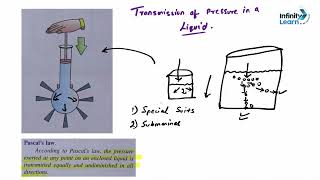
Introduction to Pressure in Liquids
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Pressure
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the concept of pressure in liquids. Can anyone tell me what they think pressure means?

Isn’t it the force applied on something?

Exactly! Pressure is the force exerted per unit area. In liquids, it specifically refers to the force that the liquid applies to a surface.

So, how does this pressure change in a liquid?

Great question! Pressure in a liquid increases with depth because of the weight of the liquid above that point—think of it as being crushed under the weight of water when you dive into a pool!

Does that mean the deeper you go, the more pressure you feel?

Correct! And we can quantify this pressure with a formula: P = ρgh, where ρ is the density of the liquid, g is the gravitational acceleration, and h is the depth.

What unit do we use for pressure?

The SI unit of pressure is the Pascal, or Pa, which is equivalent to one Newton per square meter. Now, let’s recap: pressure increases with depth, is related to the liquid's density, and is measured in Pascals.
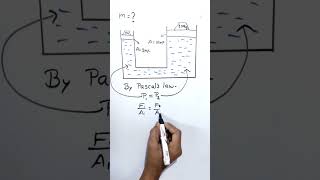
Formula for Pressure in a Liquid
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive deeper into the formula for pressure. Who can recall the formula we discussed?

It's P = ρgh!

Perfect! Can anyone explain what each of those symbols represents?

P is pressure, ρ is density, g is gravity, and h is height.

Right again! So, if we were to find the pressure at a depth of 5 meters in water, how would we do that?

We would plug in the values: density of water is 1000 kg/m³, g is 9.8 m/s², and h is 5 m.

Exactly! Let’s calculate it: P = 1000 × 9.8 × 5. Who can tell me the answer?

That would be 49,000 Pa!

Excellent! That’s how we quantify pressure at a specific depth.
Units of Pressure
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss the units of pressure. Can anyone tell me what the SI unit of pressure is?

It’s Pascal, right?

Yes! And to put it in perspective, 1 Pascal equals 1 Newton per square meter. Why do you think pressure measurements are important?

Because they help us understand how fluids behave in different situations?

Absolutely! Knowing the pressure in various conditions helps engineers design safe hydraulic systems, predict weather patterns, and more. Can anyone think of a daily example where pressure plays a role?

Water pressure in pipes?

Spot on! Understanding liquid pressure is essential for plumbing and many engineering applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces the concept of pressure in liquids, explaining how pressure increases with depth due to the weight of the liquid above. It also covers the formula for calculating pressure and the units used, emphasizing the relationships between density, gravitational force, and depth.
Detailed
Introduction to Pressure in Liquids
Pressure in liquids is defined as the force exerted by the liquid per unit area, which is influenced by three key factors: the depth of the liquid, its density, and the gravitational acceleration acting on it. The deeper you go in a liquid, the greater the pressure due to the weight of the liquid above.
The formula for calculating pressure at any point within a liquid is given by:
$$P = \rho g h$$
Where:
- P = Pressure at that point (in Pascals, Pa)
- \rho = Density of the liquid (in kg/m³)
- g = Gravitational acceleration (approximately 9.8 m/s² on Earth)
- h = Height or depth of the liquid column above that point (in meters)
The SI unit of pressure is the Pascal (Pa), which corresponds to a force of one Newton per square meter (1 Pa = 1 N/m²). Understanding this concept is fundamental in fields such as hydraulics, engineering, and fluid mechanics.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Pressure in Liquids
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Pressure in a liquid is the force exerted by the liquid per unit area. It depends on the depth of the liquid, its density, and the gravitational acceleration acting on it.
Detailed Explanation
Pressure in liquids refers to the force that the liquid applies over a specific area. This force arises from the molecules in the liquid pushing against each other and the surfaces they come into contact with. The key factors affecting this pressure are:
1. Depth: The deeper the point in the liquid, the more liquid is above it pushing down.
2. Density: A denser liquid exerts more pressure because its molecules are packed more closely together.
3. Gravitational acceleration: The force of gravity pulls the liquid down, influencing the pressure it exerts.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine going swimming in a pool. As you swim deeper, you might feel water pushing against you more strongly. This is because there is more water above you that weighs down with gravity, increasing the pressure you feel.
Increase of Pressure with Depth
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Pressure in a liquid increases with depth due to the weight of the liquid above the point where pressure is being measured.
Detailed Explanation
The principle here is straightforward: as you go deeper into any liquid, you encounter more liquid above you. Each layer of liquid exerts its weight downwards, contributing to the overall pressure at a certain depth. The cumulative weight of all the liquid layers above is what increases the pressure you feel at that deep point.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a stack of books. The books at the bottom feel the weight of all the books stacked above them. Similarly, in a liquid, the deeper you go, the greater the 'stack' of liquid. If you think of it as layers of water or air, the deeper layers feel the pressure of all the layers above.
Formula for Pressure in a Liquid
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● The pressure at a point in a liquid is given by the formula:
P=ρgh
Where:
● PP = Pressure at a point in the liquid (in Pascals, Pa)
● ρ = Density of the liquid (in kg/m³)
● g = Gravitational acceleration (approximately 9.8 m/s² on Earth)
● h = Height or depth of the liquid above the point (in meters)
Detailed Explanation
The formula for calculating pressure in a liquid combines key factors: density (ρ), gravitational acceleration (g), and depth (h). Here’s how it works:
- ρ (density) gives the mass of the liquid in a unit volume, which influences how heavy the liquid column is.
- g (gravitational acceleration), which we take as 9.8 m/s² on Earth, represents the force due to gravity acting on the mass.
- h (depth) measures how deep you are, indicating the amount of liquid above.
Thus, the pressure P increases if any of these parameters increase.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a column of syrup in a tube. The thicker (more dense) the syrup, the more pressure you would measure at the bottom of the tube. If you poured more syrup into the tube (increasing h), the pressure would rise accordingly. The formula allows you to find out exactly how much pressure there is in different conditions.
Units of Pressure
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● The SI unit of pressure is the Pascal (Pa), which is defined as one Newton per square meter (1 Pa=1 N/m²).
Detailed Explanation
The Pascal (Pa) is the standard unit used to quantify pressure in the metric system. One Pascal is defined as the pressure exerted when a force of one Newton is applied to an area of one square meter. This measurement helps us understand and quantify how much force is applied over a particular surface area, making it easier to discuss pressure in scientific contexts.
Examples & Analogies
To visualize this, think of a tire. A tire has a certain pressure measured in Pascals (or sometimes in psi for other regions). When the tire is filled with air, the amount of air exerts a force (in Newtons) against the interior walls of the tire, spread over its surface area. This is expressed as Pascals, helping us know if the tire is adequately inflated.
Key Concepts
-
Pressure in Liquids: Defined as the force exerted per unit area, influenced by depth, density, and gravitational force.
-
Formula for Liquid Pressure: P = ρgh relates pressure to the liquid's density, gravitational acceleration, and depth.
-
Units of Pressure: Measured in Pascals (Pa), where 1 Pa is equivalent to 1 N/m².
Examples & Applications
Example 1: To calculate pressure at 5 meters depth in water: P = 1000 kg/m³ * 9.8 m/s² * 5 m = 49000 Pa.
Example 2: In a swimming pool, as you dive deeper, you feel the pressure increase due to more water above you.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Deep in the sea, pressure does rise, weight of the water, is no surprise.
Stories
Imagine diving into a pool. As you swim deeper, you feel the water pushing against you. That is pressure increasing because of the water above you.
Memory Tools
D^2G for Depth, Density, Gravitational acceleration which all affect pressure.
Acronyms
P=PDG
Pressure = Pressure x Depth x Gravity.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pressure
The force exerted by a liquid per unit area, typically measured in Pascals (Pa).
- Depth
The distance from the surface of a liquid to a point below it.
- Density
The mass of a substance per unit volume, usually expressed in kg/m³.
- Gravitational Acceleration
The acceleration due to gravity, approximately 9.8 m/s² on the surface of the Earth.
- Pascal (Pa)
The SI unit of pressure, equivalent to one Newton per square meter.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
