Transmission of Pressure in Liquids
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Pascal’s Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing Pascal's Law. Can anyone tell me what they think this law states?

I think it has something to do with how pressure works in liquids?

Exactly, Student_1! Pascal's Law tells us that pressure applied to a confined liquid is transmitted evenly throughout the fluid. So if I push down on a liquid in a closed container, that pressure is felt everywhere equally.

Does this mean that every part of the liquid feels the same pressure?

Yes, that's correct! This is a fundamental principle that helps in understanding how various hydraulic systems work. Remember the phrase 'Equal pressure in all directions' to help you recall this concept.
Applications of Pascal’s Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand Pascal's Law, let's look at some applications. Can anyone give me an example of where we might see this law in action?

What about hydraulic lifts in car repair?

Absolutely, Student_3! In a hydraulic lift, when a small force is applied to a small piston, it creates high pressure that lifts the car using a larger piston. Isn’t that fascinating?

What about in everyday things, like brakes in cars?

Excellent observation, Student_4! Hydraulic brakes operate using the same principle. When you press the brake pedal, you apply pressure to the fluid, which is transmitted to the wheels, slowing down the car equally.
Real-Life Illustrations of Pressure Transmission
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Imagine we're all in a sealed room filled with liquid. If I push down on the surface, what happens to the pressure?

The pressure would increase everywhere, right?

Spot on! This showcases how pressure can be transmitted effectively in liquids. Let's remember that pressure doesn't just increase at one point but throughout.

So if I were to push harder, would the pressure be greater throughout?

Exactly, more force creates greater pressure, demonstrating Pascal's principle vividly. Great thinking, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
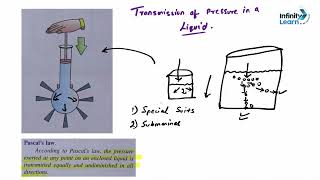
This section discusses Pascal's Law, which states that pressure applied to a confined liquid is transmitted undiminished to all points within the fluid and its container. This principle underlies various hydraulic systems, such as presses and lifts, showcasing the significant role of fluid mechanics in practical applications.
Detailed
Transmission of Pressure in Liquids
Pascal's Law states that "Pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to all parts of the fluid and to the walls of its container." This principle implies that when a force is applied to a confined liquid, the resulting pressure is consistent throughout the fluid. This uniformity means that any change in pressure at one point in the liquid is felt equally at all other points in the fluid, and it acts in all directions.
Applications of Pascal’s Law
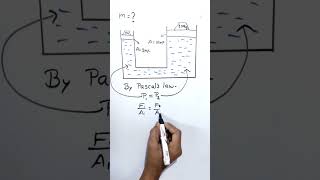
- Hydraulic Press: A mechanism where a small force applied on a small piston translates into a larger force on a bigger piston due to uniform pressure transmission.
- Hydraulic Lifts: Commonly used in car repair shops, these lifts function by applying a small force on a small piston, which amplifies to raise heavy loads via a larger piston.
These applications demonstrate how fluid pressure can be manipulated for significant mechanical advantage.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Pascal’s Law
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Pascal's Law states that:
"Pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to all parts of the fluid and to the walls of its container."
Detailed Explanation
Pascal's Law is a fundamental principle in fluid mechanics. It tells us that when you apply pressure to a confined fluid, that pressure does not get weaker as it moves through the fluid. Instead, it remains the same at every point in the fluid. This means that if you push on a fluid in one area, the entire fluid will experience the same increase in pressure. This concept is crucial in understanding how fluid systems operate, especially in hydraulic systems.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a balloon filled with air. If you squeeze the balloon at one point, every part of the balloon feels the pressure. If the balloon were filled with a fluid instead of air, squeezing it would also transmit that pressure throughout the entire fluid without losing any strength. This is similar to how hydraulic brakes in a car work; pressing down on the brake pedal applies pressure to the brake fluid, which is transmitted to all brakes equally, allowing the car to stop.
Explanation of Pascal’s Law
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If a small force is applied to a confined liquid, the pressure in the liquid will be the same at all points, and this pressure will be transmitted equally in all directions.
Detailed Explanation
When a small force is applied to a body of liquid, that force creates an increase in pressure. According to Pascal's Law, this pressure increase is not limited to the area where the force was applied; it spreads out evenly throughout the liquid. This uniformity means that every part of the liquid and its container responds to the same change in pressure, which is essential for the function of hydraulic systems, where even a small effort can result in a large movement or force.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a spray bottle. When you press the nozzle, the force you apply creates pressure in the liquid inside. This pressure pushes the liquid out of the nozzle. Even though you apply force to a small area (the nozzle), the pressure is transmitted uniformly within the bottle, allowing the liquid to spray out evenly.
Applications of Pascal’s Law
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Hydraulic Press: A hydraulic press uses Pascal's Law to amplify the force. A small force applied on a small piston creates a large force on a larger piston.
- Hydraulic Lifts: Hydraulic lifts, used in car repair shops, use Pascal’s Law to lift heavy objects by applying a small force on a small piston, which is transmitted to a larger piston, raising the load.
Detailed Explanation
Pascal’s Law has several practical applications that utilize the principle of pressure transmission in fluids. For instance, in hydraulic presses, a small input force on a small piston results in an immense output force on a larger piston. Similarly, in hydraulic lifts, when an operator applies a small force to the smaller piston, this force is transmitted through the fluid to lift much heavier loads through the larger piston. This principle makes it possible to lift cars or heavy machinery with minimal human effort.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a seesaw: if one side has a small child and the other side has an adult, the adult can easily lift the child. Similarly, in a hydraulic lift, a small person (small piston) can lift a heavy car (large piston). This is possible because the hydraulic fluid transmits the small force from the small piston to the larger one, lifting the car with ease.
Key Concepts
-
Pascal's Law: Pressure applied to an enclosed fluid transmits uniformly to all parts.
-
Hydraulic Systems: Utilize Pascal's Law to amplify force and perform work.
-
Pressure Transmission: Involves the equal propagation of pressure throughout a liquid.
Examples & Applications
In a hydraulic press, a small force applied to a small piston can lift a heavy load due to pressure transmission.
A hydraulic lift in a car repair shop allows a mechanic to raise a vehicle by pushing down on a small piston.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Pascal's Law, a pressure decree, in liquid it flows, uniformly!
Stories
Imagine a sealed thin tube with liquid. The moment you press down on it, the liquid pushes equally at every point, lifting a weight on the other side. Just like how friends share a secret evenly, that's Pascal's Law!
Memory Tools
Remember 'PEACE' for Pascal: Pressure Everywhere As Compression Equalizes.
Acronyms
P.A.C.E. - Pressure Applied Creates Equalization.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pascal's Law
A principle stating that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to all parts of the fluid and to the walls of its container.
- Hydraulic Systems
Systems that use liquid under pressure to transmit force or perform work.
- Pressure Transmission
The process through which pressure exerted on a liquid is communicated throughout the entire liquid.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
