Average Product
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Average Product
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Hello everyone! Today, we are going to discuss the concept of Average Product, or AP. Who can tell me how we define Average Product?

Isn't it the total output divided by the number of inputs used?

Exactly! The formula is AP = TP/L, where TP is the total product and L is the number of variable inputs. Can anyone give me an example?

If a firm produces 50 units of output using 5 workers, then AP would be 50 divided by 5, which is 10.

Right! So the Average Product is 10 units per worker. Remember, AP indicates how efficiently we are using our inputs. Now, why do we care about AP?

It helps us understand labor productivity and optimize input!

Perfect! Let's summarize: Average Product measures output per input unit, indicating efficiency in production.
Relationship Between AP and MP
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss the relationship between Average Product and Marginal Product. Who can explain what Marginal Product is?

It's the additional output produced by adding one more unit of input!

Great! The key point is how MP influences AP. When MP is above AP, what happens to the AP?

The Average Product increases!

Correct! Conversely, what if MP falls below AP?

Then Average Product starts to decrease.

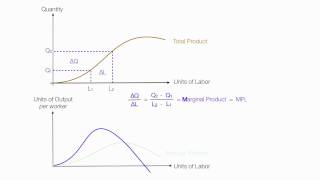
That's right! Visualize this: Both AP and MP curves are U-shaped. AP reaches its peak where MP intersects it. Let's quickly recap.

If MP is greater than AP, AP rises. If MP is less, AP falls. This shows how efficiently we’re using that input!
Practical Implications of Average Product
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s explore how businesses use Average Product in decision-making. Why do factories want to know their AP?

To determine how many workers they need for optimum production!

Exactly! A higher AP suggests more efficient use of labor. But what if the AP starts declining?

They might need to reassess their input strategies or hire fewer workers.

Exactly. Companies constantly monitor this to avoid inefficiencies. Let’s do a quick recap!

AP indicates productivity per input unit, essential for optimizing labor and ensuring maximum output efficiency.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on the concept of Average Product (AP), how it is calculated from Total Product (TP) and the number of variable inputs used (L). It further discusses its relationship with Marginal Product (MP) and its relevance in understanding the efficiency of production inputs.
Detailed
Average Product
Average Product (AP) is defined as the output produced per unit of a variable input. It is calculated using the formula:
\[ AP = \frac{TP}{L} \]
where TP is the total product and L is the quantity of the variable input employed. The last column of Table 3.2 presents a numerical example of AP, derived by dividing the Total Product by the number of labor units. This concept is essential as it helps in evaluating the productivity of inputs in the production process.
Furthermore, Average Product has a critical relationship with Marginal Product (MP). The AP curve is influenced by MP: when MP is greater than AP, AP rises; conversely, when MP falls below AP, the AP also begins to decline. Graphically, both AP and MP are generally represented as inverse 'U'-shaped curves. The intersection of the two curves occurs at the maximum point of the AP curve, demonstrating the diminishing returns associated with additional units of input.
Youtube Videos






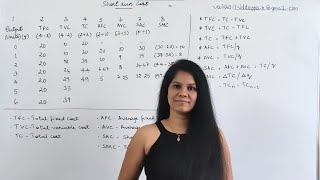

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Average Product
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Average product is defined as the output per unit of variable input. We calculate it as
AP = TP / L (3.2)
Detailed Explanation
The average product (AP) measures how much output is produced on average for each unit of variable input used. To calculate this, we take the total product (TP), which is the total output generated from a certain quantity of input, and divide it by the number of units of that input (L). For example, if a firm uses 10 hours of labor to produce 100 units of product, the average product of labor would be 100 divided by 10, which equals 10 units per hour of labor.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a pizza shop where a chef makes 20 pizzas in 4 hours. Here, the average product of labor is calculated by dividing the total pizzas (20) by the hours worked (4), giving an average of 5 pizzas per hour. This means that on average, the chef produces 5 pizzas for each hour of work.
Numerical Example of Average Product
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The last column of table 3.2 gives us a numerical example of average product of labour (with capital fixed at 4) for the production function described in table 3.1. Values in this column are obtained by dividing TP (column 2) by L (Column 1).
Detailed Explanation
In the context of a table listing various outputs for different amounts of labor input, the average product is calculated by taking the total product for each level of labor and dividing it by that number of labor units. For instance, if the total product when using 2 units of labor is 24 units of output, the average product would be 24/2 = 12. This will be consistently calculated for different levels of labor input, reflecting how efficiency in production changes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a factory where 3 operators produce 90 toys, while 5 operators produce 120 toys. To find the average product, we calculate: for 3 operators, the average is 90 / 3 = 30 toys per operator, and for 5 operators, it’s 120 / 5 = 24 toys per operator. This can help identify if adding more operators increases overall productivity or leads to inefficiencies.
Average Product in Relationship to Marginal Product
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Average product of an input at any level of employment is the average of all marginal products up to that level. Average and marginal products are often referred to as average and marginal returns, respectively, to the variable input.
Detailed Explanation
The average product can be viewed as a summary of all the marginal products (MP) leading up to that input level. If you think of marginal product as the additional output generated by one more unit of input, the average product gives an overall efficiency rating for all units used so far. When the marginal product is higher than the average product, it pulls the average up, while when it's lower, it drags the average down.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a team of runners completing laps around a track. If the group starts with an average lap time of 10 minutes, but one runner completes a lap in 8 minutes (marginal product), they improve the group’s average lap time. If subsequent runners average 12 minutes, they will affect the team’s overall average negatively. This is similar to how average product and marginal product interact in production.
Key Concepts
-
Average Product (AP): Measures output per unit of input, essential for efficiency evaluation.
-
Marginal Product (MP): Represents additional output produced by the last unit of input.
-
Total Product (TP): Total quantity produced from variable inputs.
Examples & Applications
If a firm produces 80 units of output with 4 workers, the AP is 80/4 = 20 units per worker.
As the number of workers increases, if MP initially rises, the AP will also rise until MP drops below AP.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If outputs increase, and inputs stay wise, AP goes high, a production surprise.
Stories
Imagine a baker: with more bakers, the bread output rises. But if one baker makes too much dough, they run out of ovens, and output per baker declines.
Memory Tools
Keep track of AP: Always: Output/Inputs, when AP increases, labor's efficient in pursuits.
Acronyms
AP = TP/L; remember 'AP is Total divided by Labor' for clarity!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Average Product (AP)
The output produced per unit of a variable input, calculated as AP = TP/L.
- Total Product (TP)
The total output produced by a firm using a specific combination of inputs.
- Marginal Product (MP)
The additional output resulting from employing one more unit of the variable input.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
