Inheritance
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Inheritance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the concept of inheritance in object-oriented programming. Can anyone tell me what they think inheritance means in this context?

I think it means one class can take properties from another class?

Exactly! Inheritance allows a subclass to inherit fields and methods from a superclass. This promotes code reusability. Think of it like family traits: children inherit traits from their parents.

How does this help when writing code?

Great question, Student_2! It helps by allowing us to create new classes based on existing ones without rewriting code. This also leads to a hierarchical classification of classes, making our design more organized.

Can you give us a straightforward example?

Sure! If we have a class `Animal` that has a method `eat()`, then we can create a class `Dog` that inherits from `Animal` and has its own method `bark()`. Let’s recap: Inheritance promotes reusability and leads to better-organized code.
Benefits of Inheritance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand inheritance, let’s dive into its benefits. Why should we use inheritance?

To save time and avoid rewriting code!

Exactly, Student_4! Now, can anyone tell me how inheritance relates to class hierarchy?

It helps structure classes in a way that reflects real-world relationships.

Correct! We often model our programs based on real-life scenarios. For instance, in a class hierarchy, a `Dog` is a specific type of `Animal`, and this relationship can reflect in our code design.

Does this mean I can create many types of animals using this inheritance system?

Yes! You can create subclasses like `Cat`, `Bird`, etc., all inheriting from `Animal`. This hierarchical classification keeps your code neat and organized.
Examples of Inheritance in Java
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

"Let’s look at a concrete example of inheritance in Java. Here’s the code snippet again...
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Inheritance promotes code reusability and hierarchical classification by enabling a subclass to inherit fields and methods from a superclass. This mechanism allows developers to create more complex and organized software structures and encourages cleaner code.
Detailed
Inheritance in Object-Oriented Programming
Inheritance is one of the four pillars of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) that allows a class, referred to as the subclass or derived class, to inherit fields (attributes) and methods (behaviors) from another class known as the superclass or base class. This feature plays a crucial role in promoting code reusability, which is essential for building robust software applications, as it allows developers to extend existing code without having to modify it directly.
Key Points of Inheritance
- Inheritance Mechanism: By defining inheritable classes, programmers can create a hierarchy of classes that share common behaviors, which not only simplifies code maintenance but also enhances its readability.
- Code Reusability: Instead of rewriting code, programmers can create subclasses that inherit existing functionality from superclasses, significantly reducing redundancy.
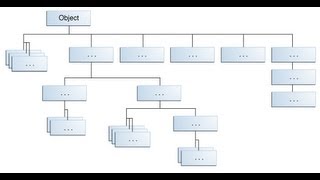
- Hierarchical Classification: Inheritance supports a logical structure that represents relationships among classes, making it easier to understand the design and architecture of the code.
Example of Inheritance
In Java, inheritance is indicated by the extends keyword, as shown in the following example:
In this example, Dog inherits the eat method from the Animal class, demonstrating the foundational aspect of inheritance.
In conclusion, inheritance allows for more efficient coding practices and a cleaner codebase, which are significant for advanced programming paradigms.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Inheritance
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Inheritance allows a class (subclass/derived class) to inherit fields and methods from another class (superclass/base class).
Detailed Explanation
Inheritance is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming that enables one class to adopt the properties and behaviors of another class. The class that receives the properties is called the subclass or derived class, whereas the class from which it inherits is referred to as the superclass or base class.
Examples & Analogies
Think of inheritance like a family tree. A child inherits traits, characteristics, and skills from their parents. For example, just like a child may inherit their parent's eye color, a subclass in programming gets methods and fields from its superclass.
Benefits of Inheritance
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Promotes code reusability
• Supports hierarchical classification
Detailed Explanation
The main advantages of inheritance are code reusability and hierarchical classification. Code reusability allows developers to use existing code, making it easier to create new classes without rewriting common functionalities. Hierarchical classification helps organize similar classes, reflecting real-world relationships, like animals categorized into mammals, birds, etc.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a company where employees are divided into departments. Each department (like Sales, HR, and IT) can have specific roles and responsibilities, while also sharing common operations (like processing payroll, which might be handled by all departments). Inheritance works similarly in programming, where different classes can share common methods while having their specific traits.
Java Example of Inheritance
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example (Java):
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("This animal eats food.");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("Dog barks.");
}
}
Detailed Explanation
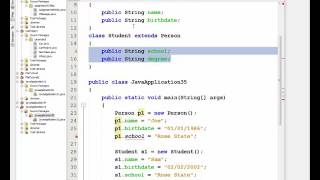
In this Java example, we have a base class called Animal with a method eat(). The class Dog extends Animal, meaning that it inherits the eat method. The Dog class can also define its own methods, such as bark(). By extending Animal, the Dog class automatically gains the eat() functionality without needing to redefine it.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a general vehicle class. From this class, you could have specific types of vehicles, such as cars and motorcycles. A car inherits the general driving ability from the vehicle class while also having its own unique features, such as a trunk.
Key Concepts
-
Inheritance: The mechanism through which a subclass can inherit properties and methods from a superclass.
-
Subclass: A class that extends another class, gaining its attributes and behaviors.
-
Superclass: The parent class from which properties and methods are inherited.
-
Code Reusability: The practice of using existing code in new contexts to improve efficiency.
Examples & Applications
If we have a class Animal with a method eat(), a class Dog can extend Animal and inherit the eat() method, while also having the bark() method.
In a payroll system, a Manager class can inherit attributes from an Employee class, gaining properties like salary and methods like calculatePay().
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When class A gives traits to class B, Inheritance is the key, it’s easy as can be!
Stories
Once upon a time, an Animal named Jack taught his puppy, Max, how to eat and play. Max the Dog didn't need to learn to eat from scratch; he inherited that lovely skill from Jack! Thus, Jack helped Max learn quickly!
Memory Tools
S-U-C-C-E-S-S: Subclass Using Class Code Eases Software System.
Acronyms
H.I.E.R
Hierarchical Inheritance Enhances Reusability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Inheritance
A mechanism in object-oriented programming where a subclass can inherit fields and methods from a superclass.
- Subclass
A class that inherits from another class (superclass), also known as a derived class.
- Superclass
The class from which a subclass inherits; also known as the base class.
- Code Reusability
The ability to reuse existing code with minimal changes in new applications.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
