Temperature
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Impact of Temperature on Photosynthesis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about how temperature affects photosynthesis. Can anyone tell me why temperature might matter for plant growth?

Maybe because enzymes in plants work better at certain temperatures?

Exactly, great point! The dark reactions, which involve enzymes, are sensitive to temperature changes. What happens to most enzymes when it gets too hot?

They can denature or stop working properly!

Right! This is crucial because if enzymes denature, photosynthesis slows down or could stop completely. Let’s not forget light reactions are less impacted — they do depend on temperature, but not as directly as the dark reactions.

So, do all plants have the same temperature requirements?

Good question! No, they don’t. Tropical plants prefer higher temperatures compared to temperate plants. This adaptation is vital for their survival.

Interesting! So growing tropical plants in cooler places might not yield well because of temperature?

Exactly! It’s essential to consider the plant’s natural habitat to maintain optimal growth conditions. Today’s lesson shows us why understanding temperature is key in agriculture.

To wrap up, remember that temperature impacts dark reactions more than light reactions, and optimum temperatures vary between plant types. Keep this in mind as we explore other factors affecting photosynthesis in the next session.
Enzyme Functioning and Photosynthesis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper! Who can recall what happens during dark reactions in photosynthesis?

That's where CO2 is fixed into sugars!

Right! And this process relies heavily on enzymes. Can anyone tell me how increased temperature affects these enzymes?

Higher temperatures usually speed up enzyme activity, but if it's too high, they can stop working.

Exactly! This brings us to a crucial point: each enzyme has an optimal temperature range. If it’s too high, they denature, and effectiveness drops drastically. What happens to photosynthesis if enzymes stop working?

Photosynthesis would slow down a lot!

Correct! And different plant types have enzymes that function best at different temperature ranges. That's essential for survival and maximizing photosynthesis.

So, it’s important to know the right temperature for the plants we’re growing?

Absolutely! As we continue learning about photosynthesis, remember the impact of temperature on the enzymes involved in each reaction.
Optimizing Growth Conditions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand temperature's role, let’s discuss how to use this knowledge practically in agriculture. How might farmers use temperature information?

They could choose what crops to plant based on the local climate!

Exactly! Knowing which plants thrive at which temperatures helps in planning and maximizing yields. What other steps can farmers take?

They might create greenhouses to control the temperature more, right?

Correct! Greenhouses are an excellent way to maintain suitable temperatures for tropical plants in cooler climates. What is one challenge they might face?

Keeping the temperature consistent can be hard.

Yes, fluctuations can affect plant growth significantly. It's vital to monitor and manage these environments carefully.

I see now why understanding temperature is vital for our food supply!

Great observation! Temperature management is a key to successful agriculture, especially as climate change affects traditional growing patterns.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Temperature plays a critical role in the rate of photosynthesis, influencing both light reactions and dark reactions. While dark reactions are mainly affected as they are enzymatic, light reactions are less sensitive. The optimal temperature for different plants varies based on their environmental adaptations, with tropical plants thriving at higher temperatures compared to temperate species.
Detailed
Temperature and Photosynthesis
Temperature significantly influences the rate of photosynthesis, particularly affecting the Calvin cycle, also known as the dark reactions. While light reactions are generally less sensitive to temperature fluctuations, the enzymes involved in dark reactions are temperature-dependent. This section emphasizes that C plants perform better at higher temperatures, whereas C plants have a much lower temperature optimum. Moreover, the optimal temperature varies according to the habitat, with tropical plants requiring higher temperatures than temperate plants. Understanding this relationship is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices and enhancing crop yields in various climates.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Impact of Temperature on Photosynthesis
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
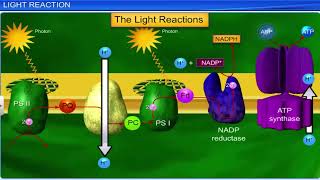
The dark reactions being enzymatic are temperature controlled. Though the light reactions are also temperature sensitive they are affected to a much lesser extent. The C4 plants respond to higher temperatures and show higher rates of photosynthesis while C3 plants have a much lower temperature optimum.
Detailed Explanation
Temperature plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, particularly affecting the dark reactions, which are driven by enzymes. As temperature rises, enzymes typically work faster, up to a certain point called the optimum temperature. For C4 plants, which thrive in warm climates, higher temperatures enhance their rates of photosynthesis. On the contrary, C3 plants, which usually grow in cooler environments, have lower optimum temperatures, meaning they become less efficient at photosynthesizing as temperatures climb beyond their comfort zone.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine cooking a dish. Each ingredient (like enzymes) works best at a specific temperature. If the temperature is too low, the dish takes longer to cook (like photosynthesis slows down in cool weather), and if it’s too high, some ingredients might get burnt or lose their flavors (like photosynthesis efficiency decreases in extremely high temperatures for C3 plants).
Habitat Adaptation and Temperature Optimum
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The temperature optimum for photosynthesis of different plants also depends on the habitat that they are adapted to. Tropical plants have a higher temperature optimum than the plants adapted to temperate climates.
Detailed Explanation
Different plants have adapted to their environments, and this adaptation influences how well they perform photosynthesis at varying temperatures. Tropical plants, which live in warm, humid environments, have evolved to optimize their photosynthesis at higher temperatures. In contrast, plants from temperate climates, which experience wider temperature fluctuations, are optimized for cooler conditions. Therefore, each plant species has its own 'best temperature range' for maximizing photosynthesis based on where it naturally grows.
Examples & Analogies
Think of athletes training for different climates. A sprinter in a humid tropical region would train to perform at high temperatures, while a winter sport athlete would excel in cooler conditions. Similarly, plants are like athletes, evolving to thrive in their unique 'training environments'—the warmer climates foster tropical plants to grow best in higher heat, while temperate plants prefer cooler breezes.
Key Concepts
-
Temperature Impact on Photosynthesis: Temperature significantly influences photosynthesis, especially dark reactions.
-
Enzyme Activity: Enzymes in dark reactions are sensitive to temperature, with optimal ranges differing among plant types.
-
Tropical vs. Temperate Plants: Tropical plants thrive at higher temperatures compared to temperate plants, affecting their growth and survival.
Examples & Applications
Tropical plants such as bananas thrive in high temperatures between 25-35°C, while temperate plants like lettuce prefer cooler ranges.
Using greenhouses allows farmers to maintain higher temperatures for tropical crops in regions that are otherwise cooler.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the sun, plants run, enzymes race, but when it's hot, they lose their place.
Stories
Once a banana tree lived in a warm land, thriving. But when it tried to grow in the snow, it found itself dying.
Memory Tools
TEMPERATURE: Trust Every Moment Ensures Better Action Towards Uplifting Resistance Every time.
Acronyms
TEMPS
Temperature Effects Metabolic Processes Significantly.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants convert light energy into chemical energy by synthesizing glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
- Dark Reactions
The phase of photosynthesis that does not require light directly; it uses ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions to fix carbon dioxide into sugar.
- Light Reactions
The phase of photosynthesis that requires light energy to produce ATP and NADPH by splitting water molecules.
- Enzymatic Reaction
Chemical reactions in living organisms that are catalyzed by enzymes; temperature can affect their rates.
- Denaturation
The process in which proteins lose their shape and function due to high temperatures or extreme pH levels.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
