Recharge Trenches
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Recharge Trenches
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing recharge trenches. These structures are vital for capturing rainwater and enhancing groundwater recharge. Can anyone tell me why it's important to manage rainwater effectively?

It's important to prevent flooding and help our water supply!

Exactly! Recharge trenches help siphon off excess rainwater, preventing surface runoff. Now, what do we think materials should be used in constructing these trenches?

I think we use things like pebbles and boulders.

That's right! We typically fill them with porous media such as pebbles and boulders to promote infiltration. Let's remember this with the mnemonic: 'Pore-Filled Trenches'—each letter reminds us of the materials used!

That helps me remember what to use!

Great! Always remember, recharge trenches play a critical role in managing our water resources efficiently.
Design and Size Specifications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about the sizing of recharge trenches. Why do you think their size is essential?

It's probably so they can hold more water!

Exactly! The size must be calculated based on the expected runoff. They are typically 0.5 to 1.0 meters wide and 1.0 to 1.5 meters deep. Can someone recall why this sizing is crucial?

If they're too small, they won't work well and might not recharge enough groundwater!

Precisely! It's essential for optimal functioning. Remember, 'The Right Width Is Key.'
Applications and Benefits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Recharge trenches can be used in various settings. Can you think of some places where they might be helpful?

Maybe in parks or near roads?

Yes! They can be constructed in parks, playgrounds, and even alongside roadside drains. How do you think they benefit these areas?

They can keep the area from flooding and save water!

Exactly! Their benefit goes beyond just saving water—they help maintain groundwater levels. Always recall: 'Recharge Areas Prevent Waste!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
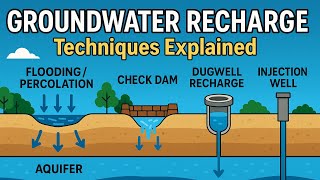
This section discusses recharge trenches, detailing their construction, purpose, and function in augmenting groundwater levels by facilitating the percolation of rainwater into the soil. It highlights their suitability for various environments and underscores the importance of their design in managing water resources.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Recharge Trenches
Recharge trenches are essential structures in sustainable water management practices aimed at recharging groundwater. These trenches are excavated in areas where the upper layer of soil is less permeable. They are typically filled with porous materials such as pebbles, boulders, or brickbats, allowing for the efficient infiltration of surface runoff rainwater, thus preventing it from flooding or running off into drainage systems.
Key Points Covered:
- Construction and Design: Recharge trenches are carefully designed based on the expected amount of runoff. Their dimensions usually range from 0.5 to 1.0 meters in width and 1.0 to 1.5 meters in depth.
- Functionality: They serve to harvest surface runoff, which can then be directed towards additional recharge mechanisms such as bore wells.
- Applications: Recharge trenches are particularly effective in small houses, playgrounds, parks, and areas adjacent to roadside drains.
- Significance: By absorbing rainwater into the ground, recharge trenches contribute significantly to groundwater supplies, which is critical in regions facing water scarcity.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition and Purpose of Recharge Trenches
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Recharge trench is provided where upper impervious layer of soil is shallow. It is a trench excavated on the ground and refilled with porous media like pebbles, boulder or brickbats. It is usually made for harvesting the surface runoff.
Detailed Explanation
Recharge trenches are specially designed to help manage water runoff, especially in areas where the top layer of soil does not absorb water well (impervious layer). When it rains, instead of allowing rainwater to run off into drains or streets, people dig trenches in the ground. They fill these trenches with materials that allow water to pass through easily, such as pebbles and bricks. This way, the water can soak into the ground, helping recharge groundwater supplies.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge sitting in a bowl of water. The sponge soaks up the water, but if it's full, the water will overflow. Similarly, recharge trenches help soak up rainwater. Just like you would want to keep the sponge in a place where it can soak up as much water as possible, we want these trenches to be placed where they can capture and absorb water effectively.
Use of Bore Wells in Recharge Trenches
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bore wells can also be provided inside the trench as recharge shafts to enhance percolation.
Detailed Explanation
In addition to using trenches for water absorption, they might also include bore wells which are deep holes drilled into the ground. By placing these bore wells within the trenches, the water can more effectively move down into the soil layers below. This combination increases the efficiency of the water absorption process, further improving groundwater levels.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water slide at a playground. The slide helps the water flow quickly into a pool below. Similarly, the bore wells act like an extension of the recharge trench, helping channel water more effectively into the ground, just like a slide helps bring water into a pool.
Design Considerations for Recharge Trenches
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The length of the trench is decided as per the amount of runoff expected. This method is suitable for small houses, playgrounds, parks and roadside drains. The recharge trench can be of size 0.50 to 1.0m wide and 1.0 to 1.5m deep.
Detailed Explanation
When planning a recharge trench, engineers need to consider how much rainwater is expected to run off from the surface. The size and length of the trench should match this projection; that way it can collect enough runoff to be effective. For instance, the trench is usually around half a meter to one meter wide and one to one and a half meters deep, making it feasible to construct in various locations like backyards or even public parks.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a rainwater collection system as similar to a funnel. If the funnel is too small for the amount of rain you expect, it will overflow. Similarly, if the trench is poorly sized for anticipated runoff, it won’t function properly. Proper sizing ensures that all the rainwater has a place to go, just like a funnel properly directs all the liquid into a container.
Key Concepts
-
Recharge trenches: Structures designed to capture rainwater.
-
Porous media: Materials that promote water infiltration.
-
Groundwater recharge: Essential for maintaining aquifer levels.
Examples & Applications
Installing recharge trenches in urban parks to manage stormwater efficiently.
Using recharge trenches alongside roads to prevent flooding during heavy rainfall.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Recharge the ground with trench anew, let rainwater flow—it's what we do.
Stories
In a small village, rainwater used to flood the streets, but once they dug recharge trenches, nature smiled back with a steady water supply.
Memory Tools
R.E.C.H.A.R.G.E - Rainwater Efficiently Captured Helps Aquifers Recharge Groundwater Environments.
Acronyms
P.A.S.T. - Pebbles And Stones Trench for rainwater.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Recharge Trench
A trench refilled with porous media designed to capture and allow rainwater to infiltrate into the ground for groundwater recharge.
- Porous Media
Materials like gravel, pebbles, or boulders that facilitate water infiltration.
- Groundwater Recharge
The process through which water from the surface infiltrates down into the groundwater supply.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
