Where does Photosynthesis Take Place?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Photosynthesis Location
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss where photosynthesis takes place in plants. Can anyone tell me the primary location of photosynthesis?

In the leaves, right?

Correct! Photosynthesis primarily occurs in the leaves, specifically in the chloroplasts of mesophyll cells. But can anyone think of other parts of a plant where photosynthesis might occur?

Maybe in the stems or the flowers if they are green?

Exactly! Other green parts of the plant, such as stems and unripe fruits, can also perform photosynthesis. This is why many plants are green overall.

What makes the leaves green, though?

Great question! The green color comes from chlorophyll, the pigment that absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. Remember, 'Chlorophyll captures light!' Let's move on to how chloroplasts are structured.

In summary, photosynthesis mainly occurs in the chloroplasts of leaves and other green structures like stems and unripe fruits.
Structure of Chloroplasts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Chloroplasts are fascinating organelles! Who can describe their structure?

They have membranes and some stacks in them, right?

Absolutely! Chloroplasts contain an inner and outer membrane, with thylakoids stacked in structures called grana. The fluid inside is called stroma, which plays a critical role in the conversion of light energy into chemical energy.

What exactly happens in the stroma?

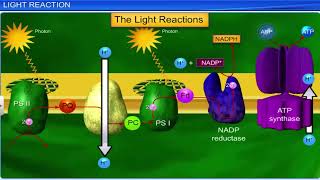
The stroma is where the Calvin cycle occurs, using ATP and NADPH produced in the thylakoids to fix carbon dioxide into glucose. This is an important distinction: light reactions occur in the thylakoids, while dark reactions, or carbon-fixing reactions, occur in the stroma.

So, it's like two different phases happening in one organelle?

Exactly! In summary, chloroplasts have a dual structure: thylakoids for light reactions and stroma for the Calvin cycle.
Role of Mesophyll Cells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about mesophyll cells. Can anyone explain their role in photosynthesis?

They're where the chloroplasts are, right? So they must be important for capturing light.

Excellent! Mesophyll cells contain a high number of chloroplasts positioned to maximize light absorption. There's a specific orientation of chloroplasts to catch optimal sunlight. Can anyone describe how this positioning might work?

Maybe they align to face the light?

Exactly! They can adjust their positioning—flat surfaces can align parallel to incoming light. Remember, it's essential for maximizing photosynthesis efficiency.

So, can you summarize the role of mesophyll cells?

Sure! Mesophyll cells with chloroplasts are the primary sites where photosynthesis occurs, enhancing light absorption through their specific positioning.
Importance of Photosynthesis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, why is photosynthesis important for life on Earth?

Because it produces oxygen and food!

Right! Photosynthesis is not only responsible for producing glucose as food for the plant but also releases oxygen into the atmosphere. It’s vital for all aerobic organisms. Can anyone think of why this would make plants so essential?

Because without plants, we wouldn’t have oxygen to breathe?

Exactly! In summary, photosynthesis is crucial because it produces food and oxygen, supporting life on Earth.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Photosynthesis is carried out mainly in the chloroplasts located in the mesophyll cells of leaves, but it can also take place in other green parts of the plant. Within the chloroplasts, distinct structures facilitate the absorption of light and the synthesis of chemical energy.
Detailed
Where does Photosynthesis Take Place?
Photosynthesis is fundamentally crucial for life on Earth, as it converts light energy into chemical energy through the production of organic compounds. In higher plants, photosynthesis predominantly occurs in green leaves, although it can also take place in other green parts such as stems and unripe fruits. The primary site of photosynthesis is the chloroplast, an organelle found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves, which contains chlorophyll pigments essential for capturing light energy. The structure of chloroplasts features a complex membrane system, including thylakoids organized into grana and a surrounding stroma where the Calvin cycle occurs.
The chloroplast's alignment and positioning of chlorophyll enable maximal light absorption. The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes, where light energy is converted into ATP and NADPH, while the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) occur in the stroma, utilizing ATP and NADPH to fix carbon dioxide into glucose. Understanding where photosynthesis occurs helps elucidate the energy flow in ecosystems and the overall dependence of life on sunlight.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Photosynthesis Locations
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You would of course answer: in ‘the green leaf’ or ‘in the chloroplasts’, based on what you earlier read in Chapter 8. You are definitely right. Photosynthesis does take place in the green leaves of plants but it does so also in other green parts of the plants. Can you name some other parts where you think photosynthesis may occur?
Detailed Explanation
Photosynthesis primarily occurs in the green parts of plants, most notably in the leaves. However, it is not limited to leaves alone. Other green parts of the plant, such as stems and unripe fruits, can also carry out photosynthesis. This is because these parts contain chlorophyll, the green pigment essential for the process, allowing them to capture light energy.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a plant like a solar panel that harvests sunlight to produce energy. Just as a solar panel can work on rooftops as well as on the walls of buildings, a plant can use its chlorophyll-containing tissues not just in its leaves but through out its green surfaces.
Chloroplast Location and Structure
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You would recollect from previous unit that the mesophyll cells in the leaves, have a large number of chloroplasts. Usually the chloroplasts align themselves along the walls of the mesophyll cells, such that they get the optimum quantity of the incident light.
Detailed Explanation
The mesophyll cells, found within the leaf, contain numerous chloroplasts, which are the sites of photosynthesis. These chloroplasts are strategically arranged along the walls of the mesophyll to capture the maximum amount of light that enters the leaf. This arrangement enhances their ability to perform photosynthesis efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a room filled with windows where people are sitting. If everyone positions themselves close to the windows, they can take in more sunlight, just like how chloroplasts gather light for the plant.
Chloroplast Structure
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You have studied the structure of chloroplast in Chapter 8. Within the chloroplast there is membranous system consisting of grana, the stroma lamellae, and the matrix stroma. There is a clear division of labour within the chloroplast.
Detailed Explanation
Chloroplasts have a complex structure that includes thylakoids, where the light reactions of photosynthesis occur, and the stroma, which is where the Calvin cycle takes place. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll and other pigments that capture light energy, while the stroma is rich in enzymes that use this energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the chloroplast like a factory. The thylakoids are the assembly lines where raw materials (light) are converted into products (energy). The stroma is the main office where decisions and calculations are made to ensure the factory runs smoothly, turning those products into usable energy for the plant.
Light and Dark Reactions
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The membrane system is responsible for trapping the light energy and also for the synthesis of ATP and NADPH. In stroma, enzymatic reactions synthesise sugar, which in turn forms starch. The former set of reactions, since they are directly light driven are called light reactions (photochemical reactions). The latter are not directly light driven but are dependent on the products of light reactions (ATP and NADPH). Hence, to distinguish the latter they are called, by convention, as dark reactions (carbon reactions). However, this should not be construed to mean that they occur in darkness or that they are not light-dependent.
Detailed Explanation
Photosynthesis consists of two main phases: light reactions and dark reactions (Calvin cycle). Light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membranes, require light to produce ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions, occurring in the stroma, use these products to convert carbon dioxide into sugar. It's important to note that while these reactions don't need light directly, they rely on the outputs from the light reactions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a two-step process like making a smoothie. In the first step, you gather and blend all the fruits (light reactions). This energy-packed smoothie is then used later as a drink (dark reactions) to fuel your body. You can't make the smoothie without the fruit, but if it's already made, you can use it at any time, day or night.
Key Concepts
-
Photosynthesis occurs primarily in the chloroplasts located in mesophyll cells of leaves.
-
The chloroplast's structure includes thylakoids and stroma, facilitating different stages of photosynthesis.
-
Chlorophyll is the pigment essential for capturing light energy, and mesophyll cells are key sites for photosynthesis.
Examples & Applications
Photosynthesis occurs not just in leaves, but also in the green stems of plants like cacti.
Young, green fruits like tomatoes can photosynthesize despite being in a developmental stage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the leaves, chloroplasts play, photosynthesis every day.
Stories
Once upon a time, in the land of green, the leaves used sunlight to make food unseen. With chloroplasts in every cell, they turned light into energy, and all was well.
Memory Tools
C-M-M: Chloroplasts, Mesophyll, and Magic (Photosynthesis).
Acronyms
P.O.L
Photosynthesis Occurs in Leaves.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Chloroplast
An organelle in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and is the site where photosynthesis occurs.
- Mesophyll Cells
Cells located in the leaf that contain a high concentration of chloroplasts, crucial for photosynthesis.
- Thylakoids
Membranous structures within chloroplasts where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place.
- Stroma
The fluid-filled space within chloroplasts where the Calvin cycle takes place.
- Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in chloroplasts that captures light energy for photosynthesis.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
