Thread Scheduling
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Thread Scheduling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we're diving into thread scheduling, a critical aspect of multithreading. Can anyone tell me why scheduling is important?

I think it helps determine which thread gets to run at a time, right?

Exactly! The scheduler decides which thread uses the CPU when, which is vital for performance. Thread scheduling keeps the CPU busy and responsive to user needs.

Are there different types of scheduling?

Great question! There are two main types: preemptive and cooperative scheduling. Let’s explore these in detail.

What does preemptive mean?

In preemptive scheduling, the OS can interrupt a running thread to allocate CPU time to another thread. This allows for better responsiveness, especially in interactive applications.

And cooperative scheduling?

In cooperative scheduling, threads yield control to the OS voluntarily. It’s simpler but can cause issues if a thread doesn't yield. What could happen in that case?

The system might become unresponsive!

That's right! In summary, thread scheduling is essential for efficient CPU usage. We'll come back to this in our next session.
Preemptive Scheduling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into preemptive scheduling. What’s its biggest advantage?

It likely provides faster response times?

Absolutely! By allowing the OS to interrupt threads, preemptive scheduling ensures high responsiveness. This is crucial for applications like web servers and gaming. Can anyone think of scenarios where responsiveness is paramount?

In online games, if the threads can’t respond fast, it could ruin the experience!

Exactly! That lag can make or break gameplay. Remember, preemptive scheduling helps maintain an active and responsive environment.

Are there any downsides?

Yes, the overhead of context switching can affect performance if too frequent. In sum, preemptive scheduling excels in responsiveness but carries potential costs.
Cooperative Scheduling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s explore cooperative scheduling. Can anyone explain how it works?

Threads take turns running and must yield voluntarily.

Correct! It simplifies the scheduling process but introduces potential pitfalls. What do you think could happen if one thread misbehaves?

It could take too long and freeze everything!

Absolutely! A misbehaving thread can halt the system, showcasing why thread cooperation is essential. To review, cooperative scheduling is straightforward but can become problematic without well-behaved threads.
Scheduling Significance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s summarize why thread scheduling is critical in multithreading.

It maximizes CPU efficiency and responsiveness!

Exactly! Effective scheduling can lead to optimized resource management and user satisfaction in applications. Why do you think balancing preemptive and cooperative scheduling is essential?

It ensures we get the benefits of both without the risks!

Spot on! In conclusion, thread scheduling plays a pivotal role in multithreaded applications, enhancing both performance and user experience.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Thread scheduling is the mechanism that the operating system (OS) uses to allocate CPU time to various threads. It can utilize either preemptive or cooperative strategies to manage how threads run, aiming to enhance system responsiveness and resource management.
Detailed
Thread Scheduling
Thread scheduling is a vital component of multithreading, influencing how effectively the CPU's processing power is utilized. The OS scheduler is responsible for determining which thread runs at any given time. This scheduling is essential for maintaining the balance and efficiency of multithreaded applications.
Scheduling Strategies
Thread scheduling can be primarily categorized into two strategies:
- Preemptive Scheduling:
- In preemptive scheduling, the OS has the authority to interrupt a currently running thread, allocating CPU time to another thread. This method allows for better responsiveness in applications, particularly those requiring real-time processing.
- Cooperative Scheduling:
- In cooperative scheduling, threads run until they voluntarily yield control back to the OS or another thread. While simpler, this method can lead to inefficiencies if a thread does not yield, potentially causing the system to become unresponsive.
The choice of scheduling strategy impacts the performance of applications and the overall system behavior, making understanding these processes fundamental for effective multithreading.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Role of the OS Scheduler
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The OS scheduler determines which thread runs at any given time, managing the CPU time allocated to each thread.
Detailed Explanation
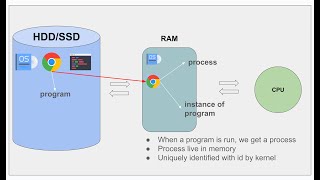
The Operating System (OS) scheduler is a fundamental component responsible for managing how CPU time is divided among active threads. Each thread represents a separate execution path, and the scheduler's job is to ensure these threads are run effectively and fairly. This involves determining which thread should be given control of the CPU based on various criteria, such as priority and availability. By managing this allocation, the scheduler optimizes CPU usage and enhances overall system performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy restaurant kitchen where several chefs (threads) are preparing different dishes. The kitchen manager (scheduler) decides which chef gets to use the stove (CPU) next based on the complexity of the dish and how quickly it needs to be served. This helps ensure that the orders are completed efficiently and that no dish is left unattended for too long.
Scheduling Strategies
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Scheduling strategies include:
- Preemptive Scheduling: The OS can interrupt a running thread to allocate time to another thread.
- Cooperative Scheduling: Threads voluntarily yield control to the OS or to other threads.
Detailed Explanation
There are two main strategies for scheduling threads: preemptive and cooperative scheduling.
- Preemptive Scheduling allows the OS to interrupt a currently running thread to allocate CPU time to another thread. This ensures that high-priority tasks receive the necessary resources to run smoothly and allows for more responsive applications.
- Cooperative Scheduling, on the other hand, relies on threads to yield control voluntarily. In this approach, a thread must pause its execution to allow other threads a chance to run. While this can lead to smoother operations, it may create issues if a thread fails to yield, potentially freezing the system.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a TV station broadcasting shows. With preemptive scheduling, the station can interrupt a show to announce breaking news, ensuring that important information is shared promptly. In contrast, cooperative scheduling resembles a talk show where guests take turns speaking—if one guest refuses to let others talk, the conversation can become one-sided, neglecting important perspectives.
Thread Termination
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When a thread finishes execution, it must be properly terminated, releasing resources like memory and processor time. This can be done either by the thread completing its task or by explicitly calling a termination function.
Detailed Explanation
Proper thread termination is crucial to avoid resource leaks. When a thread has finished executing its assigned task, it should free up the resources it was using, such as memory and CPU time. There are two common methods to accomplish this:
- A thread can terminate naturally after completing its job, ensuring that all resources are appropriately released.
- Alternatively, a thread can be explicitly terminated by calling a function that signals it to stop. Proper termination helps maintain system stability and optimizes resource usage.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a group of workers in an office where each worker (thread) completes a project (task). Once they finish, they promptly clean up their workspace (release resources) and clock out for the day. If workers leave their materials scattered or forget to clock out, it leads to clutter (resource leaks) that reduces overall efficiency in the office.
Key Concepts
-
Thread Scheduling: Crucial for determining which thread runs on the CPU.
-
Preemptive Scheduling: Allows the OS to interrupt a thread to improve responsiveness.
-
Cooperative Scheduling: Requires threads to yield control voluntarily, leading to potential inefficiencies.
Examples & Applications
A web browser that uses preemptive scheduling to ensure fast user interactions.
A text editor that relies on cooperative scheduling to allow for simpler execution.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Threads in a queue, which one to choose? Preemptive or cooperative, don’t snooze!
Stories
Imagine a classroom where students (threads) need to take turns (scheduling). If the teacher (OS) calls on a student (preemptive), the fun keeps going! If they wait too long to volunteer (cooperative), the fun might end in silence!
Memory Tools
Remember 'P' for Preemptive scheduling and 'C' for Cooperative scheduling. P is for 'Pick me!' and C is for 'Call me later!'
Acronyms
SVC for Scheduling, Volunteering, and Control in threading.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thread Scheduling
The mechanism by which an operating system allocates CPU time to various threads.
- Preemptive Scheduling
A scheduling strategy where the OS can interrupt a thread to allocate CPU time to another thread.
- Cooperative Scheduling
A scheduling strategy where threads voluntarily yield control to the operating system or other threads.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
