STREAMLINE FLOW
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Streamline Flow
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to explore the concept of streamline flow. Can anyone tell me what they believe streamline flow to be?

Isn’t it when the fluid flows without any turbulence?

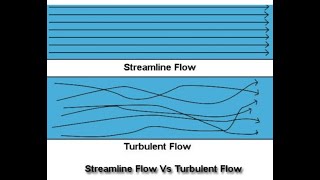
Exactly! Streamline flow occurs in a smooth, non-turbulent way, where the flow of fluid particles is steady. Each fluid particle follows a unique path called a streamline.

So, does that mean the speed of the fluid is the same everywhere?

Good question! While the speed is consistent at a specific point, different points can have different speeds. That brings us to our acronym: 'SHAPE' – Streamlines Help Analyze Pressure Everywhere.

Can you explain how streamlines are useful?

Sure! Streamlines help visualize how fluid flows, indicating how fluid particles navigate through space without crossing paths. This helps us understand fluid motion better.

To summarize, streamline flow is characterized by consistent particle paths, helping us analyze various fluid behaviors.
Characteristics of Streamline Flow
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve deeper into the characteristics of streamline flow. What can you tell me about how fluid particles interact?

They follow parallel paths?

Exactly! Streamlines run parallel to each other, and one important property of these lines is that they never intersect. Can anyone explain the significance of that?

If they crossed, fluid particles could be at two different speeds at the same point. That wouldn’t make sense!

Right! Such a situation would violate the principles of streamline flow. Now, let’s connect this to the equation of continuity. Can someone share what that means?

It relates the velocity and cross-sectional area of the flow, right? Like how if you narrow the pipe, the fluid speeds up?

Spot on! This principle helps us predict fluid behavior in varying pipe sizes. To wrap up, key characteristics of streamline flow include parallel, non-intersecting paths and the equation of continuity ensuring mass conservation.
Applications and Importance of Streamline Flow
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s explore the applications of streamline flow. Can anyone think of where we might see this in the real world?

Maybe in airplanes or cars? I believe they are designed to reduce turbulence.

That’s correct! The design of vehicles like airplanes aims to achieve streamline flow, reducing drag. This enhances efficiency and fuel performance. Why is understanding this important?

Understanding it helps engineers design better systems to optimize fluid use?

Yes! Streamline flow knowledge assists engineers and scientists in creating efficient designs. Remember, understanding fluid motion is fundamental to fields like hydraulics, fluid mechanics, and aerodynamics. In summary, real-world applications help reinforce the significance of streamline flow in our lives.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In streamline flow, fluid motion is characterized by consistent velocity at any given point, distinguishing steady flow from turbulent flow. Streamlines represent the paths of fluid particles, and the equation of continuity ensures mass conservation throughout the flow.
Detailed
Streamline Flow Summary
Streamline flow represents a fluid's behavior when it is in motion in a steady state. Defined as a flow where the velocity of each fluid particle remains consistent at any fixed point in time, this type of flow showcases the interaction between positions and fluid velocities in a controlled manner. In streamline flow, fluid particles follow smooth trajectories called streamlines.
Each streamline indicates the flow direction of fluid particles in the vicinity, and importantly, no two streamlines can cross one another; if they did, it would signify conflicting velocities for particles at the same point, contradicting the steady flow assumption. Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing fluid behavior in various applications, such as aerodynamics and hydrostatics.
Moreover, the principle of continuity applies, stating that the product of cross-sectional area and velocity is constant for incompressible fluids. This ensures that as fluid moves through varying pipe diameters, the velocity increases or decreases correspondingly, adhering to the conservation of mass. Overall, streamline flow is fundamental in fluid dynamics, serving as a foundational concept for exploring more complex fluid movement.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Fluid Dynamics
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
So far we have studied fluids at rest. The study of the fluids in motion is known as fluid dynamics. When a water tap is turned on slowly, the water flow is smooth initially, but loses its smoothness when the speed of the outflow is increased.
Detailed Explanation
Fluid dynamics is the branch of physics that focuses on the behavior of liquids and gases in motion, distinguishing it from the study of fluids at rest. For example, when water flows from a tap, at lower velocities the flow is smooth (laminar), but as velocity increases, the flow can become chaotic and irregular (turbulent). This transition from smooth to chaotic flow is a key area of study in fluid dynamics.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a gentle stream flowing through a forest; the water moves smoothly and steadily around rocks. Now picture this river during a heavy rainstorm—suddenly, the previously calm waters become turbulent, crashing against obstacles. This illustrates how fluid dynamics explains changes in flow as conditions change.
Characteristics of Steady Flow
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In studying the motion of fluids, we focus our attention on what is happening to various fluid particles at a particular point in space at a particular time. The flow of the fluid is said to be steady if at any given point, the velocity of each passing fluid particle remains constant in time.
Detailed Explanation
A steady flow means every particle that passes a particular point in the fluid behaves in the same way, maintaining a constant velocity. This does not indicate that the velocity is the same at different locations; rather, it's the same for each particle passing through the same point overtime. This property is essential for understanding and predicting fluid behavior in various applications such as pipe flows or natural water systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a moving sidewalk in an airport. If you step onto the sidewalk, you maintain a constant speed relative to the ground as long as the sidewalk is moving steadily. If the speed changes, however, you'll notice a difference in how fast you reach your destination, reflecting how steady flow contributes to predictability in moving fluids.
Streamlines and Their significance
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The path taken by a fluid particle under a steady flow is a streamline. It is defined as a curve whose tangent at any point is in the direction of the fluid velocity at that point.
Detailed Explanation
Streamlines provide a visual representation of fluid flow. Each streamline shows the pathway that fluid particles will follow, with their tangent indicating the direction of their velocity at any given point. The critical insight is that streamlines never cross; if they did, it would suggest that a particle could travel in two different directions simultaneously, which is impossible.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a line of cars following a clear road—each car travels in a single direction without crossing paths. Like these cars, fluid particles follow their designated streamlines, ensuring a cohesive flow without intersections, making it easier to model and analyze fluid motion.
Understanding the Equation of Continuity
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If we intend to show streamline of every flowing particle, we would end up with a continuum of lines. ... The mass of liquid flowing out equals the mass flowing in, holds in all cases. Therefore, ρPAPvP∆t = ρRARvR∆t = ρQAQvQ∆t (9.9)
Detailed Explanation
The equation of continuity is fundamental in fluid mechanics, stating that for an incompressible fluid, the mass flow rate must remain constant across any cross-section of a pipe. As fluid flows from a wider section (large area) to a narrower section (small area), the velocity must increase to keep the mass flow constant. This principle allows us to predict how fluid velocity changes within different pipe diameters, essential for understanding hydraulic systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of children playing in a water slide. If many kids gather at one end of a wide slide (broad area), they can slide down slowly together. But when they reach a narrow section, they must speed up to avoid piling up, analogous to how fluid velocity increases as it passes through a narrower section of a pipe.
Conclusion on Steady Flow
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Steady flow is achieved at low flow speeds. Beyond a limiting value, called critical speed, this flow loses steadiness and becomes turbulent.
Detailed Explanation
In fluid dynamics, the flow is considered steady as long as the speed remains below a certain threshold (critical speed). Exceeding this critical speed results in chaotic and irregular fluid motion known as turbulence, complicating the analysis and prediction of fluid behavior. Understanding the transition from steady to turbulent flow is crucial in applications like aircraft design and predicting weather patterns.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a calm lake—a small pebble creates ripples that travel in a steady manner. However, if you throw a large rock into the lake, the ripples become much more chaotic, illustrating how increasing energy input (akin to flow speed) can lead to turbulence.
Key Concepts
-
Streamline Flow: Fluid flow characterized by consistent paths, indicating steady movement of fluid particles.
-
Equation of Continuity: The conservation principle stating the product of area and velocity remains constant in incompressible flow.
-
Applications: Streamline flow plays a crucial role in engineering and design to optimize fluid dynamics in various systems.
Examples & Applications
When a water tap flows smoothly at a low rate, it exhibits streamline flow.
Airflow over an airplane wing minimizes drag by maintaining streamline flow to enhance aerodynamic efficiency.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a steady stream, flow like a dream, particles glide without a scream.
Stories
Imagine a river flowing smoothly, where fish glide along set paths, ensuring harmony.
Memory Tools
Use 'STRAIGHT' - Steady flow, True path, Reduced intersections, Area product constant, Incompressible, Glide path, Harmonious.
Acronyms
SLOW - Streamlines Lurk On Water.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Streamline
A path followed by a fluid particle in steady flow, indicating the direction and speed of flow.
- Streamline Flow
A type of fluid flow where every particle follows a distinct path without crossing other streamlines.
- Equation of Continuity
A principle stating that the product of cross-sectional area and flow velocity is constant; A1v1 = A2v2 for incompressible fluids.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
