Summary of Key Concepts
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Basic Functionality of PN Junction Diodes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will learn about PN junction diodes, which are essential components in many electronic devices. Can anyone tell me what they think a PN junction diode does?

It allows current to flow in one direction.

Exactly! That's called unidirectional current flow. Now, can anyone explain what happens at the junction of p-type and n-type material?

Electrons and holes move across the junction?

That's right! This movement creates a depletion region. Remember the acronym *D.U.C.* for Depletion-Uniformity-Current which summarizes the effects of the diode: Depletion region formation leads to Unidirectional current flow.
Biasing the PN Junction Diode
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about the depletion region, let's discuss biasing. What's the difference between forward bias and reverse bias?

In forward bias, the p-side is positive, and current flows easily.

Correct! And how does this relate to the depletion region?

The depletion region narrows in forward bias.

Right again! In contrast, in reverse bias, we see the depletion region widen, and only a tiny leakage current flows. Remember *F.R.E.*: Forward-Region narrows, Reverse-Expansion widens!
Applications of PN Junction Diodes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up our discussion, let's talk about applications. Can someone give me an example of how we use PN junction diodes?

They are used in rectifiers to convert AC to DC.

Great! And what are the two types of rectifiers?

Half wave and full wave rectifiers!

Exactly! Additionally, Zener diodes are a special kind of diode used for voltage regulation. Think of *R.A.Z.E.* - Rectification, Applications, Zener, Efficiency - as a way to recall the primary functions of these diodes.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
PN junction diodes serve as essential components in electronics, allowing unidirectional current flow. This section discusses their operational principles, the significance of the depletion region and biasing, and various applications, including rectifiers and optoelectronic devices such as LEDs and photodiodes.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Key Concepts in PN Junction Diodes
The PN junction diode is a crucial component in modern electronics, enabling controlled unidirectional current flow. The key concepts covered in this section include:
- Unidirectional Current Flow: PN junction diodes facilitate current flow in only one direction, making them invaluable for rectification in power supplies.
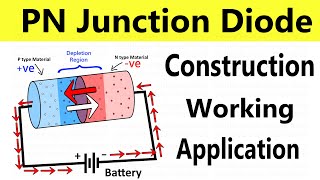
- Depletion Region and Biasing: The behavior of the diode is significantly influenced by the depletion region formed at the junction of p-type and n-type materials. Biasing the diode either narrows or widens this region, thus controlling the current flow:
- In forward bias, the depletion region narrows, promoting high current flow once the threshold voltage is reached.
- In reverse bias, it widens, resulting in minimal current flow.
- Applications: The applications of PN junction diodes are diverse:
- Rectifiers: There are half wave and full wave rectifiers, which convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
- Voltage Regulators: Zener diodes operate in reverse bias to provide stable output voltage.
- Optoelectronic Devices: LEDs emit light when current flows in the forward direction, while photodiodes generate current when exposed to light.
- Significance of Zener Diodes: The Zener diode is specifically designed for operating in the reverse breakdown region, ensuring precise voltage regulation in circuits.
- LEDs and Photodiodes: Both serve dual roles in electronic applications, converting electrical energy to light and vice versa.
This summary captures the essence of PN junction diodes and their critical roles in various electronic applications.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Unidirectional Current Flow
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
PN junction diodes allow unidirectional current flow.
Detailed Explanation
PN junction diodes are designed to allow current to flow in one direction only. This property is essential for converting alternating current (AC) signals into direct current (DC) in various applications. Current can move easily from the p-type region to the n-type region when the diode is forward biased but cannot flow in the reverse direction.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a one-way street where cars can only go in one direction. Just like that street prevents cars from entering the opposite direction, a PN junction diode allows electrical current to flow in just one direction, making it crucial for ensuring that electrical devices operate correctly.
Depletion Region and Biasing
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Depletion region and biasing control diode behavior.
Detailed Explanation
The depletion region forms at the junction of p-type and n-type materials, where the electrons and holes cancel each other out. This region plays a crucial role in how the diode operates, especially under different biases. In forward bias, the depletion region narrows, allowing current to flow. In reverse bias, the depletion region widens, limiting current flow to a minimal leakage.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a dam holding back water. When you push the water (current) toward the dam (diode), if you remove the block (apply forward bias), water flows through easily, while if the dam is reinforced (reverse bias), the flow is obstructed, allowing just a trickle to escape.
Applications of PN Junction Diodes
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Applications include rectifiers, voltage regulators, and optoelectronic devices.
Detailed Explanation
PN junction diodes are used in various technologies. As rectifiers, they convert AC to DC by allowing current to pass in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. They also play a role in voltage regulation, ensuring that devices receive a steady voltage. Additionally, they are integral to optoelectronic devices such as LEDs and photodiodes, which either emit or sense light.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a coffee maker as an analogy. The diode acts like the coffee filter: it lets the brewed coffee (the current) through but keeps the grounds (reverse current) out, ensuring you only get the clean coffee. Similarly, the diode's role in circuits ensures that energy flows correctly for various applications.
Zener Diodes for Voltage Regulation
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Zener diodes are used for precise voltage regulation.
Detailed Explanation
Zener diodes are a special type of diode designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage exceeds a certain value, known as the Zener breakdown voltage. This property is used in voltage regulation applications, where a stable voltage level is required for various electronic components.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a pressure relief valve in a water system. When water pressure rises too high, the valve opens to release some pressure, keeping everything safe and stable. Similarly, a Zener diode opens up to regulate and maintain a steady voltage level, preventing damage to sensitive electronics.
LEDs and Photodiodes
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
LEDs and photodiodes convert electrical energy to/from light.
Detailed Explanation
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) emit light when an electric current passes through them in forward bias. They are widely used in displays, indicator lights, and lighting. Conversely, photodiodes generate an electric current when exposed to light and are used in applications like light sensors and solar cells.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sun-friendly plant for a moment. During the day, it absorbs sunlight and transforms it into energy. This is similar to how a photodiode works. Now consider a light bulb that lights up when you flip a switch – that’s akin to how an LED functions, turning electrical energy into visible light when power is applied.
Key Concepts
-
Unidirectional Current Flow: The ability of a diode to allow electrical current to flow in only one direction.
-
Depletion Region: The area within a diode where no charge carriers are present, influencing diode behavior.
-
Forward Bias: A configuration that allows current to flow easily through the diode.
-
Reverse Bias: A configuration that restricts current flow within the diode.
-
Zener Diodes: Specialized diodes for voltage regulation allowing reverse breakdown.
-
LED: A type of diode that emits light.
-
Photodiode: A diode that generates current in response to light exposure.
Examples & Applications
A half-wave rectifier uses a single diode to convert AC to DC, allowing current to flow only during one half of the AC cycle.
In voltage regulation, Zener diodes maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If the diode's a gate, open in light's fate; Close in the dark, no current to embark.
Stories
Imagine a road with a one-way sign. Cars can only flow forward - just like current through a diode! But when the sign is flipped, no cars can move backward, just like in reverse bias.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym D.U.C. (Depletion-Uniformity-Current) to connect depletion region effects to current flow in diodes.
Acronyms
Use *F.R.E. (Forward-Region decreases, Reverse-Expansion increases)* to recall how the depletion region behaves under different bias conditions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- PN Junction Diode
A semiconductor device formed by the junction of p-type and n-type materials that allows current to flow in one direction.
- Depletion Region
A charge-free zone created at the junction of p-type and n-type semiconductors, which affects current flow.
- Forward Bias
A condition where the positive terminal of a power supply connects to the p-side of the diode, reducing the depletion region and allowing current flow.
- Reverse Bias
A condition where the positive terminal is connected to the n-side, widening the depletion region and limiting current flow to a minimum.
- Zener Diode
A diode that permits current to flow in reverse when the voltage exceeds a certain level, used for voltage regulation.
- LED
A light-emitting diode that converts electrical energy into light.
- Photodiode
A diode that generates current upon exposure to light.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
