Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Power Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are discussing the conclusion of our chapter on power management in CMOS and FinFET technologies. Why do you think power management is crucial in semiconductor designs?

I think it's important to save energy, especially in mobile devices that need to run longer on batteries.

Exactly! Energy efficiency not only extends battery life but also ensures that devices operate within thermal limits. Can anyone remember some methods we discussed for managing power?

There are techniques like DVFS and sleep modes!

Great! DVFS helps manage power dynamically according to the load, and sleep modes drastically reduce leakage during inactive times.

And we mentioned that FinFET technology improves efficiency, right?

Yes! FinFETs provide better leakage control, enhancing overall system performance.

So to summarize this session, effective power management in CMOS and FinFET technologies is essential for building systems that are both scalable and reliable.
Combining Power Strategies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into how we can combine different power management strategies. What do you think are the benefits of using multiple strategies together?

Combining strategies could optimize performance while minimizing power consumption.

Absolutely! For example, using DVFS in conjunction with clock gating allows for significant dynamic power savings. Can someone tell me how these techniques are applied in real-world scenarios?

Like in mobile SoCs, where different cores can operate in various power states?

Exactly! Mobile systems utilize these techniques to deliver high performance while keeping idle power consumption low.

In conclusion, leveraging multiple power strategies can tailor designs to meet the needs of specific applications—enhancing both efficiency and functionality.
Application Tailoring
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about how we can tailor power management techniques to different applications. Why do we need to customize these strategies?

Different devices have varying requirements for power and performance!

Right! Performance-critical applications, like gaming, require different management techniques compared to ultra-low-power applications, like IoT sensors. Can anyone suggest examples of such applications?

For gaming, you'd want high performance, while for IoT, you'd want to maximize battery life.

Exactly! That balance is essential to meet the demands effectively. In conclusion, understanding the unique requirements of different applications allows for better power management strategies.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This conclusion recaps the necessity for effective power management in CMOS and FinFET technologies, highlighting methods such as DVFS, clock gating, and architecture-level strategies. The discussion centers on balancing performance needs with energy efficiency tailored to specific application requirements.
Detailed
Conclusion
Effective power management is paramount in designing scalable, reliable, and energy-efficient systems using CMOS and FinFET technologies. As advancements in semiconductor technologies continue, the methods developed for power management become increasingly crucial.
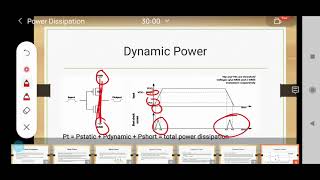
- CMOS Techniques: CMOS technology benefits from a wealth of mature techniques for managing both dynamic and static power, which are essential for addressing challenges like increased power density and leakage issues.
- FinFET Enhancements: FinFET technology goes further by improving energy efficiency with better leakage control and a more favorable subthreshold behavior.
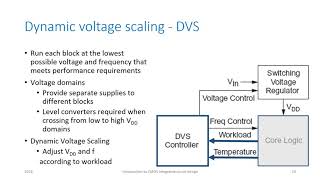
- Key Strategies: It is essential to integrate multiple strategies effectively. Using dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS), clock and power gating, alongside multi-threshold design techniques, helps tailor power management techniques to specific applications.
- Application Focus: Furthermore, the choice of power management techniques should align with application needs, balancing performance-critical tasks against ultra-low power usage scenarios.
By implementing these strategies thoughtfully, designers can achieve not only optimal performance but also significant energy savings.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Effective Power Management
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Effective power management in CMOS and FinFET technologies is essential for building scalable, reliable, and energy-efficient systems.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the necessity of effective power management when designing electronic systems using CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) and FinFET (Fin Field-Effect Transistor) technologies. Successful power management strategies help ensure that devices are not only efficient in utilizing energy but also remain scalable for future advancements and reliable in their operation under different conditions. Essentially, power management plays a crucial role in every aspect of device performance, specifically in compact, high-performance environments.
Examples & Analogies
Think of power management like managing your household budget. Just as you need to track your income and expenses to avoid overspending and ensure you have enough for essentials, effective power management helps electronic systems track their energy usage, ensuring they don't exceed their energy supply while maintaining necessary functionalities.
Comparison of CMOS and FinFET Technologies
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
While CMOS offers mature techniques for dynamic and static power control, FinFET enhances efficiency further with better leakage suppression and subthreshold behavior.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk compares two technologies—CMOS and FinFET—highlighting their strengths in power management. CMOS has been around for longer and comes with established methods to manage power both when circuits are active (dynamic) and when they are inactive (static). In contrast, FinFETs improve upon these methods by offering enhanced capabilities, especially in terms of controlling leakage current (which is the unwanted power consumed when a device is off) and maintaining efficient operation at lower voltage levels (subthreshold behavior). Thus, FinFETs represent an evolution of CMOS technology, allowing for even greater energy efficiency.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine CMOS as an old but reliable car with established fuel management strategies, while FinFET is a newer electric car that not only knows how to use fuel effectively but can also regenerate energy while driving. The electric car is ultimately more efficient, especially in urban environments where frequent stops and starts occur.
Key Takeaways for Power Management Strategies
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Key takeaways:
● Combine multiple power strategies (DVFS, clock/power gating, multi-Vt).
● Leverage architecture-level partitioning and hardware-software co-design.
● Tailor techniques to application needs: performance-critical vs ultra-low-power.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines major strategies for effective power management, which includes combining different techniques like Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS), clock and power gating, and utilizing multi-threshold voltage (multi-Vt) designs. By integrating these various strategies, designers can better handle the diverse power needs of modern systems. Furthermore, the mention of architecture-level partitioning means that the structure of the circuit can be designed to maximize efficiency, while hardware-software co-design stresses the collaboration between hardware functionalities and the software controlling them to achieve optimal performance. Tailoring the approaches to meet specific application needs is also crucial; for instance, a device focused on performance will require different strategies than one designed primarily for minimal power use.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a multi-purpose kitchen. If you're cooking a gourmet meal (performance-critical), you'll need various power tools (like blenders, food processors) set up for easy access, prioritizing functionality. Conversely, if you're just reheating leftovers (ultra-low-power), you might only need the microwave. Effectively managing your kitchen space (like managing power in a system) allows you to meet both needs without clutter or waste.
Key Concepts
-
Power Management: Critical for balancing performance and energy efficiency in semiconductor designs.
-
DVFS: Technique that adjusts voltage and frequency based on workload to reduce power consumption.
-
FinFET Technology: Provides enhanced control over leakage power and subthreshold behavior.
-
Multi-Strategy Approach: Combining various power management strategies enhances effectiveness for specific applications.
Examples & Applications
Mobile SoCs that utilize DVFS and clock gating to optimize performance and power efficiency.
IoT devices that implement ultra-low-power modes for extended battery life.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Voltage and frequency, scale them right, save some power, day or night.
Stories
Imagine a city where every light turns on only when someone is present, just like clock gating, which turns off unused circuits to conserve energy.
Memory Tools
P-F-C-M: Power management - FinFET benefits - Combine strategies - Meet application needs.
Acronyms
DSA
Dynamic Scaling and Adjustment for power management.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Power Management
The process of managing and optimizing energy consumption in electronic devices.
- DVFS
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling, a technique to adjust voltage and frequency according to the workload.
- Leakage Power
Power consumption in a device when it's in an idle state, which can degrade energy efficiency.
- FinFET
A type of transistor technology that offers better control of leakage currents than conventional planar transistors.
- Clock Gating
A technique to reduce power consumption by disabling the clock signal in inactive circuits.
- MultiVt Design
A design strategy using multiple threshold voltages to optimize speed and leakage in circuits.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
