Potential energy of a single charge
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Potential Energy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into potential energy within electrostatics. When we move a charge in an electric field, we need to consider the work done against the electric force. Can anyone tell me why this concept is important?

It's related to how energy transforms from potential to kinetic energy when the force is removed.

Exactly! When a charge is moved against an electric field, it gains potential energy. This energy is released as kinetic energy when we let it go.
Calculating Work Done
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at how we actually calculate the work done when moving a charge q from a point R to P against an electric force. This is represented by W = q(VP - VR). Who can explain what this means?

It means we're considering the potential energy difference between the two points!

Correct! This shows us the importance of understanding electric potential because it directly relates to how much work is required.
Path Independence
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Electrostatic forces are conservative. What does this tell us about work done on a charge?

It says that the work done is independent of the path taken between points R and P!

Exactly! Whether you take a straight line or a curved path, the work done remains the same as only the endpoints matter.
Understanding Electric Potential
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've discussed both potential energy and electric potential. How are they connected?

Oh! Electric potential is like the potential energy per unit charge, right?

Exactly! The potential energy U at a point r in an electric field can also be given by U = qV(r). Great connection!
The Significance of Potential Energy Difference
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When we talk about potential energy differences, why do we consider them significant?

Because potential itself can be arbitrary, but the difference helps us understand the energy transfer better!

Exactly! The absolute value isn't as crucial; rather, what matters is how much energy change occurs as charges move.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
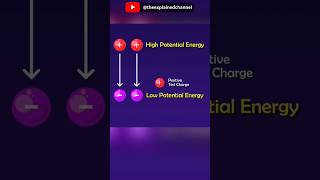
Potential energy for a single charge in an electric field is defined as the work done against the electric force to move the charge from infinity to a point in the field. It elaborates on how this energy is impacted by the nature of the electric field and influences kinetic energy upon release.
Detailed
In electrostatics, potential energy is a crucial concept that describes how energy is stored when a charge is positioned in an electric field. Specifically, the potential energy of a test charge q in an electric field due to a fixed charge configuration can be expressed through the work done by an external agent when moving the charge from a reference point (often taken as infinity) to a designated point within the field. This work can be computed as the potential difference multiplied by the charge, leading to the potential energy being path independent due to the conservative nature of electrostatic forces. The relationship is encapsulated in the equation for potential energy, revealing that the energy stored is determined solely by the positional difference between points in the electric field.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Electrostatic Potential Energy
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In Section 2.7, the source of the electric field was specified – the charges and their locations - and the potential energy of the system of those charges was determined. In this section, we ask a related but a distinct question. What is the potential energy of a charge q in a given field?
Detailed Explanation
Here, we are trying to quantify the energy associated with placing a charge q in an electric field created by other charges. This potential energy indicates how much energy would be required to move a charge from one point to another in this electric field. In a typical electrostatic scenario, the energy depends on the strength of the electric field and the amount of charge, providing insight into the forces acting on these charges.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine pushing a heavy box up a hill. The higher you push the box, the more work you do against gravity, similar to how moving a charge in an electric field requires energy to overcome electric forces.
Work Done in Bringing a Charge Into an Electric Field
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The external field E is not produced by the given charge(s) whose potential energy we wish to calculate. E is produced by sources external to the given charge(s). The work done in bringing a charge q from infinity to the point P in the external field is qV.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk explains the principle that the energy stored when moving a charge into an external electric field depends on the field strength at that point and the charge being moved. When you bring a charge from a point at infinity to point P in an electric field, the work you do against the electric force manifests as potential energy of that charge at point P.
Examples & Analogies
Consider filling a balloon with air. When you blow into the balloon (applying energy), you are transferring potential energy to the air inside the balloon, which can affect its shape and size. Similarly, moving a charge into an electric field adds potential energy to that charge.
Potential Energy Calculation
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Thus, potential energy of q at r in an external field = qV(r) where V(r) is the external potential at the point r.
Detailed Explanation
This section states the formula for calculating the potential energy of a charge q in an electric field produced by external chargers. The potential at a point r, denoted V(r), dictates how much energy is associated with having charge q at that location in the field. Essentially, the external situation determines how much work must be done to place a charge q at position r.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this as placing an electric toy (charge q) on a shelf at a certain height (point r). The energy you used to lift the toy up to that height is analogous to the potential energy due to the electric field at that position.
Energy and Electric Charges
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When the point P has position vector r relative to some origin, we can write: Potential energy of q at r in an external field = qV(r).
Detailed Explanation
This concludes that for any positioned charge in an electric field, there’s a direct relationship involving its potential energy and the field's potential at that point. It’s a critical point that expresses how energy is stored relative to the position of charges in fields.
Examples & Analogies
This can be related to a water tank. The water at a certain height has gravitational potential energy. Similarly, an electric charge has potential energy relative to its position in an electric field, which acts like gravity for electrical forces.
Key Concepts
-
Potential Energy: Defined by the work done against electric forces.
-
Path Independence: The work done between two points does not vary with the route taken.
-
Electric Potential: Measured as energy per unit charge.
Examples & Applications
Moving a charge from infinity to a point in an electric field and calculating its potential energy as the work done against the field.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In fields where charges dance and sway, energy's stored in work and play.
Stories
Imagine moving a ball uphill against gravity. The work done fills the ball with energy, just like charges gaining potential energy in an electric field.
Memory Tools
PE = qV to remember: Potential Energy equals charge times potential.
Acronyms
COV stands for 'Conservative, Only, Value' for how potential energy changes depend only on endpoints.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electric Potential Energy
The work done to bring a charge from infinity to a specific position in an electric field.
- Conservative Force
A force where the work done is independent of the path taken, depending only on the initial and final positions.
- Electric Potential
The work done per unit charge to bring a charge from infinity to a point in an electric field.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
