Splitting of Water
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Water Splitting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about how water splitting works in photosystem II during photosynthesis. Can anyone tell me why water is essential in this process?

Is it because water provides the oxygen we breathe?

Exactly! Water splitting creates oxygen as a byproduct. It also provides electrons that replace those lost from chlorophyll when light energy is absorbed. This replenishment is critical for the continuation of the light reactions. Let’s remember: H<sub>2</sub>O - Water = Oxygen + Electrons!

So, without water, the chlorophyll wouldn't be able to keep producing energy?

Right! The reaction can be summarized: 2H<sub>2</sub>O → 4H<sup>+</sup> + O<sub>2</sub> + 4e<sup>-</sup>. This is fundamental for sustaining the entire photosynthesis process.
Understanding the Byproducts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our last session, we talked about the splitting of water. What are the byproducts of this reaction?

It produces oxygen, protons, and electrons.

Correct! The oxygen is released into the atmosphere. Why is this significant?

Because it's crucial for us and other living organisms that require oxygen to survive!

Exactly! It's like a breath of fresh air that plants give us. And don’t forget the protons—they play a vital role in creating a proton gradient that will help synthesize ATP later!
Mechanism of Water Splitting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into the mechanism of water splitting in PS II. Can anyone explain where this splitting occurs?

In the thylakoid membrane, right?

Correct! The water-splitting complex is located on the inner side of the thylakoid membrane. What’s produced there?

Electrons, protons, and oxygen are formed there!

Exactly! These electrons then move on to help in the electron transport chain. This reaction is vital in replenishing lost electrons from chlorophyll, enabling the entire light reaction process to continue.
Overall Importance of Water Splitting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s sum up why water splitting is important for photosynthesis. What are some key points?

It provides electrons for the light reactions and produces oxygen.

And the protons help create energy in the form of ATP later on!

Great answers! Remember, without water splitting, plants couldn’t sustain photosynthesis effectively, which means they couldn't feed themselves or us. It’s a crucial part of the cycle of life!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore how the splitting of water molecules in photosystem II replaces electrons lost during the light reactions of photosynthesis. This process releases protons and oxygen, vital for sustaining life on Earth. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for grasping the broader context of photosynthesis.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
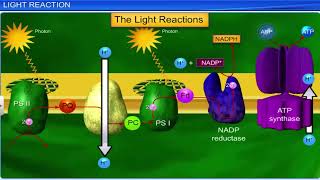
The splitting of water, known as photolysis, occurs in photosystem II (PS II) of chloroplasts during the light reactions of photosynthesis. When light is absorbed, it excites electrons in chlorophyll molecules, prompting their transfer through an electron transport chain. To sustain this process, PS II must continually replenish its electrons. This replenishment is achieved by splitting water molecules into protons (H+), electrons (e-), and oxygen (O2) as per the reaction:
2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e-.
The oxygen produced is released as a byproduct into the atmosphere, which is critical for aerobic life forms, including humans. In the luminal side of the thylakoid membrane where this splitting occurs, the protons contribute to a chemical gradient that is crucial for ATP generation later in the photosynthetic process. Understanding water splitting and its role in oxygen production is essential in the study of plant physiology and the broader implications of photosynthesis for life on Earth.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Replacement of Electrons in Photosystem II
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You would then ask, How does PS II supply electrons continuously? The electrons that were moved from photosystem II must be replaced. This is achieved by electrons available due to splitting of water. The splitting of water is associated with the PS II; water is split into 2H+, [O] and electrons. This creates oxygen, one of the net products of photosynthesis. The electrons needed to replace those removed from photosystem I are provided by photosystem II.
2H₂O → 4H⁺ + O₂ + 4e⁻
Detailed Explanation
Photosystem II (PS II) is crucial for photosynthesis as it needs a constant supply of electrons. When PS II absorbs light, it excites electrons to a higher energy state, and these electrons must be replaced to keep the process going. This replacement is facilitated by the splitting (or photolysis) of water molecules. During this process, each water molecule (H₂O) is split into hydrogen ions (H⁺), oxygen (O₂), and electrons (e⁻). The electrons produced here are utilized to replenish those lost from PS II, ensuring the photosynthesis process can continue effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a factory assembly line where workers are constantly needed to keep production going. If a worker leaves the line, they must be replaced quickly for production to continue. In this case, the 'factory' is photosynthesis, and the workers are electrons. Water acts like a source that ensures there's always enough 'workers' (electrons) available to keep the line running smoothly.
Location of Water Splitting
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
We need to emphasise here that the water splitting complex is associated with the PS II, which itself is physically located on the inner side of the membrane of the thylakoid. Then, where are the protons and O₂ formed likely to be released – in the lumen? or on the outer side of the membrane?
Detailed Explanation
The water-splitting complex is an essential component of Photosystem II, located within the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts. When the water molecules are split, the oxygen produced is released into the atmosphere, while the hydrogen ions (protons) accumulate in the lumen (the interior space of the thylakoids). This accumulation of protons is vital as it contributes to the formation of a proton gradient used later for ATP production during photosynthesis.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water reservoir where water is constantly being released to irrigate plants. Just as water flows from the reservoir outwards to nourish the plants, the oxygen produced during water splitting 'flows' out into the atmosphere, while the protons remain in the reservoir, where they help create pressure essential for pushing more water (energy) through the irrigation system (the process of making ATP).
Key Concepts
-
Photolysis: The splitting of water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons through light energy.
-
Importance of Oxygen: The oxygen produced is a vital byproduct necessary for aerobic organisms.
-
Role of Protons: The protons from water splitting contribute to a concentration gradient that aids ATP synthesis.
Examples & Applications
The oxygen released during water splitting is essential for human and animal respiration.
Chloroplasts utilize water from the plant's roots for photosynthesis, showcasing the interconnectedness of plant physiology.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Water splits in the light of day, / Oxygen, protons lead the way.
Stories
Imagine a tiny factory inside leaves where water arrives, splits, and turns into oxygen—its gift to the world!
Memory Tools
Remember: WHEO - Water splits to make Hydrogen (H⁺), Electrons (e⁻), and Oxygen (O₂).
Acronyms
P.O.E - Photolysis
Oxygen and Protons each lead to energy!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Photosystem II (PS II)
A protein and pigment complex in plants responsible for the light reactions of photosynthesis, where water is split.
- Photolysis
The process of splitting water molecules into protons, electrons, and oxygen by light energy.
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
A series of proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane where electrons are transferred, leading to ATP production.
- Oxygen (O<sub>2</sub>)
A byproduct of water splitting during photosynthesis, essential for aerobic respiration in living organisms.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
