Introduction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Power Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss the principles of power management. Can anyone tell me why power management is so critical in modern technology?

Because it helps devices run efficiently without wasting energy.

Exactly! Efficient power management balances performance and energy use. Another reason is to mitigate thermal issues, especially in compact environments like mobile devices or data centers.

What happens if we don't manage power effectively?

Without effective management, devices may overheat, leading to reduced reliability and performance. Remember, the goal is to optimize energy use throughout different operational states.

So, what technologies are we focusing on?

We'll primarily focus on both CMOS and FinFET technologies, exploring their unique characteristics and the specific strategies for power management.

To summarize, effective power management is critical for optimizing performance while minimizing energy consumption, particularly in modern applications.
Applications in Power Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now look at applications of power management strategies. Can someone give an example of where these are crucial?

Mobile phones!

Great example! Mobile devices are battery-operated, necessitating strict power management to extend usage time. What about data centers?

They consume a lot of power and need cooling, so managing power is essential!

Exactly. In data centers, power optimization impacts operational costs and environmental footprint. Can anyone think of other examples?

IoT devices must also manage power since they often run on battery and need to last long.

Correct! IoT devices require battery efficiency, reinforcing the importance of power management techniques across various sectors.

In summary, power management is essential across multiple applications, including mobile devices, IoT, and large data centers, to ensure efficiency and sustainability.
Framework for Power Management Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we proceed, we'll explore specific strategies for power management. What do you think are some techniques we might cover?

I guess we might look at voltage scaling.

Good point! Voltage and frequency scaling is crucial for dynamic power management. We will also explore techniques like clock gating and sleep modes. Why do you think these methods are useful?

They help reduce energy when the device is idle.

Exactly! Each technique has its place in the overall strategy for maximizing efficiency. Finally, we will discuss how these techniques can be applied specifically to CMOS and FinFET technologies.

To summarize, we will be looking at various power management techniques, including voltage scaling, clock gating, and sleep modes, tailored for CMOS and FinFET applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this introduction, the focus is on the importance of power management in semiconductor technologies, particularly for applications that demand high energy efficiency, such as mobile devices and data centers. It highlights the need for hardware-level control, architectural optimizations, and system-wide strategies relevant to CMOS and FinFET technologies.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section sets the foundation for Chapter 8, which delves into power management and optimization in CMOS and FinFET technologies. With the evolution of semiconductor technologies, maintaining energy efficiency has become increasingly critical in a variety of applications, particularly in power-sensitive environments like mobile devices, IoT, and data centers. The introduction underscores the significance of effective power management strategies that ensure a balance between performance, reliability, and thermal constraints.
The chapter will cover various techniques, including hardware-level power control and architectural-level optimizations, as well as system-wide strategies tailored to the characteristics of both CMOS and FinFET technologies. It emphasizes the guiding principles that drive the efficient design and operation of these semiconductor devices.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Power Management and Optimization
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This chapter explores the principles of power management and optimization strategies essential for energy-efficient CMOS and FinFET-based designs.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk provides a brief introduction to the chapter’s focus on power management and optimization. It emphasizes the importance of these strategies in designing energy-efficient systems using CMOS and FinFET technologies. The mention of both principles and optimization strategies indicates that the chapter will cover theoretical concepts as well as practical techniques for improving power efficiency.
Examples & Analogies
Think of power management in electronics as managing your car’s fuel consumption. Just like optimizing fuel usage can help you drive longer distances without refueling, power management techniques help electronic devices use less energy, enabling them to run longer and cooler.
Importance of Power Management in Evolving Technologies
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As semiconductor technologies evolve, effective power management is crucial to balancing performance, reliability, and thermal constraints, especially in power-sensitive applications like mobile, IoT, and data centers.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses the significance of power management as semiconductor technologies advance. It highlights a critical challenge: balancing three key aspects - performance (how fast the device operates), reliability (how long it lasts without failure), and thermal constraints (the heat generated during operation). The applications listed, such as mobile devices and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, further emphasize the urgency of power management as these systems often rely on batteries and have strict energy consumption limits.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how smartphones use power management; they need to perform many tasks fast while also ensuring the battery lasts all day. Features like automatic brightness adjustment and background app management help keep the phone running smoothly without draining the battery.
Focus Areas in Power Management
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
We focus on hardware-level power control, architectural-level optimizations, and system-wide strategies tailored to the unique characteristics of CMOS and FinFET technologies.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, the chapter outlines its specific focus areas within power management. It identifies three primary levels: hardware-level control, which involves direct management of power at the component level; architectural-level optimizations, which refer to design choices that enhance efficiency; and system-wide strategies, indicating holistic approaches that consider the entire system. The mention of CMOS and FinFET highlights the distinct features and requirements of these technologies in power management.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a sustainable house; you might use energy-efficient appliances (hardware-level), design the house to maximize natural light (architectural-level), and incorporate smart home technology that regulates energy use throughout the home (system-wide). Each level contributes to overall energy efficiency.
Key Concepts
-
Power Management: Strategies to optimize the energy efficiency of semiconductor designs, especially in power-sensitive applications.
-
CMOS Technology: A fundamental technology for integrated circuits, known for low power performance.
-
FinFET Technology: An advanced transistor structure aimed at reducing leakage and improving performance.
-
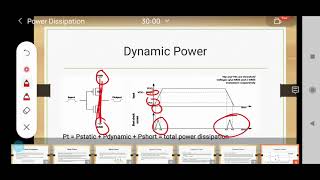
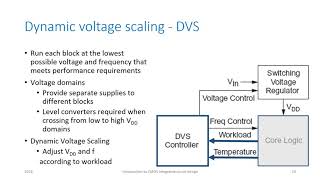
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS): A method used to manage power dynamically based on workload, optimizing power consumption.
-
Clock Gating: A method to cut off the clock signal to inactive modules, thereby conserving energy.
Examples & Applications
Mobile devices require power management to enhance battery life, impacting how design strategies are implemented.
In data centers, power management techniques directly affect energy consumption and cooling costs.
IoT devices often operate on limited battery life, necessitating rigorous power optimization strategies.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the power's low, let it flow slow; use DVFS, to save is the goal.
Stories
Once upon a time, in the land of silicon, devices struggled to drink up power. They learned to adjust their voltage and frequency, discovering that less energy coud extend their lifespans, and soon they ruled the land of gadgets with efficiency and grace.
Memory Tools
Remember 'COG' for power management: Clock Gating, Optimizing Voltage, and Gating inactive blocks.
Acronyms
DREAM for power management techniques
for DVFS
for Reducing Leakage
for Energy Saving Modes
for Adaptive Scheduling
for Multiple Domains.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a technology used for constructing integrated circuits, known for low power consumption.
- FinFET
Fin Field-Effect Transistor, a type of multi-gate transistor used in modern semiconductor devices to improve performance and reduce leakage.
- Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS)
A method of adjusting the voltage and frequency of a processor to save power and manage performance levels.
- Power Gating
A design technique that cuts off power to inactive parts of a circuit to reduce leakage current.
- Clock Gating
A technique used to disable the clock signal to parts of a circuit that are not currently in use to save energy.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
