Problem Statement
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Power Density Challenges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s start with the issue of power density. Can anyone tell me what this term means?

I think it refers to how much power is used per area of the chip.

Exactly! Increased power density means more heat generation in smaller areas, which can affect performance and reliability. Why do you think this is a concern for engineers?

Because more heat can lead to thermal issues and can affect the operation of the circuit.

Great point! Managing this heat is critical, as it helps maintain system integrity. Remember, Power Density means 'Power per Unit Area.' Let’s move on to the next point about standby leakage.
High Standby Leakage in CMOS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about standby leakage in CMOS. What do you understand about this issue?

Isn’t it about power being consumed even when the chip is not active?

Yes, that's correct! High standby leakage can lead to significant power losses, impacting battery life in mobile devices. Can anyone think of a situation where this might be problematic?

In devices like smartphones, it can drain the battery quickly even when they are idle.

Absolutely! So how can power management strategies mitigate this?
Complex Power Behavior in FinFETs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s explore FinFETs. What challenges do you think arise due to complex multi-core and mixed-domain power behavior?

I think it must be harder to control the power usage when different cores might be doing different tasks.

Correct! The varying workloads and requirements can complicate power management significantly. What do you remember from our last session about power management strategies?

We talked about Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling and how it helps manage power.

Exactly! Managing across diverse domains is key to maintaining efficiency and performance.
The Importance of Robust Power Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s wrap up this section by discussing the crucial role of power management. What can happen if we don’t address these power issues?

Systems might overheat or fail to perform properly, right?

Correct! Without robust power management, it could lead to compromised system integrity and poor user experiences. What takes priority in power management?

Minimizing power while ensuring reliable performance.

Exactly! So that summarizes the problem statement. Now you can see why effective power management is vital for modern IC designs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Problem Statement outlines the increasing power density associated with transistor scaling, high standby leakage in CMOS technology, and the complexity involved with mixed-domain power management in FinFETs. It emphasizes the need for effective power management to ensure system integrity and user experience.
Detailed
In this section, we examine the growing challenges faced by modern integrated circuits. The problems highlighted include increased power density resulting from transistor scaling, significant standby leakage encountered in CMOS technologies, and the intricate multi-core and mixed-domain power behavior observed in FinFET devices. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive design strategy aimed at minimizing power consumption across various technological layers while maintaining reliable and predictable performance. Without effective power management strategies, the integrity and user experience of electronic systems may be compromised.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Challenges of Modern Integrated Circuits
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Modern integrated circuits face growing challenges:
● Increased power density from transistor scaling
● High standby leakage in CMOS
● Complex multi-core and mixed-domain power behavior in FinFETs
Detailed Explanation
The world of integrated circuits (ICs) is constantly evolving, especially with advancements in technology that allow for smaller and more efficient transistors. However, this miniaturization leads to certain challenges.
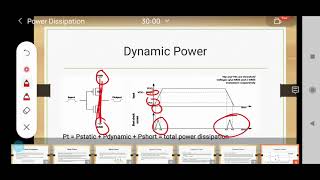
1. Increased Power Density: As transistors become smaller, more transistors can fit into the same chip area, which can cause the total power output to increase significantly. This is referred to as increased power density.
2. High Standby Leakage in CMOS: CMOS technology, while efficient during active operation, can waste power in a state of inactivity due to leakage currents that flow even when the device is not in use.
3. Complex Power Behavior in FinFETs: FinFETs, which are three-dimensional transistors, introduce new complexities in managing power across multiple cores and functional domains, adding to the overall design challenge.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a busy city where more cars (transistors) are continuously coming in due to increased population (transistor scaling). This creates traffic jams (high power density) that slow down the commute time. Meanwhile, some cars left on the road (high standby leakage) continue using fuel even when not moving, and managing traffic across different parts of the city (mixed-domain behavior) becomes increasingly complicated.
Design Challenges and Requirements
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The design challenge is to minimize power at every abstraction layer while ensuring predictable performance and reliability. Without robust power management, system integrity and user experience suffer.
Detailed Explanation
Designing integrated circuits involves addressing the fundamental issue of power management at several levels.
- Minimizing Power: Engineers must focus on reducing power consumption not just at the circuit level, but also at architectural and system-wide levels. This means considering how components function together and ensuring that innovations don’t just optimize performance but also maintain or reduce power usage.
- Predictable Performance and Reliability: It's not enough to just save energy; the system must also work reliably and efficiently under all conditions. This includes operating under various loads and temperatures.
- Impact of Poor Management: If power management isn't prioritized, it can lead to system failures, overheating, and a poor overall user experience, making devices unreliable or unresponsive.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant where the kitchen (integrated circuit) needs to prepare meals (perform tasks) efficiently without wasting ingredients (power). If the chefs (engineers) don’t manage how much food they use, the restaurant might run out of supplies (failures) or food will spoil (overheating), leading to unhappy customers (bad user experience).
Key Concepts
-
Power Density: Refers to the power usage per unit area which can lead to significant heat management issues.
-
Standby Leakage: The loss of power in idle states impacting overall energy efficiency.
-
Complex Multi-Core Behavior: The challenge of managing diverse workloads across multiple processing cores, particularly in FinFET designs.
Examples & Applications
In modern smartphones, increased power density leads to thermal throttling during intensive tasks.
High standby leakage in IoT devices can significantly reduce battery life, requiring robust power management strategies to ensure longevity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Power density causes trouble, heat is a big bubble.
Stories
Imagine a small chip getting hotter and hotter until it can't work properly, causing your phone to freeze.
Memory Tools
DOME: Density, Overheating, Management, Efficiency to remember key power challenges.
Acronyms
SLEEK
Standby Leakage Energy Efficiency Kills to remember the consequences of leakage.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Power Density
The amount of power consumed per unit area in an integrated circuit.
- Standby Leakage
Power consumed by a device in its idle state when it is not performing any active tasks.
- FinFET
A type of multi-gate transistor used in advanced semiconductor technology to improve performance and reduce leakage.
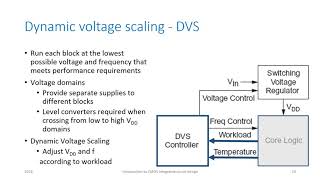
- Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS)
A technique used to adjust the voltage and frequency of a processor dynamically according to workload.
- Integrated Circuit (IC)
A set of electronic circuits on a small flat piece of a semiconductor material, mainly silicon.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
