What do we Know?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Photosynthesis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the concept of photosynthesis – the process that allows plants to create their own food. Can anyone tell me why this is important?

It's important because animals, including us, depend on plants for food.

And they also release oxygen, which is essential for us to breathe.

Exactly! So, plants are known as autotrophs because they can synthesize their own food through photosynthesis.

What do heterotrophs do then?

Great question! Heterotrophs, like animals, cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms to survive.

Let's remember this: AUTOTROPHS MAKE (A = Autotrophs, M = Make). Heterotrophs EAT (H = Heterotrophs, E = Eat).

Photosynthesis will be our focus today as it serves as the foundation for life on Earth.
Necessity of Light, Water, and CO2
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What do you think are the essential components needed for photosynthesis?

I think it needs light and carbon dioxide.

And water! It's mentioned in the chapter too.

That's correct! Light, water, and carbon dioxide are all critical for photosynthesis. Can anyone explain why plants need these?

Plants use light energy to convert CO2 and water into glucose.

Exactly! The light energy drives the chemical reactions to produce energy-rich compounds. Let's remember: LIGHT is the key to energize (LIGHT = L for Light, E for Energy).
Early Experiments on Photosynthesis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into some historical experiments that demonstrated how photosynthesis works. Could someone share what they recall?

Joseph Priestley’s experiment showed that plants restore air quality.

And Ingenhousz found out that sunlight is needed for this process.

Exactly! These experiments helped establish that plants release oxygen and that light is crucial for their growth and energy production.

Remember: PRIESTLEY RESTORES AIR (PRA = Priestley, R = Restores, A = Air).
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Photosynthesis is a crucial process where green plants convert light energy into chemical energy, serving as the primary source of food and oxygen for all life forms. Autotrophs, such as green plants, synthesize their own food using sunlight, while heterotrophs rely on plants for nourishment.
Detailed
What do We Know?
Photosynthesis is a vital biological process that enables green plants to convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, thus supporting life on Earth. Plants, known as autotrophs, produce their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, while heterotrophs, including animals and humans, depend on these plants for sustenance. This section introduces the core concepts of photosynthesis, focusing on its significance in food production and oxygen release.
Key Points Covered:
- Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs: Green plants synthesize their food, while all non-plant organisms depend on them.
- Importance of Photosynthesis: It is the primary source of food and oxygen, essential for life.
- Photosynthetic Processes: Light energy is absorbed and transformed into chemical energy, emphasizing the complex reactions that form the basis of life on Earth.
- Experiments Demonstrating Photosynthesis: Experiments illustrate that chlorophyll, light, and CO2 are necessary for photosynthesis, highlighting the scientific understanding achieved through early experiments.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Dependence of Organisms on Plants
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
All animals including human beings depend on plants for their food. Have you ever wondered from where plants get their food?
Detailed Explanation
All living organisms, including humans, depend on plants as a source of food. While animals obtain their energy and nutrients from consuming plants or other animals, plants themselves generate their food through a unique process. This underscores the interdependence within ecosystems, where plants form the foundation of the food chain.
Examples & Analogies
Think of plants as chefs in a restaurant. Just as chefs prepare meals for diners, plants produce food through photosynthesis. Without these 'chefs,' no one would have meals to enjoy, illustrating the vital role that plants play in supporting life.
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Green plants have to make or rather synthesise the food they need and all other organisms depend on them for their needs. The green plants make or rather synthesise the food they need through photosynthesis and are therefore called autotrophs.
Detailed Explanation
Plants, classified as autotrophs, have the ability to produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis. This process involves using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to create glucose, which serves as energy for the plant. In contrast, organisms that cannot make their own food and rely on others for nutrition are known as heterotrophs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a factory producing goods. In this case, the factory represents a plant that creates its own products (food). Meanwhile, people who buy these goods from the factory represent heterotrophs, who depend on the factory for their supplies.
Photosynthesis Basics
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You have already learnt that autotrophic nutrition is found only in plants and all other organisms that depend on the green plants for food are heterotrophs. Green plants carry out ‘photosynthesis’, a physico-chemical process by which they use light energy to drive the synthesis of organic compounds.
Detailed Explanation
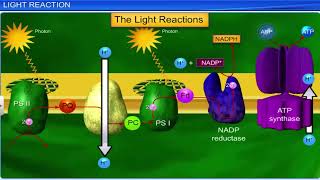
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process performed by green plants that allows them to convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. This process involves the absorption of light by chlorophyll, leading to a series of reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a solar panel. Just as it converts sunlight into electricity that powers our homes, plants convert sunlight into chemical energy that fuels their growth and survival through photosynthesis.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Ultimately, all living forms on earth depend on sunlight for energy. The use of energy from sunlight by plants doing photosynthesis is the basis of life on earth. Photosynthesis is important due to two reasons: it is the primary source of all food on earth. It is also responsible for the release of oxygen into the atmosphere by green plants.
Detailed Explanation
Photosynthesis is crucial for life on Earth as it provides the primary source of energy for nearly all organisms through food production. Moreover, it generates oxygen, which is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms, including humans. Without photosynthesis, the ecosystem would collapse, leading to a lack of food and oxygen.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the sun as the ultimate power source for a city. Just as a city relies on electricity (from a power plant) for light, appliances, and productivity, all life on Earth relies on the sun as the primary energy source through the process of photosynthesis.
Experiments Confirming Photosynthesis
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Some simple experiments you may have done in earlier classes have shown that chlorophyll (green pigment of the leaf), light and CO2 are required for photosynthesis to occur.
Detailed Explanation
Experiments in classrooms have demonstrated the necessity of chlorophyll, light, and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis to happen. These experiments often show that green parts of plants (where chlorophyll is found) are essential for food production, indicating that without these elements, photosynthesis cannot occur.
Examples & Analogies
Consider baking a cake. To make a cake, you need specific ingredients (like flour, sugar, and eggs). If any ingredient is missing, you simply can't bake. Similarly, for photosynthesis, the absence of chlorophyll, light, or carbon dioxide means plants can't produce their food.
Starch Formation Experiment
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You may have carried out the experiment to look for starch formation in two leaves – a variegated leaf or a leaf that was partially covered with black paper, and exposed to light. On testing these leaves for the presence of starch, it was clear that photosynthesis occurred only in the green parts of the leaves in the presence of light.
Detailed Explanation
In this experiment, students typically observe that only the green parts of leaves produce starch when exposed to sunlight. This highlights that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis since starch is a product of this process. When parts of the leaf are covered and not exposed to light, starch formation does not occur in those areas.
Examples & Analogies
This can be compared to a person trying to bake a cake by only mixing the ingredients but not turning on the oven. Without baking (or light), the cake (or starch) cannot form, illustrating the need for specific conditions for photosynthesis to occur.
Carbon Dioxide Requirement Experiment
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Another experiment you may have carried out where a part of a leaf is enclosed in a test tube containing some KOH soaked cotton (which absorbs CO2), while the other half is exposed to air. The setup is then placed in light for some time. On testing for the presence of starch later in the two parts of the leaf, you must have found that the exposed part of the leaf tested positive for starch while the portion that was in the tube tested negative. This showed that CO2 was required for photosynthesis.
Detailed Explanation
In this experiment, students set up a leaf to test for starch presence. The part of the leaf exposed to air (and thus CO2) produced starch, while the covered part did not. This experiment demonstrates the requirement of carbon dioxide for the photosynthesis process, reinforcing the earlier points regarding photosynthesis essentials.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a plant as a factory that needs all components to produce a product. If one essential component (like carbon dioxide in this case) is missing, the factory cannot produce goods, demonstrating how crucial each element of photosynthesis is for the plant's survival.
Key Concepts
-
Photosynthesis: The process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
-
Autotrophs: Organisms that produce their own food, primarily through photosynthesis.
-
Heterotrophs: Organisms that rely on consuming other organisms for nourishment.
Examples & Applications
A typical plant, such as an oak tree, synthesizes food via leaves using sunlight, CO2, and water.
Humans and animals exhibit heterotrophic behavior by consuming plants or other animals for energy.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the light, plants take a bite, turning CO2 and water right.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a lush green forest, plants whispered secrets about how they create food using sunshine, water, and air.
Memory Tools
A helpful mnemonic for remembering photosynthesis: LIGHT (Light + CO2 + H2O -> Glucose + O2).
Acronyms
Acronym for photosynthesis
= Plants
= Harness
= Oxygen
= Food.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants use light energy to produce food from carbon dioxide and water.
- Autotrophs
Organisms that can produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- Heterotrophs
Organisms that cannot produce their own food and rely on other organisms for sustenance.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
