Subthreshold and Superthreshold Operation of CMOS Transistors
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Subthreshold operation occurs when the gate-source voltage is below the threshold voltage, allowing a small current to flow, which is critical for low-power applications. Superthreshold operation takes place above the threshold voltage, where significant current flows through the transistor, forming the basis for conventional digital circuit operations.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Subthreshold and Superthreshold Operation of CMOS Transistors
In CMOS transistors, the operation can be categorized into two distinct modes: subthreshold and superthreshold operation. These modes define how the transistors behave in terms of current flow based on the gate-source voltage (VGS) relative to the threshold voltage (Vth).
Subthreshold Operation
When the gate-source voltage (VGS) is below the threshold voltage (Vth), a phenomenon known as subthreshold conduction occurs. Here, even though the transistor is effectively
Youtube Videos
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Subthreshold Operation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Subthreshold Operation
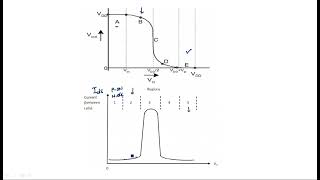
- Subthreshold Conduction: When the gate-source voltage (VGS) is below the threshold voltage (Vth), a small current can still flow through the channel. This is called subthreshold conduction.
- Current Behavior: The current in subthreshold operation increases exponentially with the gate voltage and follows the equation:
\[ I_D = I_0 e^{\frac{V_{GS} - V_{th}}{V_T}} \]
Where V_T is the thermal voltage and I_0 is a constant. - Low Power: Subthreshold operation is used in low-power circuits, such as low-power processors and sensors, as the current is very small.
Detailed Explanation
Subthreshold operation occurs when the voltage applied to the gate of a CMOS transistor is not enough to fully turn it on. However, a small amount of current can still flow through the transistor in this state. The current behaves exponentially, meaning that as the gate-source voltage increases towards the threshold voltage, the current increases rapidly. This feature is advantageous for low-power applications where conserving energy is essential because the current in this state is minimal, allowing for more efficient operations in devices like low-power processors and sensors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a subthreshold operation like a water tap that is slightly open. Even though it's not fully opened, a small stream of water can still flow out. Similarly, in a subthreshold operation, even though the gate voltage isn’t high enough to allow maximum current flow, a small amount can still pass through, which is useful in devices that need to conserve energy.
Superthreshold Operation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Superthreshold Operation
- Above Threshold: When VGS is above Vth, the transistor operates in its linear or saturation region, providing significant current flow through the channel. This is called superthreshold operation and is the typical mode of operation for digital circuits.
Detailed Explanation
Superthreshold operation takes place when the gate-source voltage exceeds the threshold voltage, allowing the transistor to operate fully. In this mode, the transistor can conduct a large amount of current, making it suitable for high-speed switching in digital circuits such as microcontrollers and processors. The transistor can be in either the linear region, where it behaves like a variable resistor, or in the saturation region, where the current is constant despite increases in voltage.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine turning on a faucet all the way. When you do that, a large flow of water gushes out, similar to how a transistor allows significant current to flow once it’s fully on. This mode is like having everything running smoothly in your home, such as appliances, which need enough 'water flow' (current) to function effectively, especially during peak usage times.
