Procedural Programming Paradigm
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Procedural Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, what is procedural programming? It's based on the concept of procedure calls, where programs are organized as sequences of commands. Does anyone know what a 'procedure' means in programming?

Isn't it just a way to run a task or a function?

Exactly! Procedures can be thought of as functions that perform specific tasks. We break down complex problems into smaller pieces. This is called the top-down approach. Can anyone guess why we use this approach?

Probably to make it easier to solve the main problem piece by piece?

That's right! Smaller tasks are easier to manage and understand. Remember, we often use local and global variables to manage our data within these procedures.
Key Features of Procedural Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into key features. Procedural programming emphasizes algorithmic flow. What do you think that means, Student_3?

I think it refers to how instructions are executed in a specific order to solve a problem?

Exactly! The sequence of instructions is crucial. It impacts how efficiently we can solve problems. Plus, using functions promotes code reusability. Why do you think reusability is essential?

It saves time! We can use the same function in different parts of our code.

Great insight! This makes code easier to maintain as well. But, what about the limitations of procedural programming?
Advantages and Limitations of Procedural Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about the advantages first. Procedural programming is simple and efficient, making it suitable for straightforward programs. Can anyone name a language that uses this paradigm?

C is a big one, right?

Correct! However, for larger systems, it can become difficult to manage. What challenges might we face with a lack of data encapsulation?

We could accidentally modify global variables, leading to bugs?

Spot on! With procedural programming, there's a higher risk of side effects. To wrap this up, understanding these pros and cons is vital for developers. Let's summarize: procedural programming is easy to learn and effective for small tasks but poses challenges on a larger scale.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
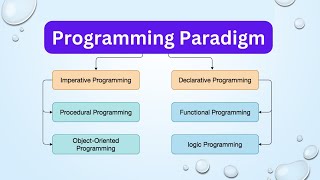
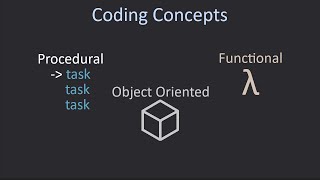
This section discusses the procedural programming paradigm, including its definition, key features, advantages, and limitations. It highlights its organization into procedures that call one another to perform specific functionality, mainly through the use of functions. Languages like C, Pascal, and Fortran exemplify this paradigm.
Detailed
Procedural Programming Paradigm
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm based on the concept of procedure calls. This paradigm is structured into procedures or functions, which perform specific tasks. Key features of procedural programming include:
- Sequence of Instructions: Programs are written as a sequence of commands to execute.
- Use of Functions/Procedures: Tasks are organized into subroutines or functions to enhance modularity.
- Emphasis on Algorithmic Flow: The focus is on how the operations lead to the solution of a problem through structured steps.
- Local and Global Variables: Allows for variable scoping to manage data effectively.
- Top-Down Approach: Breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable units.
Languages Supporting Procedural Programming
Languages such as C, Pascal, Fortran, and BASIC are prominent examples that utilize this paradigm, making it simple and efficient for small programs.
Advantages and Limitations
Procedural programming is generally easy to understand and promotes code reusability through functions. However, it becomes challenging to manage in large-scale systems, offers poor data encapsulation, and carries risks of side effects due to global variables.
Understanding procedural programming is essential for aspiring developers as it lays the groundwork for grasping more complex paradigms.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Procedural Programming
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm based on the concept of procedure calls, also known as routines, subroutines, or functions. The program is divided into procedures, each performing a specific task.
Detailed Explanation
Procedural programming focuses on structuring a program into smaller sections called procedures. Each procedure is a set of instructions that performs a specific task. This organization helps in managing complex programs by breaking them down into manageable components, allowing for better structure and readability.
Examples & Analogies
Think of procedural programming like following a recipe in cooking. Each step in the recipe represents a procedure. You have a distinct task to follow, like chopping vegetables or boiling water, and each step needs to be completed in a specific order to create the dish successfully.
Key Features of Procedural Programming
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Sequence of instructions
• Use of functions/procedures
• Emphasis on algorithmic flow
• Local and global variables
• Top-down approach
Detailed Explanation
Procedural programming has several key features:
1. Sequence of Instructions: Programs execute instructions in a specific order, which is crucial for the logical flow of operations.
2. Use of Functions/Procedures: It encourages the use of functions, which are reusable blocks of code that perform specific tasks.
3. Emphasis on Algorithmic Flow: Programmers focus on how to solve problems algorithmically, outlining clear steps to achieve a desired outcome.
4. Local and Global Variables: Variables can be defined within a function (local) or be accessible across multiple functions (global), allowing for different scopes of usage.
5. Top-Down Approach: This approach involves breaking down a problem into smaller sub-problems, creating a structured solution that is easier to implement.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine organizing a party. The sequence of instructions involves planning, inviting guests, preparing food, and decorating. Each task (function) can be handled separately, but they all contribute to the successful execution of the party, similar to procedures in a program.
Languages that Utilize Procedural Programming
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• C
• Pascal
• Fortran
• BASIC
Detailed Explanation
Several programming languages utilize the procedural programming paradigm. Examples include:
1. C: A powerful language widely used in system programming.
2. Pascal: Often used for teaching programming concepts.
3. Fortran: Primarily used in scientific computing.
4. BASIC: Known for its simplicity, making it accessible for beginners. These languages share common characteristics of the procedural paradigm, allowing developers to write instructions that follow a logical sequence.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these languages as different tools in a toolbox. Each tool is specialized for specific tasks, just like different procedural programming languages are suited for different types of programming tasks, such as system coding or educational purposes.
Example of Procedural Programming in C
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
include
void greet() {
printf("Hello, World!\n");
}
int main() {
greet();
return 0;
}
Detailed Explanation
The provided example demonstrates a simple procedural program in C. Here’s how it works:
1. The greet function is defined, which contains the instruction to print 'Hello, World!'.
2. The main function serves as the entry point of the program. It calls the greet function to execute the instructions within it.
3. The program ends by returning 0, indicating successful completion. This structure highlights how functions can be used to segment tasks within a program.
Examples & Analogies
You can liken this to a phone call where the main function is the caller, and the greet function is the person on the other end who answers and says hello. The caller (main function) initiates the interaction (function call), resulting in a response (output).
Advantages of Procedural Programming
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Simple to understand
• Efficient for small, straightforward programs
• Encourages code reusability through functions
Detailed Explanation
Procedural programming has several advantages:
1. Simple to Understand: Its straightforward structure makes it easier for new programmers to grasp basic programming concepts.
2. Efficient for Small Programs: This paradigm works well for smaller, simple tasks where quick solutions are needed.
3. Encourages Code Reusability: Functions allow for reusing code blocks across different parts of a program, saving time and effort.
Examples & Analogies
Consider procedural programming like a basic assembly line in factories, where each section does a specific task repeatedly. This simplicity is easy for workers (programmers) to understand, and they can refine or reuse the same task without starting from scratch.
Limitations of Procedural Programming
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Difficult to manage for large-scale systems
• Poor data encapsulation
• Higher risk of side effects due to global state
Detailed Explanation
While procedural programming has its advantages, it also comes with notable limitations:
1. Difficult to Manage for Large-Scale Systems: As programs grow larger, keeping track of all procedures can become complex, making maintenance difficult.
2. Poor Data Encapsulation: It does not enforce encapsulation well, leading to unintended interactions between different parts of the program.
3. Higher Risk of Side Effects: Since global variables can be changed by any part of the program, this can lead to unpredictable behaviors or bugs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a large city with many roads (functions) connecting various buildings (data). In a small town, it's easy to navigate, but as the city grows, the complexity increases, making it harder to avoid getting lost or causing traffic jams (errors) due to too many intersections (global state).
Key Concepts
-
Procedure: A function or routine that is designed to perform a task.
-
Code Reusability: The practice of using existing code for new tasks without rewriting.
-
Encapsulation: The restriction of direct access to some of the object's components.
-
Algorithmic Flow: The logical sequence of steps taken in the function for problem-solving.
Examples & Applications
The function 'greet' in C that prints 'Hello, World!' is a simple example of a procedure in action.
In a payroll system, calculating employee salaries can be broken down into procedures like 'calculateTax' and 'generatePayslip'.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Procedures work like a recipe’s task, swift and clear, they help programs last!
Stories
Imagine a chef creating a complex dish. Each part of the dish is like a procedure – from preparing ingredients to cooking them one by one, ensuring every step is needed for a perfect meal.
Memory Tools
R.A.C.E.: Reusability, Algorithmic flow, Complexity management, Encapsulation.
Acronyms
P.A.C.E.
Procedural programming
Algorithmic processes
Code organization
Easy to understand.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Procedural Programming
A programming paradigm that focuses on the concept of procedure calls and organizes a program into procedures or functions.
- Function
A reusable block of code designed to perform a specific task.
- TopDown Approach
A problem-solving strategy that breaks down complex tasks into simpler components to tackle them more effectively.
- Local Variable
A variable that is declared within a procedure and can only be accessed within that procedure.
- Global Variable
A variable that is accessible from any part of the program, leading to potential side effects.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
