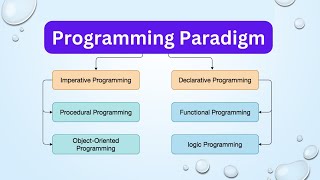
Declarative Programming Paradigm
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Declarative Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the declarative programming paradigm. Can anyone tell me what they think it means to program declaratively?

Does it mean focusing on what the program does instead of how it does it?

Exactly! In declarative programming, we describe the desired outcome rather than outlining specific steps to get there. This is different from procedural programming, where we dictate every step. A helpful acronym to remember this is 'WHAT,' which stands for 'What to achieve, How Not Required!'

What are some types of declarative programming?

Great question! We have several types, including logic programming, constraint programming, and SQL-based querying. Let's explore these further in the next session.
Types of Declarative Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into the types of declarative programming we talked about. Can anyone mention an example of logic programming?

I think Prolog is an example?

That's correct! Prolog allows us to declare facts and rules. For example, you could say 'father(john, mary).' This tells the program that John is Mary's father without detailing how to search or traverse that relationship. Who can explain constraint programming to me?

Isn't it like defining the limits that solutions must fit within?

Exactly! It allows us to specify certain conditions that must be met in our solutions. Now, can anyone share an example of SQL usage?

Like querying a database to find all students with grades over 90?

Correct again! SQL's strength lies in data querying, and its syntax allows for clear and concise requests, focusing on the data you want rather than how to retrieve it. We’ll wrap up this session by defining one more aspect—the limitations.
Advantages and Limitations of Declarative Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've covered the types, let's address the advantages of the declarative programming paradigm. What do you think is an advantage?

It's more readable, I guess? Like, it seems simpler to understand.

That's a key point! High-level abstraction leads to concise and clear code, making it much more maintainable. What about limitations? Can anyone think of a drawback?

Debugging might be harder because you don’t control each step?

Exactly! Since less control can make debugging challenging, it might feel less intuitive than other paradigms. Also, performance tuning is often not in the programmer's hands. Remember, 'Less Control Isn't Best for Debugging!'

So, even though it's easier to write, it can be harder to troubleshoot?

That's right! To wrap up, always consider both the advantages and limitations when selecting a programming paradigm.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section delves into the declarative programming paradigm, emphasizing its approach of defining goals rather than control flow. Key types include logic programming, constraint programming, and SQL. It outlines the benefits, such as readability and high-level abstraction, alongside potential limitations like debugging challenges and less control over program flow.
Detailed
Declarative Programming Paradigm
Declarative programming is a programming paradigm that emphasizes what the program should do rather than how it should accomplish that task. This distinction allows programmers to focus on the desired outcome rather than the specifics of execution.
Types of Declarative Programming
- Logic Programming: Such as Prolog, which uses facts and rules to derive conclusions.
- Constraint Programming: Solving problems by specifying constraints that must be met.
- SQL-based Data Querying: Using SQL (Structured Query Language) to manage and retrieve data from databases.
Example
A simple SQL query, SELECT name FROM Students WHERE grade > 90;, illustrates how users can extract information from not just a simple list of students but based on specific conditions.
Advantages
- Concise and readable, making it easier to understand and maintain code.
- High-level abstraction that allows foci on the end results.
- Particularly well-suited for database operations and artificial intelligence applications due to its inherent flexibility and expressiveness.
Limitations
- Programmers have less control over the precise flow of the program; it can lead to inefficiencies in certain cases.
- Debugging can present unique challenges, as reasoning through declarative statements may be less intuitive.
- Performance tuning often falls outside the developer's control, which can lead to less optimized solutions.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Declarative Programming
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Declarative programming focuses on what the program should accomplish rather than how to accomplish it.
Detailed Explanation
Declarative programming is a paradigm that emphasizes the desired outcome or end result of a program instead of the specific steps and procedures to achieve that result. Unlike procedural programming, where the programmer explicitly defines each step in the computation, a declarative approach allows the programmer to state what they want in a more abstract manner. This abstraction simplifies coding by letting the computer handle the underlying process details.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like giving a chef a recipe. Instead of telling them how to chop vegetables or boil water, you simply say you want a 'vegetable soup.' The chef (the computer) takes care of all the steps necessary to create that soup (the desired outcome), letting you focus on what you want rather than how to make it.
Types of Declarative Programming
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Logic Programming (e.g., Prolog)
• Constraint Programming
• SQL-based data querying
Detailed Explanation
Declarative programming encompasses various subtypes, each serving different needs:
1. Logic Programming: This type allows you to define rules and facts. For example, in Prolog, you can declare relationships and then query them to infer new information.
2. Constraint Programming: This focuses on defining constraints and letting the system find solutions that satisfy all constraints. It's often used in scheduling and resource allocation problems.
3. SQL-based Data Querying: SQL (Structured Query Language) is widely used for managing and retrieving data from databases. You specify what data you want, and the SQL engine determines how to get it, exemplifying a declarative approach.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a librarian (the SQL engine) who understands a library’s entire catalog. When you ask them to 'give me all the books written after 2000,' you don't need to tell them how to sort through the shelves or check the publish dates. You simply state what you want, and they fetch it efficiently, reflecting the declarative nature of SQL.
Example of Declarative Programming (SQL)
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example (SQL)
SELECT name FROM Students WHERE grade > 90;
Detailed Explanation
This SQL statement is a perfect example of declarative programming. The statement specifies that you want to select the names of students who have a grade higher than 90. It does not detail how the database should perform this selection—such as how it should access the data, filter it, or arrange it. The database engine abstracts these operations, allowing you to focus on the 'what' instead of the 'how.'
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you’re placing an order at a restaurant. You don’t need to know how to cook the food; you just tell the waiter what dish you want. For example, you might say, 'I’d like the grilled salmon.' The kitchen handles the preparation and cooking, exemplifying the declarative approach. Similarly, in SQL, you specify the data you want, and the database takes care of the details.
Advantages of Declarative Programming
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Concise and readable
• High-level abstraction
• Suitable for database operations and AI
Detailed Explanation
Declarative programming has several advantages:
1. Concise and Readable: Code is often shorter and easier to understand since you express the intent rather than the implementation details.
2. High-level Abstraction: It abstracts away the complexity of implementations, making it easier for programmers to work at a higher conceptual level.
3. Suitable for Database Operations and AI: This paradigm is particularly effective for applications like databases and artificial intelligence, where the 'what' is often more critical than the 'how.'
Examples & Analogies
Consider using a high-level language to communicate, such as English, instead of a coding language, like Morse code. In high-level language, you articulate your thoughts clearly without getting bogged down by the technical details. This is akin to how declarative programming allows developers to specify what they want without delving into the complexities of how it will happen.
Limitations of Declarative Programming
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Less control over program flow
• Debugging can be more difficult
• Performance tuning is often out of the programmer's hands
Detailed Explanation
Despite its benefits, declarative programming has limitations:
1. Less Control Over Program Flow: Because the programmer states what they want without detailing how to get it, they have less control over execution flow, which can lead to inefficiencies.
2. Debugging Can Be More Difficult: Understanding errors or bugs can be challenging since the programmer isn’t involved in specifying the execution steps.
3. Performance Tuning is Often Out of the Programmer's Hands: Programmers may not be able to optimize how operations are performed because the abstracted processes are managed by the execution environment or engine.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine ordering a custom-built home. You might describe the overall design and desired features to the builder, but you might have little control over the construction process. If something goes wrong, it may be difficult for you to pinpoint the exact issue since you weren't directly involved in how the builder executed your vision. This is similar to the challenges faced in debugging or optimizing declarative programs.
Key Concepts
-
Declarative Programming: Focuses on the 'what' rather than the 'how' in programming.
-
Logic Programming: Uses facts and rules, enabling powerful querying capabilities.
-
Constraint Programming: Offers a way to solve problems by specifying constraints.
-
SQL: A practical example of declarative programming used for database queries.
Examples & Applications
SQL Query: SELECT name FROM Students WHERE grade > 90;
Prolog Fact: father(john, mary).
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In declarative land, we say it plain, we want a result, not a code train.
Stories
Imagine a wise king who only states what he wants in his kingdom. Instead of detailing how his workers should build a bridge, he just tells them he wants the bridge done by spring. This is like declarative programming!
Memory Tools
WHATS: What we want, How is N/A, To specify simply.
Acronyms
D.O.E. for Declarative Output Emphasis.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Declarative Programming
A programming paradigm focused on what the program should accomplish rather than how to accomplish it.
- Logic Programming
A type of declarative programming that uses facts and rules to derive conclusions.
- Constraint Programming
A programming paradigm where solutions are defined by constraints that must be satisfied.
- SQL
Structured Query Language used for managing and querying relational databases.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
