fluorescent Antibodies
Antibodies labeled with a fluorescent dye to detect specific proteins on the surface of cells.
- Cell Population
A group of cells sharing common characteristics, often analyzed in immunological studies.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
