Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to SMT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore Simultaneous Multithreading, or SMT. It's a technique that allows multiple threads to execute on a single processor core at the same time. Can anyone tell me why this might be beneficial?

Is it to improve performance by using all available resources?

Exactly! By utilizing both threads on a single core, we can maximize resource use. This is especially useful when one thread might be waiting for data, allowing the other thread to keep processing.

Does that mean we can get more done in the same amount of time?

Yes! More work can be done concurrently, leading to better throughput without requiring additional hardware.
Real-world applications of SMT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss applications of SMT. Can anyone think of areas where executing multiple threads simultaneously would be useful?

What about in gaming or video rendering? Those tasks can be quite complex.

Excellent examples! Gaming and video rendering benefit significantly from SMT because they can leverage parallelism to improve performance.

So, SMT can make the experience smoother for users?

Absolutely! It enhances responsiveness in applications that handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
Comparison with Multicore Processors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's compare SMT to multicore processors. While both improve performance, how do they differ?

Multicore processors can run separate threads on different cores, whereas SMT uses one core to handle multiple threads.

Correct! SMT is about improving a single core's efficiency, while multicore processors increase the overall number of cores available for processing.

Does using SMT mean we need to write different code?

Not necessarily! Most applications will run efficiently on an SMT-enabled core without needing any changes. However, optimization can help maximize thread utilization.
Challenges and considerations of SMT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

While SMT offers benefits, there are also challenges. Can anyone think of some downsides to SMT?

Perhaps increased contention for resources? Like, if two threads are fighting for the same execution unit.

Exactly! Resource contention can lead to inefficiencies if not managed well. Additionally, some workloads may not benefit from SMT as much as others.

So it might not always make things faster?

Correct! Understanding the workload is key to determining if SMT will provide performance benefits.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
SMT utilizes unused execution units in a processor to run multiple threads concurrently, improving performance and resource utilization. A well-known implementation is Intel's Hyper-Threading, which enables two threads to operate on a single physical core, increasing throughput and efficiency.
Detailed
Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT)
Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) is a technique used in modern processors that allows multiple threads to share resources and execute simultaneously on a single physical core. This approach can lead to significant performance improvements by maximizing the utilization of underutilized execution units within the core. An example of SMT is Intel's Hyper-Threading technology, which enables the processor to present two logical processors for each physical core, allowing two threads to be processed in parallel. SMT is particularly effective in workloads that can benefit from parallel execution, as it enhances responsiveness and resource efficiency in computing tasks.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT)
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) allows multiple threads to execute simultaneously on a single core by taking advantage of unused execution units. An example is Intel's Hyper-Threading, where two threads are run on a single physical core.
Detailed Explanation
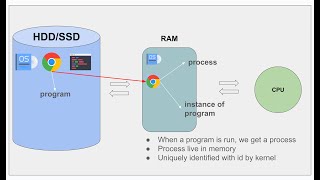
Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) is a technology that enhances the performance of processors by enabling them to run more than one thread of execution at the same time. When a processor core has multiple execution units—essentially, different parts that can carry out tasks simultaneously—SMT can efficiently utilize these units. For instance, if a core can handle two threads, like in Intel's Hyper-Threading technology, it allows these threads to work together rather than waiting for one to finish before the other starts. This approach helps to improve the overall throughput of the CPU, making it more efficient.
Examples & Analogies
Think of SMT like a coffee shop with multiple baristas (execution units) working at the same time. If one barista takes a break or is busy making a latte for a customer, another barista can serve other customers or prepare different drinks. By having more baristas (threads) available, the shop serves more customers faster, just as SMT allows the CPU to complete more tasks in a given time.
Benefits of SMT
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
SMT improves performance by allowing multiple threads to share the core's resources, leading to better CPU utilization and responsiveness.
Detailed Explanation
The primary benefit of SMT is how it enhances the performance of CPU cores. By allowing multiple threads to share the same core's resources, SMT means that the CPU can keep busy without wasting execution units during idle times. This results in better CPU utilization—meaning the processor is doing more work—and improved responsiveness, especially in applications that require real-time processing or handle multiple tasks at once. Apps like video games, simulations, and complex software can run smoother due to this effective management of tasks.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a classroom where a single teacher (CPU core) handles multiple students (threads) simultaneously. If the teacher can help one student with math while another student reads aloud, the class progresses more quickly than if the teacher had to wait for one student to finish before moving to the next. This simultaneous attention leads to a more productive learning environment, similar to how SMT improves digital task management.
Use Cases of SMT
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
SMT is particularly effective in multi-threaded applications and environments where multiple tasks need to be executed concurrently.
Detailed Explanation
SMT shines in scenarios where applications are designed to take advantage of parallel processing. Multi-threaded applications, such as web servers, data processing systems, and scientific simulations, benefit the most from SMT. By allowing these applications to harness the power of multiple threads sharing a core, performance is significantly enhanced, particularly in tasks that involve heavy computations or simultaneous processing, such as rendering graphics or executing complex algorithms.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a multi-tasking chef in a busy kitchen who can handle multiple dishes at once—putting one dish in the oven, stirring another on the stove, and preparing ingredients for a salad simultaneously. The kitchen runs smoothly, and meals are prepared faster with the chef managing different tasks efficiently, just like how SMT enables the CPU to handle multiple threads at the same time.
Key Concepts
-
Simultaneous Multithreading: A method allowing multiple threads to run simultaneously on the same core.
-
Hyper-Threading: Intel's specific implementation of SMT.
-
Resource Utilization: The effective use of CPU resources to improve performance.
Examples & Applications
Intel's Hyper-Threading is a practical example of SMT, allowing two threads to run on a single core for improved performance.
Video games often utilize SMT for simultaneous processing of graphics rendering and game logic.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Threads together, side by side, SMT brings performance, a smoother ride.
Stories
Imagine a two-lane road, one car for each lane. Both cars (threads) can drive simultaneously, speeding up travel. SMT is that road, allowing efficient driving!
Memory Tools
S - Simultaneous, M - Multithreading, T - Threads run together.
Acronyms
SMT
Squeeze More Tasks.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT)
A technique that allows multiple threads to execute on a single processor core simultaneously by sharing execution resources.
- HyperThreading
Intel's implementation of SMT that allows two threads to run on a single physical processor core.
- Throughput
The amount of work performed by a system in a given period of time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
