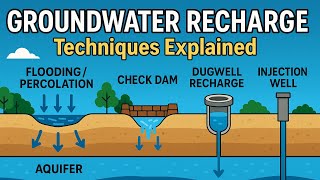
Recharging of dug well
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Dug Wells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we’re focusing on dug wells and their importance for groundwater recharge. Can anyone tell me why dug wells are significant?

They provide water for drinking and irrigation.

Exactly! Dug wells are critical sources of water. They help maintain groundwater levels, especially in dry areas.

How does rainwater help recharge these wells?

Good question! When rainwater is collected and directed into the dug well, it infiltrates through the soil, replenishing the groundwater. This process is vital especially during dry seasons.

Do we need to clean the wells often if we are using rainwater?

Yes! Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial to ensure that pollutants are removed and the recharge rate remains high.
Filtration Bed for Rainwater
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss filtration beds. Why do we filter rainwater before it enters the dug well?

To remove dirt and pollutants?

Yes, that's right! By filtering the rainwater, we prevent silt and debris from clogging the well, which maintains water quality and flow.

What materials are used in a filtration bed?

Common materials include gravel, sand, and sometimes charcoal to enhance filtration. Remember, the quality of water entering the well is crucial for health and usability.

How frequently should it be maintained?

It's recommended to check and clean the filtration bed regularly, especially following heavy rains.
Maintenance of Dug Wells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now focus on maintenance practices for dug wells. What do you think is important for maintaining a dug well?

Cleaning it regularly?

Precisely! Regularly cleaning the well helps prevent contaminants from affecting the water quality and enhances the recharge capacity.

Are there specific cleaning methods we should know about?

Yes! Using proper tools to remove silt and debris without damaging the structure is crucial. It’s also beneficial to check for cracks or damages to the well casing.

And how does all this relate to water conservation?

Maintaining dug wells and ensuring they are recharged efficiently supports water conservation by preserving our groundwater reserves.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines different approaches to recharge dug wells, emphasizing the significance of properly filtered rainwater and various construction techniques that enhance groundwater replenishment while ensuring water quality through filtration and maintenance.
Detailed
Recharging of Dug Well
This section details the process of recharging dug wells functionally and effectively. Dug wells can be effectively used as structures for groundwater recharge, particularly through the collection and diversion of rainwater from rooftops. The methodology includes passing rainwater through filtration beds to remove pollutants before it enters the dug well. Regular maintenance such as cleaning and desalting is essential to sustain a high recharge rate. It emphasizes the necessity of implementing filtration methods similar to those used for recharging bore wells, ensuring a consistent and safe inflow of water that contributes to groundwater levels.
Importance of Dug Well Recharge
Dug wells are pivotal in areas relying heavily on groundwater. They serve as a prime source of irrigation for agriculture and provide drinking water in rural regions. However, due to over-extraction and changes in rainfall patterns, these wells can run dry. Therefore, recharging methods are crucial for maintaining sustainable groundwater levels and supporting the local ecosystem.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Dug Wells for Recharge
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Dug well can be used as recharge structure. Rainwater from the rooftop is diverted to dug wells after passing it through filtration bed. Cleaning and desalting of dug well should be done regularly to enhance the recharge rate. The filtration method suggested for bore well recharging could be used.
Detailed Explanation
A dug well can serve as a structure to recharge groundwater. This is done by collecting rainwater that has been directed from rooftops into the well. However, before the rainwater enters the dug well, it should pass through a filtration bed to remove any debris and impurities. Moreover, to maintain efficiency, regular cleaning and desalting of the dug well are essential as this can significantly improve the rate at which groundwater is recharged. The techniques used for filtering water entering a bore well can also be applied here to ensure cleaner water reaches the well.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine having a sponge that absorbs water. Just as you would want to keep the sponge clean to ensure it absorbs water effectively, maintained dug wells work similarly. By regularly cleaning these wells, we ensure they absorb as much rainwater as possible, helping to replenish groundwater.
Importance of Filtration
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cleaning and desalting of dug well should be done regularly to enhance the recharge rate. The filtration method suggested for bore well recharging could be used.
Detailed Explanation
Filtration is crucial in maintaining the quality of water that enters the dug well. By keeping the well clean, we can prevent the buildup of silt and other unwanted materials that might obstruct water flow. The filtration method recommended for bore wells can also be applied here, which typically involves layers of sand, gravel, and other suitable materials that effectively trap pollutants before the water reaches the well. This ensures only clean rainwater makes it into our groundwater system.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a coffee filter. Just as it allows liquid coffee to pass through while trapping coffee grounds, a filtration system in the dug well allows only clean rainwater into the well. By maintaining these filters, we ensure that our groundwater remains pure and healthy, much like enjoying a great cup of coffee free of grit.
Key Concepts
-
Rainwater recharge: Collecting and directing rainwater to dug wells improves groundwater levels.
-
Filtration importance: Effective filtration is necessary to prevent clogging and maintain well water quality.
-
Maintenance practices: Regular cleaning and checks are vital for ensuring sustained water quality and accessibility.
Examples & Applications
Using a filtration bed made of gravel and sand to clean rainwater before it flows into a dug well.
Regularly inspecting a dug well for cracks to prevent contaminants from entering.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Water flows, it never slows, through the gravel and cloth that only cleans, replenishing wells from our rooftops scenes.
Stories
Imagine a village that relied on a dug well. They discovered rainwater could be captured and filtered, ensuring their well was always full, keeping their crops flourishing and families thriving.
Memory Tools
Remember F.W.M: Filtration for water Management.
Acronyms
CLEA
Clean
Living well
Efficient maintenance
Always recharged.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Dug Well
A manually excavated well used primarily for accessing groundwater, which can be recharged with rainwater.
- Recharge
The process of replenishing groundwater aquifers with water from surface sources, such as rainwater.
- Filtration Bed
A constructed system using various materials to clean rainwater before entering a well.
- Maintenance
Regular checks and cleaning processes required to ensure the well operates efficiently and safely.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
