Aggregation vs Composition
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Aggregation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are diving into aggregation. Can anyone tell me what aggregation means in object-oriented programming?

Is it when one class contains another class?

Exactly, but there's more to it! Aggregation is a 'has-a' relationship where even if the parent object goes away, the child object can still live independently. Let’s think about a car and its engine. Can anyone write a simple Java code to represent this?

"Sure! I would write it as:
Understanding Composition
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand aggregation, let’s move on to composition. Who can explain what composition means?

I think composition is similar but stronger, right? It's where the child can't exist without the parent.

Exactly! It’s also a 'has-a' relationship but in this case, if the parent is destroyed, the child is too. For example, consider a `Car` and its `Wheels`. Write some code demonstrating composition.

"Here’s how it would look:
Comparison of Aggregation and Composition
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about both, how would you summarize the differences between aggregation and composition?

For aggregation, the ‘has-a’ relationship allows both parts to live on their own, while in composition, they are interdependent.

Right! You could think of aggregation like a school with students, where students could walk away after class, but in composition, it would be like a tree and its leaves; if the tree goes, the leaves go too!

Excellent analogy! Remember these relationships as they play a major role in system design. In summary, aggregation is flexible while composition is strict—always dependent on its parent.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains the differences between aggregation and composition in object-oriented design. Aggregation represents a 'has-a' relationship where both entities can exist independently, while composition signifies a stronger 'has-a' relationship where the life cycle of the child is strictly tied to the parent.
Detailed
Aggregation vs Composition
In object-oriented programming, understanding how objects relate to one another is fundamental. Two significant types of relationships are aggregation and composition, which are both forms of a *
Youtube Videos


![Association(HAS-A) Aggregation And Composition in Java [MOST COMMONLY ASKED INTERVIEW QUESTION]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/wbvW3w47QRw/mqdefault.jpg)


![Composition over Inheritance [Object Oriented Programming]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/jfE7Ie93b9g/mqdefault.jpg)



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Aggregation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
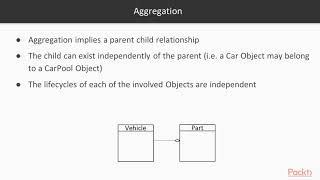
• Aggregation: "Has-a" relationship where both entities can exist independently.
Detailed Explanation
Aggregation describes a relationship where one object contains another, but both can exist independently. For example, a 'Car' object can have an 'Engine' object. Even if the 'Car' is removed, the 'Engine' can exist on its own—this illustrates aggregation. In general terms, think of it like a person owning a book; the book can exist without the person, and the person can exist without the book.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a teacher and a classroom. A teacher can teach in multiple classrooms, and if a teacher leaves, the classroom remains. Therefore, they have an aggregated relationship where both can exist independently.
Understanding Composition
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Composition: "Has-a" relationship where the child cannot exist without the parent.
Detailed Explanation
Composition is a stronger form of association than aggregation. In this case, when one object (the parent) is removed, the other object (the child) cannot exist on its own. For example, a 'House' cannot exist without 'Rooms'; if you remove the 'House', the 'Rooms' cease to exist as part of that house structure. This leads us to think of composition as a whole-part relationship.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a tree and its leaves. If the tree dies (parent), the leaves (children) cannot survive or exist independently. This illustrates composition, where the existence of one is dependent on the other.
Code Example of Aggregation
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example (Aggregation):
class Engine {}
class Car {
Engine engine; // Car has-a Engine
}
Detailed Explanation
The code shows a simple example of aggregation in Java. The 'Car' class has an attribute 'engine', which is an instance of the 'Engine' class. In this way, a car is characterized by having an engine, but the engine itself does not depend on the car for its existence, exemplifying aggregation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a library and the books within it. The library is the 'Car', and the books are the 'Engine'. The library can have many books, and the books can exist in other libraries too; thus, they are independent in the aggregation relationship.
Key Concepts
-
Aggregation: Represents a weak 'has-a' relationship where both entities can exist independently.
-
Composition: Signifies a strong 'has-a' relationship where the child cannot exist without the parent.
Examples & Applications
An Engine and a Car signify aggregation where both can exist independently.
A Car and its Wheels illustrate composition since if the Car is destroyed, the Wheels are as well.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In aggregation, they'll stay alive, / The parent and child can both survive.
Stories
Think of a library with many books. Each book can be checked out, but if the library closes, those books can still exist elsewhere—this is aggregation. Now consider a room in a house; if the house is torn down, the room ceases to exist, illustrating composition.
Memory Tools
A for Aggregation, A for Alone: both can exist, each on their own.
Acronyms
C for Composition
Child confined to parent
they are one together.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Aggregation
A relationship that represents a 'has-a' association where both entities can exist independently.
- Composition
A strong relationship indicating 'has-a' where the child cannot exist without the parent.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
