Logic Programming Paradigm
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Logic Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the Logic Programming Paradigm. Can anyone share what they think logic programming might involve?

Is it about using logic to solve problems?

That's correct! Logic programming focuses on defining facts and rules using logical inference. Think of it as stating relationships rather than specifying steps to solve a problem.

What language do we use for this?

Great question! The main language used in this paradigm is Prolog. Let’s memorize this by using the acronym 'P LOG' — 'Programming Logical'.

What are some examples of facts in Prolog?

Excellent! A fact could look like 'father(john, mary)', which states a relationship between John and Mary.

So, can I use rules to derive new information based on facts?

Exactly! For instance, you can create a rule defining 'child(X, john) :- father(john, X)'. This lets you query who John's children are.

In summary, logic programming abstracts problem-solving into facts and rules, making it suitable for AI-related tasks.
Advantages and Limitations of Logic Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve deeper into the advantages of the logic programming paradigm. What do you think might be a key benefit?

I guess it could be helpful for AI applications?

Absolutely! It's great for AI due to its ability to handle logical statements naturally. Remember, 'AI Relies on Logic' as a mnemonic for this advantage.

Are there any downsides to using logic programming?

Good point! While it offers many benefits, it does come with a steep learning curve and might not be suitable for performance-critical systems. So, keep in mind 'Learning Curve High, Performance Low'.

Can it handle large-scale programs?

Limited scalability can be an issue with logic programming. It tends to be more effective for smaller to medium-sized systems, especially in academic or exploratory contexts.

In summary, while logic programming is powerful for AI and reasoning, its complexity and performance constraints are significant considerations.
Practical Applications of Logic Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s look at some practical applications of logic programming. Can anyone suggest where we might see Prolog being used?

How about in natural language processing?

Correct! Logic programming is used in natural language processing to parse and understand human languages. Let’s remember that using the phrase 'Words in Logic'.

What about expert systems?

Exactly! Expert systems use logic programming to make deductions based on a set of encoded knowledge. A way to remember this is 'Experts in Logic'.

Are there any specific industries that utilize this?

Yes! Areas like healthcare, education, and customer service often leverage logic programming for decision support and reasoning tasks.

In summary, logic programming is not just theoretical. It's applied in diverse fields where reasoning and inference are critical.
Comparison with Other Paradigms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s compare logic programming with other paradigms. How does it differ from procedural programming?

Is procedural programming more about writing direct instructions?

Exactly! Procedural programming emphasizes step-by-step instructions, while logic programming focuses on relationships. Let's use 'Steps vs. Statements' as a slogan for this.

How about functional programming? What's the main contrast there?

Functional programming centers on functions and avoids mutable state, whereas logic programming emphasizes logical inference. A mnemonic to remember this is 'Functions Focus vs. Facts Focus'.

So, which situations are best for each paradigm?

Procedural suits straightforward tasks, functional excels in mathematics and transformations, while logic programming is ideal for tasks that require inference, like AI.

In conclusion, understanding these contrasts helps enhance our choice of programming paradigms based on the problem at hand.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Logic programming is a paradigm where problems are expressed in terms of facts and rules, facilitating inference through queries. This approach is particularly effective for applications like artificial intelligence and knowledge representation, although it comes with challenges such as a steep learning curve and limited scalability.
Detailed
Logic Programming Paradigm
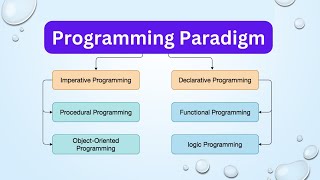
Logic programming is a declarative programming paradigm that emphasizes expressing facts and rules about a problem domain. Instead of providing a sequence of instructions to achieve a solution, logic programming allows programmers to declare relationships within the data and use a logical inference engine to resolve queries based on these declarations.
The most well-known language in this paradigm is Prolog (Programming in Logic). In Prolog, programs consist of facts and rules that define the relationships between objects.
Key Features:
- Facts and Rules: Core elements used to represent knowledge.
- Queries: Mechanisms to derive information based on declared facts and rules.
Advantages:
- Particularly suited for artificial intelligence (AI) and situations involving logical analysis.
- Provides a natural way to express and manipulate logical statements, making problem-solving more intuitive at times.
Limitations:
- The paradigm can have a steep learning curve and may be unintuitive for those familiar with other programming paradigms.
- Limited scalability for extensive systems and not generally suited for performance-critical applications.
Example (Prolog):
In this example, we declare that John is the father of Mary and Mike, and we can query child(X, john) to get the values of X that satisfy this relationship.
Overall, mastering logic programming aligns well with tasks that require reasoning and can significantly enhance the understanding of logical constructs in coding.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Logic Programming
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Logic programming involves declaring facts and rules about problems and querying them to derive conclusions.
Detailed Explanation
Logic programming is a programming paradigm that is based on formal logic. In this approach, programmers define logical relationships or rules about their data and the program's execution revolves around drawing inferences or conclusions from these defined rules and facts. This contrasts with other paradigms where the focus may be more on procedures or functions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a detective solving a case using clues. The detective gathers all the facts (like fingerprints, alibis) and applies certain rules (like 'if the alibi doesn't match, the suspect is guilty'). Similarly, in logic programming, you define facts and rules, and the computer deduces conclusions from them.
Programming Language Used: Prolog
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Language
• Prolog
Detailed Explanation
Prolog is the primary programming language associated with logic programming. It is designed for symbolic reasoning and is heavily used in fields like artificial intelligence. In Prolog, you write facts and rules, and the language takes care of querying and inferring answers based on those inputs.
Examples & Analogies
Consider Prolog like a legal system where laws (rules) and evidence (facts) are established. A court (the Prolog interpreter) processes cases (queries) based on existing laws and evidence to reach a verdict (conclusion).
Example in Prolog
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example (Prolog)
father(john, mary).
father(john, mike).
child(X, john) :- father(john, X).
Detailed Explanation
This example shows how you define facts and rules in Prolog. The first two lines declare that 'john' is the father of 'mary' and 'mike'. The third line is a rule that defines how to find out if someone is a child of 'john'—if 'john' is said to be their father. The ':-' symbol is used to denote that the right side must be true for the left side to be true.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this like a family tree. If 'john' is established as the father of 'mary' and 'mike', then you can infer that anyone who is a child of 'john' is directly related to him. It is similar to how a family might logically deduce relationships based on known facts.
Advantages of Logic Programming
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Advantages
• Great for AI and knowledge representation
• Natural way to encode logical rules and inference
Detailed Explanation
Logic programming excels particularly in domains like artificial intelligence because it mirrors how humans reason—using known facts and rules to derive new knowledge. This makes it an intuitive fit for problems that require logical reasoning, such as expert systems and natural language processing.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how experts like doctors use their knowledge. They don't simply memorize facts; they apply logic to deduce a diagnosis from symptoms based on established medical rules. Logic programming behaves in a similar manner, using defined rules to draw conclusions.
Limitations of Logic Programming
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Limitations
• Steep learning curve
• Limited scalability
• Not suited for performance-critical systems
Detailed Explanation
Despite its strengths, logic programming can be challenging for beginners due to its abstract nature and requirement for a different mode of thinking compared to traditional programming paradigms. Additionally, logic programming approaches may not scale well with more complex applications and aren't optimal for performance-critical systems, like real-time applications, where speed is essential.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine learning a new language. Initially, it may feel complex and confusing, leading to a steep learning curve. Over time, it can become easier, but some might find practical use cases limiting. Similarly, logic programming is powerful but may not suit every type of project, especially where performance is crucial, much like walking instead of running for a sprint.
Key Concepts
-
Facts: Basic assertions in logic programming.
-
Rules: Statements defining relationships for logical inference.
-
Queries: Requests to retrieve information based on facts and rules.
-
Prolog: The primary language used in logic programming.
Examples & Applications
In Prolog, 'father(john, mary).' defines a fact.
'child(X, john) :- father(john, X).' is a rule for querying relationships.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In Prolog we declare, facts that are fair, rules to compare, logic to share.
Stories
Imagine a detective using Prolog to piece together evidence (facts) and draw conclusions (rules) about a mystery.
Memory Tools
Remember 'FQR' - Facts, Queries, Rules to recall the three main components of logic programming.
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'P.L.O.T.' for Prolog, Logic, Objectives, Truth—key elements of logic programming.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Logic Programming
A programming paradigm that declaratively states facts and rules to infer conclusions.
- Prolog
A logic programming language used to express facts and rules.
- Fact
A basic assertion in logic programming, such as relationships between entities.
- Rule
A statement that defines logical relationships and inference in logic programming.
- Query
A request to the logic programming system to derive information from facts and rules.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
