Use of GIS in EIA
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to GIS in EIA
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’ll discuss how GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, is utilized in Environmental Impact Assessments, commonly known as EIA. Can anyone tell me what they think GIS allows us to do?

Does it help us analyze geographic data?

Absolutely! GIS helps us collect and analyze spatial data. It’s not only about collecting data but also transforming it into understandable visuals, which is crucial during an EIA. Can anyone remember why visual representation might be important?

Visuals help stakeholders understand the impact quickly?

Exactly! Visual aids make complex data more accessible. Remember, 'See it to Believe it!' is our mnemonic for visualizing data. Let’s dive deeper into specific ways GIS is being utilized in EIA.
Project Definition with GIS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In the project definition phase, GIS is crucial. How do you think it assists in this step?

It shows the project site and surrounding resources, right?

Exactly! GIS can visualize locations concerning resources like raw materials or labor sources. Think of it as a map that shows us what’s around! Can anyone think of another example?

Maybe it helps identify climate influences?

Correct! Knowing climatic conditions helps in project planning. Remember, 'Location, Location, Location' is our key phrase. Let’s move on to evaluating environmental impacts.
Evaluating Environmental Impacts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss how GIS evaluates environmental impacts. What specific impacts do you think we could assess?

Visual impacts, like how a new road affects the scenery?

Right! GIS can model visual impacts of projects, using tools like Digital Elevation Models or DEM. What’s another type of impact?

Maybe impacts on air or water quality?

Exactly! By assessing air and water quality changes spatially, we can predict and manage potential issues. "Impact Analysis is Key" can be our phrase to remember this.
Scoping and Determining Impact Significance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about scoping and determining the significance of impacts. Why do you think scoping is vital in EIA?

It helps focus on the most important environmental aspects to consider?

Exactly! GIS provides the data needed to identify significant impacts efficiently. Without scoping, we risk overlooking vital environmental issues.

How do we determine if an impact is significant?

Great question! GIS helps analyze spatial distributions of impacts to determine their significance. Remember, 'Identify and Analyze' is crucial in this step.
Limitations of GIS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

While GIS has many benefits, it also has limitations. What do you think might hinder its use in EIA?

Maybe the availability of data?

Correct! Lack of reliable digital data can be a significant barrier. Other considerations involve costs of software and system maintenance. Let's remember, 'Data and Cost Matter' as our take-home message.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the significance of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Environmental Impact Assessments. It explains how GIS facilitates project definitions, evaluates environmental impacts, assists in scoping, and determines impact significance, enhancing overall environmental management.
Detailed
Use of GIS in EIA
GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, plays a crucial role in Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) by facilitating data collection, storage, analysis, and visualization of geographic information relevant to environmental management.
Benefits of GIS in EIA
- Project Definition: GIS aids in defining project parameters by illustrating the project's geographic context relative to resources and infrastructure.
- Evaluating Environmental Impacts: It assists in assessing various impacts, including visual aspects and terrain alterations that come with new developments.
- Scoping: GIS helps in scoping environmental effects by providing a systematic way to identify potential impacts based on accurate geographic data.
- Significance Determination: It enables the assessment of environmental impact significance by analyzing spatial distributions of effects on areas such as air and water.
Limitations
While GIS has numerous advantages, limitations exist, including the availability of digital data, startup costs, and database management challenges.
In summary, GIS enhances the EIA process by providing comprehensive data analysis capabilities, supporting better project decision-making while facing certain operational limitations.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
GIS in Project Definition
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- In Project definition: During project identification and definition, the project proponent conducts feasibility studies and defines the usefulness of the study. GIS can be very well used for defining the project by showing the location of the project and its need can be established with respect to other geographical identities like source of raw material, market for selling, source of labourer, climatic conditions favorable for the project etc.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we learn about the role of GIS in the initial stages of a project. When someone is planning a new project, they first need to identify and define it clearly. This involves studying its feasibility—the likelihood of the project's success given available resources and conditions. GIS (Geographical Information System) comes into play here by providing valuable spatial data. With GIS, project planners can visualize the exact location of the project and assess important factors like where the necessary raw materials will come from, where the market for the product is, the availability of labor, and the climate conditions that might affect the project. Essentially, GIS helps in making informed decisions about the new project’s design and viability by analyzing geographical factors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of GIS in project definition like using a detailed map before starting a road trip. Just as the map shows the best routes, gas stations, and rest stops, GIS helps project managers pinpoint key elements like resources and potential challenges in relation to the project's site.
Evaluating Environmental and Visual Impacts
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
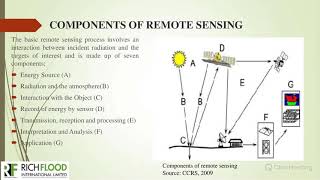
- In evaluating environmental and visual impacts: Using GIS various types of visual impacts can be evaluated like, how a road will look like? How much portion of the road will be visible from a particular point? By using DEM we can calculate and visualize the impact on ground levels either in filling or cutting and area of quarries etc (Oterholm, 1999).
Detailed Explanation
This chunk addresses how GIS can evaluate both environmental impacts and visual aspects of projects. Using specialized tools within GIS, planners can analyze how a new road or structure will change the landscape visually. For instance, they can determine what portion of the road will be visible from different points around the area, helping to assess any potential aesthetic concerns. Furthermore, techniques like Digital Elevation Models (DEM) allow for calculations on how the land will be affected, whether ground levels are being raised (filling) or lowered (cutting). This capability of GIS to create visual representations helps in understanding the environmental alterations that a project might cause.
Examples & Analogies
Consider planning a new amusement park next to a forest. Using GIS is like using a virtual reality tool where you can see how the park will change the view of the forest. You can simulate how many trees will be cut down or how the park structures will look against the backdrop of nature, ensuring that planners can address any visual issues before construction begins.
GIS in Scoping Environmental Effects
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- In scoping system: GIS can serve as a basis for scoping of environmental effects. Once the basic databases are available, a GIS based system may provide better-targeted guidelines for EIS. A centralized institutional scoping structure, where by EIS guidelines are issued by a single entity, is found to be important for the operation of such a system as it can enjoy the Economies of scale and scope involved in setting up and operating a GIS system for scoping purpose (Haklay et al., 1998).
Detailed Explanation
This segment discusses how GIS can help in the scoping process of environmental effects. Scoping is essentially the process of identifying which impacts need to be studied more closely in an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS). With a GIS system, planners can directly access basic environmental data, which allows for more precise guidelines. The idea is that if one centralized entity issues these guidelines, the management and usage of GIS become more efficient and cost-effective. This centralization can lead to a more uniform approach to managing environmental assessments associated with projects, ensuring that nothing is overlooked.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are part of a committee tasked with evaluating the environmental impact for multiple new construction projects in a city. Using GIS is like having a master planner who collates information from varied sources, providing you with a clear picture of which areas need deeper investigation while streamlining the process so you don’t have repeat work across numerous projects.
Determining Impact Significance
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- In impact significance determination: A spatial impact assessment methodology based on the assumption that the importance of environmental impact is dependent, among other things, on the spatial distribution of the effects and of the affected environment.
Detailed Explanation
This part elaborates on the methodology for assessing the significance of environmental impacts using GIS. It posits that understanding how and where impacts occur spatially is crucial for evaluating their significance. Each component of the environment (like air, water, and plants) can have its own impact index, which helps decision-makers gauge how severe the effects are based on their geographic distribution. For example, if a proposed factory will emit pollutants, the assessment will consider how far those pollutants may spread and how they affect different environmental characteristics, helping to prioritize areas for remedial action or mitigation efforts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of considering the significance of environmental impact like evaluating which areas of a garden are most affected by shadow when a new building is erected. By analyzing the shadow pattern across different times of the day, we can understand which plants will suffer the most and need relocation or special care, similarly assessing how a project impacts various environmental aspects based on their locations.
Limitations of GIS in EIA
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The fact that GIS is not used in practice to the extent that it could be used in principle may also be the due to a number of limitations of GIS like: Availability of digital data, Cost of start up, System maintenance, Database construction, Availability of hardware and software.
Detailed Explanation
In this concluding chunk, we address the challenges that may hinder the widespread use of GIS in Environmental Impact Assessments. Although GIS is a powerful tool, practical usage can be limited by factors like the availability of digital data, which may not always be accessible or up-to-date. The costs associated with initiating a GIS system, maintaining it, constructing databases, and ensuring adequate hardware and software can also be significant barriers to entry. Understanding these limitations is crucial for organizations aiming to implement GIS for environmental management.
Examples & Analogies
Consider GIS limitations comparable to setting up an elaborate new kitchen. While having the best tools would make cooking easier, if you lack certain ingredients (data) or if your kitchen space (funds and technology) is limited, it becomes hard to create the complicated recipes (impact assessments) you want. Thus, even with the right plans, practical issues can often prevent successful implementation.
Key Concepts
-
GIS: A crucial tool for analyzing geographic information in EIA.
-
EIA: A systematic approach to evaluate environmental effects.
-
Spatial Distribution: Key in determining the significance of environmental impacts.
Examples & Applications
Using GIS to visualize the potential visual impacts of a new highway on local landscapes.
Implementing GIS to assess water quality changes near a proposed factory site.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the GIS land, we see and plan, projects blend with nature, that’s the man’s stand.
Stories
Imagine a village where a new school will be built. Before construction, the planners use GIS to assess traffic, views, and community resources, ensuring the project benefits everyone and impacts are minimized.
Memory Tools
Remember: SPiC for GIS – Spatial Planning in Construction.
Acronyms
GAP - Geographic Assessment Process, reminding us of GIS's role in assessing and managing geographical data in EIA.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- GIS
Geographic Information Systems; a system designed for capturing, storing, analyzing, and managing spatial or geographic data.
- EIA
Environmental Impact Assessment; a process used to evaluate the environmental effects of a proposed project.
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
A 3D representation of terrain created from elevation data.
- Spatial Distribution
The arrangement of a phenomenon across space.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
