How many types of Pigments are involved in Photosynthesis?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Chlorophyll a and its Role
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about chlorophyll a, the most vital pigment in photosynthesis. Can anyone tell me what color it reflects and why that matters?

Chlorophyll a reflects green light, which is why plants appear green!

Precisely! It primarily absorbs blue and red light. Does anyone know why chlorophyll a is essential for photosynthesis?

Because it helps convert light energy into chemical energy!

Great job! Remember the acronym ABC—Absorption, Blue, and Conversion. Chlorophyll a's absorption leads to the conversion of light energy. How do you think other pigments assist in this process?

They probably capture different wavelengths of light that chlorophyll a might not absorb.

Absolutely correct! Let's summarize: chlorophyll a absorbs light effectively in specific wavelengths to drive photosynthesis.
Accessory Pigments
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now onto accessory pigments! Chlorophyll b is one of them. Why do you think we need it if chlorophyll a is already doing the work?

Chlorophyll b absorbs light in a different part of the spectrum.

Spot on! It helps increase the range of light that plants can use. And what about xanthophylls and carotenoids? What are their purposes?

I remember that they protect chlorophyll a from damage and help absorb light too.

Exactly! To recall these pigments, think of the term 'PEACH': Pigments Enhance Absorption, Chlorophyll, and Help! They ensure the plant uses the maximum amount of light possible.

So they work together to make photosynthesis more efficient!

Yes, they do! To sum up, accessory pigments play crucial roles in enhancing light absorption and protecting chlorophyll a.
Photon Absorption Spectrum
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a. Why do you think it’s significant to compare it with the action spectrum of photosynthesis?

To see which wavelengths are most effective in promoting photosynthesis!

Exactly! In which regions do we see maximum absorption for chlorophyll a?

In the blue and red regions of the spectrum!

That's right! When looking at the action spectrum, we can see that photosynthesis overlaps in those regions too. Can anyone think of how this enhances plant productivity?

By efficiently using different wavelengths, plants can maximize their energy production!

Well said! Remember the phrase 'Light is Life' as it encapsulates the essence of why we study these pigments: They are fundamental to the life processes of plants. Let's conclude by summarizing the key roles of pigments in photosynthesis.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, four key pigments are identified: chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, xanthophylls, and carotenoids. Their roles in light absorption, energy transfer, and protecting chlorophyll a from damage during photosynthesis are explored. The relationship between pigment absorption spectra and the rates of photosynthesis is also addressed.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Pigments in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a crucial process in plants where light energy is converted into chemical energy, and various types of pigments play significant roles in this process. The primary pigments involved in photosynthesis are:
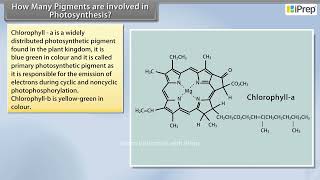
- Chlorophyll a: This is the most abundant pigment responsible for the green color of plants. It primarily absorbs light in the blue (around 430 nm) and red (around 662 nm) spectra, making it essential for photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll b: This accessory pigment absorbs light mainly in the blue (around 453 nm) and red-orange (around 642 nm) regions. It supports chlorophyll a by broadening the spectrum of light that can be used for photosynthesis.
- Xanthophylls: These yellow pigments absorb light in regions that chlorophylls do not effectively capture. They help in light absorption and protect chlorophylls from photodamage by dissipating excess energy.
- Carotenoids: Also yellow to orange pigments, carotenoids absorb light in the blue and green regions. They assist in photosynthesis and protect chlorophyll from oxidative damage.
Through techniques like paper chromatography, these pigments can be separated, and analysis of their absorption spectra reveals critical information about their functional roles in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll a is particularly significant as it is directly involved in the light reactions, while accessory pigments such as chlorophyll b, xanthophylls, and carotenoids enhance the efficiency of the process by absorbing different wavelengths of light and transferring that energy to chlorophyll a.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Leaf Pigments and Their Colors
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Looking at plants have you ever wondered why and how there are so many shades of green in their leaves – even in the same plant? We can look for an answer to this question by trying to separate the leaf pigments of any green plant through paper chromatography. A chromatographic separation of the leaf pigments shows that the colour that we see in leaves is not due to a single pigment but due to four pigments: Chlorophyll a (bright or blue green in the chromatogram), chlorophyll b (yellow green), xanthophylls (yellow) and carotenoids (yellow to yellow-orange).
Detailed Explanation
Leaves can appear in various shades of green due to the presence of multiple pigments. By using a technique called paper chromatography, scientists can separate these pigments to study them individually. There are four key pigments involved in photosynthesis: Chlorophyll a is blue-green and is the primary pigment, Chlorophyll b is yellow-green and supports Chlorophyll a, xanthophylls are yellow and help in light absorption, and carotenoids are yellow to orange, which also assist in capturing light energy for photosynthesis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the pigments in a leaf as colors in a painter's palette. Just as a painter mixes various colors to create different shades in a painting, plants mix pigments to create a variety of greens, making each leaf unique yet part of a collective green landscape.
Roles of Pigments in Photosynthesis
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Pigments are substances that have an ability to absorb light, at specific wavelengths. Can you guess which is the most abundant plant pigment in the world? Let us study the graph showing the ability of chlorophyll a pigment to absorb lights of different wavelengths. Of course, you are familiar with the wavelength of the visible spectrum of light as well as the VIBGYOR. From Figure 11.3a can you determine the wavelength (colour of light) at which chlorophyll a shows the maximum absorption? Does it show another absorption peak at any other wavelengths too?
Detailed Explanation
Pigments are crucial because they absorb light energy at specific wavelengths. Chlorophyll a is the most abundant pigment in plants and is primarily responsible for photosynthesis. It absorbs mainly blue and red light, which are the most effective wavelengths for driving the photosynthetic process. Understanding the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a helps us identify which wavelengths of light are most useful for photosynthesis, with peaks typically found in the blue (around 430 nm) and red (around 680 nm) regions of the spectrum.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a solar panel that only works well with certain colors of light; similarly, chlorophyll acts like a solar panel, efficiently capturing light in specific colors (wavelengths). This “tuning” allows plants to effectively convert sunlight into energy for growth.
Accessory Pigments and Their Importance
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
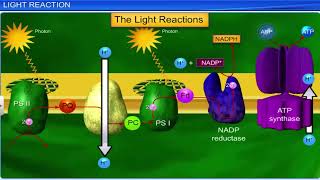
Though chlorophyll is the major pigment responsible for trapping light, other thylakoid pigments like chlorophyll b, xanthophylls and carotenoids, which are called accessory pigments, also absorb light and transfer the energy to chlorophyll a. Indeed, they not only enable a wider range of wavelength of incoming light to be utilised for photosynthesis but also protect chlorophyll a from photo-oxidation.
Detailed Explanation
Accessory pigments play a supportive role in photosynthesis by capturing light energy that chlorophyll a cannot absorb. They absorb light in different parts of the spectrum, ensuring that the plant can utilize as much sunlight as possible for energy conversion. Additionally, these pigments help protect chlorophyll a from damage caused by excessive light—a vital function that maintains the health of the plant and optimizes photosynthesis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of accessory pigments as backup singers in a choir. While the lead singer (chlorophyll a) has the forefront role, the backup singers (accessory pigments) enhance the overall performance by providing depth and richness, all while helping keep the main singer (chlorophyll a) from burning out too quickly.
Key Concepts
-
Pigments play a crucial role in capturing light energy for photosynthesis.
-
Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment; chlorophyll b and carotenoids serve as accessories.
-
The absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a peaks in blue and red light, aligning with the action spectrum for photosynthesis.
Examples & Applications
Chlorophyll a absorbs light at wavelengths around 430 nm and 662 nm, primarily using this energy for photosynthesis.
Carotenoids provide extra protection for chlorophyll a, absorbing light in the blue and green regions to prevent damage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Chlorophyll is green and bright, absorbs the sun to give plants light.
Stories
In a sunlit garden, the plants use chlorophyll a to trap sunlight, while chlorophyll b and carotenoids cheer along, adding colors and support, keeping the plants strong!
Memory Tools
Remember 'CLEC': Chlorophyll, Light, Energy, Cartenoids – for Plant Energy Absorption!
Acronyms
P.E.A.C.H.
Photosynthetic Energy Absorption Capture by Helpers - for all pigments involved!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Chlorophyll a
The primary pigment in photosynthesis, absorbing mainly blue and red light.
- Chlorophyll b
An accessory pigment that complements chlorophyll a by absorbing additional wavelengths of light.
- Carotenoids
Pigments that absorb light in blue and green regions and protect chlorophyll from damage.
- Xanthophylls
Yellow pigments that assist in photosynthesis and protect chlorophyll from oxidative damage.
- Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
- Absorption Spectrum
A graph plotting a pigment's absorption of various wavelengths of light.
- Action Spectrum
A graph describing the rate of photosynthesis at different light wavelengths.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
