DEFAULT Constraint
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the DEFAULT constraint
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the DEFAULT constraint. Can anyone tell me what they think a default value might be?

Is it a value that is automatically provided when nothing else is specified?

Exactly! The DEFAULT constraint automatically fills in a value for a column if no value is provided during an INSERT operation. This ensures that every row has valid data. Can you think of a scenario where this might be useful?

What if you have a column for a student's enrollment date? You might want it to default to the current date.

Good example, Student_2! This prevents errors from having no data in a critical column. Remember the acronym 'D.A.T.A.' - Default Always Trumps Absence.
DEFAULT constraint syntax and examples
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at the syntax of the DEFAULT constraint now. It typically looks like this: `column_name data_type DEFAULT default_value`. Can someone provide an example?

What if I have an `EnrollmentDate` that should be today's date if nothing is given? Would it be `EnrollmentDate DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE`?

Exactly, Student_3! That's a perfect example. Anyone else curious about how this interacts with other constraints?

Does it conflict with the NOT NULL constraint?

Great question! The DEFAULT constraint does not conflict with NOT NULL. In fact, it can complement it by ensuring a column is never NULL, as a default value will always be inserted if none is specified.
When and why to use the DEFAULT constraint
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Using a DEFAULT constraint can streamline data entry. What benefits do you think this could bring?

It saves time since you don't have to enter data for every row.

It reduces errors too, like forgetting to enter a date.

Exactly! It enhances data integrity by ensuring that every row has a value, defaulting if necessary. Can anyone summarize what we learned about the DEFAULT constraint today?

The DEFAULT constraint provides a preset value for a column if no value is given during INSERT and helps maintain data integrity.

Well said, Student_3! Remember, the DEFAULT constraint is your ally in ensuring consistent, valid entries in your database.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the DEFAULT constraint in SQL, explaining how it specifies a default value for a column when no values are explicitly specified during an insertion. It includes its syntax, purpose, an example, and distinctions from other constraints.
Detailed
DEFAULT Constraint in SQL
The DEFAULT constraint plays a crucial role in SQL table definitions, automatically assigning a value to a column when no data is input for that column during an INSERT operation. This feature enhances data integrity and simplifies database management by ensuring that every row in a table maintains valid data without requiring manual entry for every field.
Key Points:
- Purpose: Simplifies data entry and maintains consistency by automatically inserting default values.
- Syntax: The syntax involves defining the column with the DEFAULT keyword followed by the default value:
column_name data_type DEFAULT default_value;. - Example: In the Students table, for instance, if we have
EnrollmentDate DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE, any new student added without an explicit enrollment date will automatically be assigned the current date as their enrollment date. - Distinctions: The DEFAULT constraint is different from constraints like NOT NULL or UNIQUE because it specifically dictates a backup value rather than enforcing data uniqueness or presence.
This constraint alleviates both the administrative burden on users and the potential for null values, paving a smoother experience while working with SQL databases.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Purpose of DEFAULT Constraint
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The DEFAULT Constraint:
- Purpose: Specifies a default value for a column. If no value is explicitly provided for this column during an INSERT operation, the default value will be automatically inserted.
Detailed Explanation
The DEFAULT constraint allows you to set a predefined value that will be automatically used in a column if no value is specified when a new record is inserted into the database. This helps maintain consistency and ensures that essential fields are not left empty. For instance, if you define a column for enrollment date and set its default value to the current date, every time a new student is added without specifying the enrollment date, the database will use the current date as the default value.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're setting up a new account at a coffee shop that tracks how many points customers earn. If a new customer doesn't specify their referral points during their first visit, you can set a DEFAULT value of 0 points. This way, the system automatically assigns 0 points to customers who do not indicate any referral points, ensuring no customer starts with undefined points.
Syntax of the DEFAULT Constraint
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Syntax (Inline): column_name data_type DEFAULT default_value
Detailed Explanation
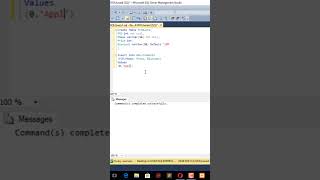
The syntax for implementing the DEFAULT constraint is straightforward. It is specified at the time of defining the table. You include it after the data type of the column where you want to apply the default value. For example, if you want to set the EnrollmentDate of students to automatically take the value of the current date unless specified otherwise during insertion, you can define the column like this: EnrollmentDate DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a software application for managing an online store. You might want to ensure that customers who order items without specifying a preferred delivery date will have their orders shipped within a week by default. So, you set a rule (or constraint) that specifies the delivery date will default to one week from the current date.
Example of DEFAULT Constraint in Action
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
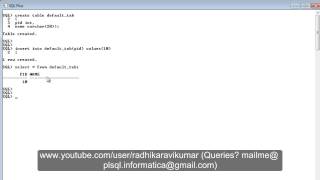
Example from Students table: EnrollmentDate DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE
- CURRENT_DATE is a function that returns the current system date.
Detailed Explanation
In the example provided, the EnrollmentDate is set to automatically use the current date when a new record is created in the Students table. This is done by defining the column with a DEFAULT value of CURRENT_DATE. Whenever a new student is added to the database without specifying an enrollment date, the system will automatically fill in this field with the date when the record was created.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a high school registering new students at the start of the school year. If a student doesn't provide a specific enrollment date during the registration, the school automatically records the date of the registration, which is essentially the start of the academic year. This ensures every student officially has an enrollment date even if they forget to provide one.
Key Concepts
-
DEFAULT Constraint: Automatically assigns a value to a column when no value is provided during an INSERT.
-
INSERT Operation: SQL command to add data to a table.
-
CURRENT_DATE: A function that retrieves the current date for default assignments.
Examples & Applications
Example of DEFAULT Constraint usage: EnrollmentDate DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE - This sets the default enrollment date to the current date if no value is provided during the insertion.
In a Products table, if we have Price DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT 0.00, any product added without a price will have a default price of $0.00.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Default values fill the gaps in data's direction, ensuring columns always have some connection.
Stories
Imagine a classroom where every student stands ready to greet the day; those without a pencil receive a default one, ensuring everyone is equipped to play.
Memory Tools
D for Default, A for Always, T for Trumps, A for Absence - remembering that default values fill the gaps.
Acronyms
D.A.T.A. - Default Always Trumps Absence helps remember the importance of just filling in what's missing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- DEFAULT Constraint
A SQL constraint that specifies a default value for a column when no value is provided during an insertion.
- INSERT Operation
An SQL command to add new records (rows) to a table.
- CURRENT_DATE
A SQL function that returns the current system date.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
