Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Internal Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're exploring what internal factors affect photosynthesis. Can anyone name some factors related to the plant itself?

The size and number of leaves, maybe?

Absolutely! The number and size of leaves directly impact the surface area for photosynthesis. What else?

I think the amount of chlorophyll is important too.

Correct! Chlorophyll is vital for capturing light energy. Now, let's remember this with the acronym 'SOME' for Size, Orientation, Mesophyll, and Enzymes. Can you summarize what each letter stands for?

S for size of leaves, O for their orientation, M for mesophyll cells, and E for the enzymes involved in photosynthesis!

Great recap! These factors show how plants are genetically predisposed to their photosynthetic effectiveness.
Analyzing External Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s move on to external factors. Can you tell me which environmental factors play a role in photosynthesis?

Light, temperature, carbon dioxide, and water!

Exactly! Light is crucial; it has a direct impact on the rate of photosynthesis. What happens when it gets too much?

Too much light can damage chlorophyll!

Right! Light has an optimal saturation point. The next factor is carbon dioxide. Why is it vital?

It's a reactant in photosynthesis. More CO2 can increase the rate up until it saturates!

Exactly! Finally, let’s not forget about temperature. Each plant has an optimal temperature range for photosynthesis which depends on its habitat.
Understanding the Limiting Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s connect everything now. How do you think these factors interact with each other?

If one factor is low, like water, it could limit photosynthesis even if light and CO2 are available.

Exactly! That’s where Blackman’s Law of Limiting Factors comes in. Can someone explain this law?

It states that the rate of a process is determined by the factor that is closest to its minimum value.

Yes, very well put! So, if water availability is low, the overall rate of photosynthesis might not reach its potential, even with perfect light conditions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Photosynthesis is affected by several factors, including light, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and water availability. Both internal factors related to the plant's structure and genetics, and external environmental conditions play crucial roles in determining photosynthesis rates.
Detailed
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is essential for plant growth and agricultural productivity, making it critical to understand the various factors that influence its rate. These factors can be categorized into internal (plant-related) and external (environmental) factors.
Internal Factors
- Plant Structure: The number, size, age, and orientation of leaves impact the surface area available for photosynthesis.
- Cellular Composition: The number of mesophyll cells and chloroplasts within the leaves is crucial as they house the machinery necessary for photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll Content: The amount of chlorophyll directly influences the plant’s ability to capture light energy.
- Genetic Factors: The plant's genetic makeup determines its inherent capabilities and limits in photosynthesis.
External Factors
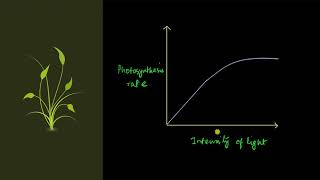
- Light: Availability and quality of light significantly affect photosynthesis. Photosynthesis increases with light intensity up to a saturation point, after which more light can damage chlorophyll.
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration: As one of the main reactants in photosynthesis, higher carbon dioxide levels enhance photosynthesis rates until saturation is reached.
- Temperature: Temperature affects enzyme activity in the photosynthetic process, with different plants having specific temperature optima tailored to their environments.
- Water: Water stress can limit photosynthesis by causing stomatal closure, which reduces carbon dioxide uptake.
Conclusion
These factors interact simultaneously, with the rate of photosynthesis often being determined by the limiting factor — the one present at sub-optimal levels according to Blackman’s Law of Limiting Factors.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Photosynthesis Factors
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An understanding of the factors that affect photosynthesis is necessary. The rate of photosynthesis is very important in determining the yield of plants including crop plants. Photosynthesis is under the influence of several factors, both internal (plant) and external. The plant factors include the number, size, age and orientation of leaves, mesophyll cells and chloroplasts, internal CO concentration and the amount of chlorophyll.
Detailed Explanation
Photosynthesis is vital for plant growth and directly impacts agricultural productivity. Several factors influence the rate of photosynthesis. These can be categorized into internal and external factors. Internal factors include aspects related to plant structure—such as the quantity and size of leaves, the presence of chlorophyll, and the internal concentration of carbon dioxide. Each of these factors plays a role in determining how efficiently a plant can photosynthesize.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a factory that produces goods (plants) using raw materials (sunlight, CO2, and water). If the factory is missing machines (like chloroplasts) or if the machines are too small or poorly arranged, the production will suffer. The internal factors are the machinery settings and efficiency.
External Factors Influencing Photosynthesis
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The external factors would include the availability of sunlight, temperature, CO concentration and water. As a plant photosynthesises, all these factors will simultaneously affect its rate. Hence, though several factors interact and simultaneously affect photosynthesis or CO fixation, usually one factor is the major cause or is the one that limits the rate.
Detailed Explanation
External factors critical to photosynthesis include sunlight, temperature, carbon dioxide levels, and water availability. These factors interact, but one often becomes the limiting factor in the process. For example, a plant may have sufficient sunlight and CO2, but if the temperature is too low, photosynthesis will not occur at an optimal rate. The overall rate of photosynthesis can thus be seen as a balance of these varying influences.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to cook a meal (photosynthesis) that requires several ingredients: oil (light), spices (CO2), and heat (temperature). If you run out of oil, no matter how much heat and spices you have, you cannot cook the meal well because one crucial ingredient is missing.
Blackman’s Law of Limiting Factors
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When several factors affect any [bio] chemical process, Blackman’s (1905) Law of Limiting Factors comes into effect. This states the following: If a chemical process is affected by more than one factor, then its rate will be determined by the factor which is nearest to its minimal value: it is the factor which directly affects the process if its quantity is changed.
Detailed Explanation
Blackman’s Law explains that among multiple factors affecting a process, the one that is closest to its minimum level will limit the process's overall rate. For instance, if a plant has sufficient light and a good level of CO2, but the temperature is too low, then temperature becomes the limiting factor affecting photosynthesis. This principle helps in understanding how to optimize plant growth conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a race where several runners can only run as fast as the slowest runner. If one runner is lagging (limiting factor) due to tiredness, it sets the pace for the entire group despite the others potentially being able to run faster. Thus, focusing on improving that one runner’s stamina may enhance the team’s speed.
Impact of Light on Photosynthesis
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
We need to distinguish between light quality, light intensity and the duration of exposure to light, while discussing light as a factor that affects photosynthesis. There is a linear relationship between incident light and CO fixation rates at low light intensities. At higher light intensities, gradually the rate does not show further increase as other factors become limiting.
Detailed Explanation
Light is crucial for photosynthesis, with its quality (wavelength), intensity, and exposure duration all playing significant roles. Initially, an increase in light intensity results in more CO2 fixing; however, beyond a certain point, additional light does not significantly affect the rate of photosynthesis, as other factors can become limiting. Understanding this relationship helps in managing plant growth and ensuring optimal conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a plant in full sunlight as a child playing in a well-lit room; they can play and be active (photosynthesize) as long as they have space to move (other resources). However, if the room becomes cramped (limited nutrients), even bright light won't help them perform better.
Carbon Dioxide Concentration
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Carbon dioxide is the major limiting factor for photosynthesis. The concentration of CO is very low in the atmosphere (between 0.03 and 0.04 per cent). Increase in concentration up to 0.05 per cent can cause an increase in CO fixation rates; beyond this the levels can become damaging over longer periods.
Detailed Explanation
CO2 is key in the photosynthesis process, with its atmospheric concentration being relatively low. An increase in this concentration can enhance the rate of photosynthesis, but if levels are too high for extended periods, they can cause stress or damage to plants. Different plants also have varying responses to these concentrations, especially in relation to light availability.
Examples & Analogies
Think of carbon dioxide as a flavoring agent in food. A little enhances the taste (photosynthesis), but too much can overpower it and ruin the dish. This is why growers might use controlled environments to optimize CO2 levels for plant growth.
Temperature's Role in Photosynthesis
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
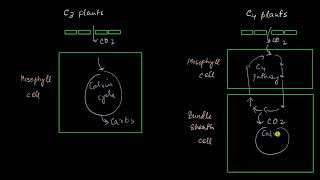
The dark reactions being enzymatic are temperature controlled. Though the light reactions are also temperature sensitive they are affected to a much lesser extent. The C plants respond to higher temperatures and show higher rate of photosynthesis while C plants have a much lower temperature optimum.
Detailed Explanation
Temperature affects the rate of photosynthesis significantly because biochemical reactions are temperature-sensitive. C4 plants tend to thrive at higher temperatures compared to C3 plants, which have a lower optimal temperature for photosynthesis. This adaptability highlights how different plants have evolved to cope with their environments.
Examples & Analogies
Just like a cake bakes faster in a hotter oven (optimal temperature for enzymes) but might burn if it’s too hot, different plants have their specific 'temperature sweet spot' for achieving the best photosynthesis performance without stress.
Water's Impact on Photosynthesis
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Even though water is one of the reactants in the light reaction, the effect of water as a factor is more through its effect on the plant, rather than directly on photosynthesis. Water stress causes the stomata to close hence reducing the CO availability. Besides, water stress also makes leaves wilt, thus, reducing the surface area of the leaves and their metabolic activity as well.
Detailed Explanation
While water is essential for the light reactions of photosynthesis, its influence primarily comes from its impact on plant health. Insufficient water leads to stomatal closure, limiting CO2 entry and causing leaf wilting, reducing photosynthesis overall. This stress factor can significantly limit plant growth and productivity.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine how you’d feel trying to breathe while wearing a mask that’s too tight (stomatal closure during water stress). You can’t take in enough air (CO2), making it hard to function (photosynthesize) well. Adequate hydration is necessary for optimal functionality.
Key Concepts
-
Photosynthesis: The process by which green plants convert sunlight into chemical energy using chlorophyll.
-
Limiting Factors: Environmental or internal aspects that can impede the effectiveness of photosynthesis.
-
Light Saturation: A condition where increasing light intensity stops enhancing photosynthesis rates.
-
Chlorophyll Content: A key factor in determining a plant's ability to perform photosynthesis effectively.
-
Temperature Optimum: The optimal temperature at which photosynthesis occurs most efficiently.
Examples & Applications
A plant may grow poorly in low light conditions even if carbon dioxide and water are plentiful.
Enrichment of the atmosphere with carbon dioxide can significantly improve the growth of greenhouse plants.
Tropical plants generally have higher photosynthetic efficiency at elevated temperatures compared to temperate plants.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Photosynthesis in the sun, brings us meals, a tasty run.
Stories
A little plant grows tall in the sun; it stretches its leaves to soak up fun. But if it gets too cold or dry, it'll hold back, oh my, oh my!
Memory Tools
Remember 'LCTW' for the four factors: Light, Carbon dioxide, Temperature, Water.
Acronyms
Use 'P-FEEL' to remember
Photosynthesis
Factors
External
Environmental
Limiting.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Limiting Factor
A condition that limits the rate of a process, such as photosynthesis, by being at its minimal level.
- Chlorophyll
The green pigment found in plants that is crucial for photosynthesis by absorbing light.
- Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll.
- Carbohydrates
Organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, essential for energy storage in plants.
- Enzyme
Proteins that catalyze or speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
