Superthreshold Operation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Superthreshold Operation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll explore superthreshold operation. When the gate-source voltage exceeds the threshold voltage, the transistor can conduct significant current. Can anyone tell me what we call this value, at which the transistor begins to switch on?

That would be the threshold voltage, Vth.

Exactly! So, when VGS is higher than Vth, what regions can the transistor operate in?

The linear region and the saturation region.

Great! Let's remember that 'LS' stands for Linear and Saturation. In this mode, what does the transistor mainly do?

Conducts significant current.

Correct! Thus, superthreshold operation is crucial for ensuring that digital circuits perform effectively.

To summarize key points: superthreshold operation occurs when VGS is above Vth, allowing significant current in linear and saturation regions, vital for digital performance.
Importance in Digital Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what superthreshold operation is, why is it particularly important for digital circuits?

Because it allows for fast switching and operational efficiency.

Exactly! Think of it as the active phase of a CMOS digital circuit. Can someone explain what happens when we provide a sufficient input voltage in this mode?

The transistor responds quickly, which is essential for processing digital signals.

Correct! Thus, robust performance in digital applications relies on successful superthreshold operation.

In conclusion, the significance lies primarily in ensuring stable and efficient circuit behaviors in digital settings.
Transition from Subthreshold to Superthreshold
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the transition between subthreshold and superthreshold operation. Why is this transition important?

It helps in determining when a transistor can effectively switch states and manage power consumption.

Great point! When the voltage crosses the threshold voltage, what's the effect on current flow?

Current dramatically increases as the transistor fully turns on.

Spot on! That sharp increase shows us how critical this transition is for operational efficiency in circuits. Who can sum up the consequences of remaining in subthreshold for too long?

We might end up having higher response times and limited circuit performance.

Exactly! In summary, transitioning into superthreshold is vital for unlocking a transistor's full capabilities and ensuring efficient performance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In superthreshold operation, the gate-source voltage (VGS) of a CMOS transistor is above the threshold voltage (Vth), which enables the transistor to operate in either its linear or saturation region. This mode supports higher current flow and is standard for digital circuits, providing necessary performance for integrated circuits.
Detailed
Superthreshold Operation
In CMOS technology, the superthreshold operation is a critical phase where the gate-source voltage (VGS) exceeds the threshold voltage (Vth). During this state, the transistor can effectively conduct significant current through its channel, placing it in either the linear or saturation region, depending on other voltage conditions in the circuit.
This operational mode is typically employed in digital circuits where high-speed switching and low delay are necessary. Understanding superthreshold operations is crucial as it ensures the reliable performance of various electronic applications. Notably, transistors are designed to be switched on during this mode, maximizing their effectiveness in digital logic operations and ensuring rapid response to input changes.
Youtube Videos
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Above Threshold Condition
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
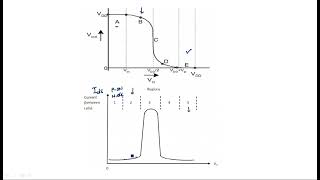
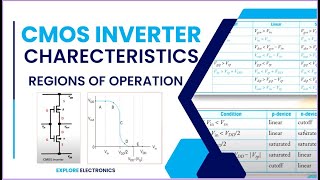
When VGSV_{GS} is above VthV_{th}, the transistor operates in its linear or saturation region, providing significant current flow through the channel.
Detailed Explanation
In superthreshold operation, the gate-source voltage (VGS) exceeds the threshold voltage (Vth). This condition activates the transistor, allowing current to flow freely through it. When VGS is above Vth, the transistor can be either in the linear region, where it behaves somewhat like a resistor, or in the saturation region, where it can carry a constant current. This is critical for digital circuits because it means that when we want to turn the transistor on, it can conduct electricity efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water faucet. When you turn the handle (applying voltage), if you turn it a little (below the threshold), only a few droplets of water trickle out (subthreshold operation). However, when you fully open the faucet (above the threshold), a strong stream of water flows freely (superthreshold operation). Just like in water flow, once you exceed a certain point, the system functions efficiently.
Key Concepts
-
Superthreshold Operation: The mode of operation when VGS exceeds Vth, allowing high current flow.
-
Threshold Voltage (Vth): The minimum voltage at the gate necessary for the transistor to conduct.
-
Linear Region: A state where the transistor behaves linearly and current varies proportionally to applied voltage.
-
Saturation Region: A state where the transistor conducts maximum current, primarily controlled by VGS.
Examples & Applications
In typical digital CMOS circuits, the superthreshold operation enables quick transitions from high to low states, facilitating rapid logic processing.
Integrated circuits use superthreshold operation to ensure that signals are processed without delay, leading to efficient functioning of computers and machines.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In superthreshold, current flows high; when VGS is above Vth, time flies by.
Stories
Imagine a gate that opens only at a specific voltage, allowing a flood of electrons to pass through, just like a floodgate in a dam that opens to let water flow only when pressure is high.
Memory Tools
SLS: Superthreshold means Lots of current Surging!
Acronyms
VGS - Vth = Current Surge
Voltage Gate Source minus Voltage threshold gives you the current that flows!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Superthreshold Operation
The mode of operation in which the gate-source voltage exceeds the threshold voltage, allowing significant current flow.
- Threshold Voltage (Vth)
The minimum gate voltage required to turn on the transistor, beyond which it transitions to conductive states.
- Linear Region
An operating region of the transistor where it behaves like a resistor and current flows linearly with voltage.
- Saturation Region
The operating region of a transistor where current is maximized and primarily controlled by gate-source voltage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
