Recharging of bore wells
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Components of the Rainwater Harvesting System
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll discuss the components of a rainwater harvesting system, which is crucial for recharging bore wells. What do you think are some important components?

Maybe gutters? They catch and direct the rainwater.

Absolutely! Gutters channel rainwater from the roof to storage. They can be made of materials like galvanized iron or PVC. Anyone else knows another component?

How about conduits? They carry the water to where it needs to go, right?

Exactly! Conduits are vital for transporting the harvested rainwater. Let's remember this with the acronym 'G.C.F.S.' - Gutters, Conduits, Filtration, Tanks.

That’s a great way to remember it!

Alright, so we will summarize: Gutters collect water, conduits transport it, filtration purifies it, and storage tanks hold it. Any questions?
Importance of First Flushing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's talk about first flushing. Why do we want to flush out the initial rainwater?

It's probably because the first rain catches a lot of dirt and pollutants.

Exactly right! The first flush device ensures any pollutants are removed, promoting cleaner water quality for storage. Can anyone explain how it works?

It’s a valve that lets the first bit of water flow away, making sure only clean water goes in!

Correct! This process is crucial to maintain safe water. Anyone want to share how we can remember this?

Maybe we could say 'First out, then in' to remember the flushing process!

That's a clever phrase! So, remember, always flush the first rainwater out to keep your system clean.
Recharge Methods for Bore Wells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss methods to recharge bore wells. What are some ways you've heard of?

I think using recharge pits is one method.

Yes! Recharge pits are specially constructed to infiltrate rainwater into the ground. Can you name another method, Student_4?

How about soakaways?

Exactly! Soakaways are boreholes that allow water to percolate into less permeable soil. Remember the acronym 'P.T.T.': Pits, Trenches, and Tanks for recharge methods.

Got it! Pits, Trenches, and Tanks!

Fantastic! Always consider the best method based on local conditions for effective groundwater recharge.
Quality Control during Recharge
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Quality control during recharge is crucial. How can we prevent contaminants from getting into our water source?

By making sure the first few rain showers are flushed away?

Exactly! Flushing away the first showers removes debris and pollutants. What else can we do?

Using fine filters before the water reaches the storage tank?

Yes, effective filtration systems help keep the water clean! Let’s use 'C.L.E.A.N.' to recall: Check flow, Limit contaminants, Ensure filtration, Assess water quality, Never compromise quality.

I like that! It’s easy to remember!

Great! Quality is key to effective water management. Always keep it in mind!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the process of recharging bore wells is detailed, including the use of different systems like gutters, conduits, filtration processes, and methods of rainwater collection. Various structures are introduced for effective recharge, and the significance of managing water quality during this process is emphasized.
Detailed
Recharging of Bore Wells
This section elaborates on effective methods for recharging bore wells as part of groundwater resource management. It outlines the components involved in the rainwater harvesting system, including:
Components of Rainwater Harvesting System
- Gutters: Channels around the roof edges that collect rainwater and transport it to storage tanks. Different materials such as galvanized iron, PVC, bamboo, or betel trunks can be used to construct these gutters.
- Conduits: These are pipes or drains carrying collected rainwater from rooftops to the harvesting system. Common materials include PVC and galvanized iron.
- First Flushing: A first flush device is essential to remove any initial contaminants from the first rain. This step helps maintain the quality of water entering the system.
- Filtration: It involves the use of filters to eliminate debris and suspended pollutants from rainwater before it reaches the storage tank. Simple filters can be constructed using charcoal, sand, and gravel.
- Storage Tanks: These tanks collect the filtered water and can be constructed from various materials like reinforced concrete or metals. Proper maintenance is necessary to ensure water quality.
Recharge Methods
The section further delves into specific methods for recharging groundwater aquifers, focusing on bore wells:
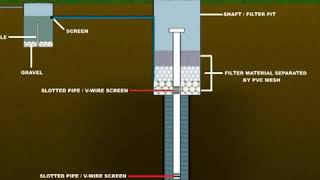
- Recharging of Bore Wells: Rainwater is collected from rooftops, filtered, and then diverted into bore wells to replenish deep aquifers. Abandoned bore wells can also be utilized for this process.
- Other Recharge Structures: Other methods include recharge pits, trenches, soakaways, and percolation tanks, each designed based on local conditions and methods to improve groundwater replenishment.
The text underscores the importance of preventing contaminants during the recharge process to maintain water quality, emphasizing that the first rain should be flushed out effectively to avoid pollution.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Bore Well Recharge
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Rainwater collected from the rooftop of the building is diverted through drainpipes to a settlement or filtration tank. After settlement, filtered water is diverted to bore wells to recharge deep aquifers. Abandoned bore wells can also be used for recharge.
Detailed Explanation
The first step in recharging bore wells involves collecting rainwater that falls on rooftops. This rainwater is collected using pipes that direct the water to a tank for settling or filtering. In this tank, any sediments or impurities settle at the bottom, allowing cleaner water to flow over and be directed into the bore well. The bore well, which accesses deep underground water sources or aquifers, can also utilize unused or abandoned bore wells for this process, helping to replenish the groundwater supply.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the bore well recharge process like a coffee filter. When you pour water through the filter (representing the settlement tank), it allows only the liquid to pass through while trapping the coffee grounds. Similarly, rainwater is cleaned in the tank before it enters the bore wells.
Designing the Settlement Tank
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The optimum capacity of settlement tank/filtration tank can be designed on the basis of area of catchments, intensity of rainfall, and recharge rate as discussed in design parameters.
Detailed Explanation
The capacity of the tank where rainwater is stored and filtered is crucial for effective recharge of bore wells. The design must consider several factors: the size of the area that collects rainwater (catchment area), how heavy the rainfall is in different seasons (intensity), and how quickly the surrounding soil can absorb the water (recharge rate). Designing the tank to accommodate these factors ensures that it can handle water effectively and improve groundwater levels.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planning a picnic on a rainy day. You need to make sure you have enough buckets or containers to catch all the rainwater without overflow. If you don’t consider how much rain will fall and how quickly it will fill your containers, you might end up with a mess. Similarly, those designing the settlement tank must ensure it's big enough for the expected rainfall.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
While recharging, entry of floating matter and silt should be restricted because it may clog the recharge structure. The first one or two showers should be flushed out through rain separator to avoid contamination. This is very important, and all care should be taken to ensure that this has been done.
Detailed Explanation
To maintain the efficiency of bore well recharge, it's essential to prevent debris and silt from entering the system. The initial rainfalls often carry pollutants and debris, so it's advised to divert the first few showers away from the recharge structure using a rain separator. Properly managing what water enters the recharge system keeps it functioning well and prevents blockages that could reduce its effectiveness.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a water fountain. If the first few drops of dirty water flow into it, they can cloud the whole fountain. If we catch those first drops and discard them, the fountain remains clean and clear, similar to how rain separator works for rainwater harvesting.
Key Concepts
-
Gutters: Essential for collecting rainwater from rooftops.
-
Conduits: Essential for transporting the collected rainwater.
-
Filtration: Vital for ensuring clean water enters the system.
-
First Flushing: Important for removing contaminants before storage.
-
Recharge Methods: Various techniques to enhance groundwater replenishment.
Examples & Applications
Gutters can be made from galvanized iron or PVC, designed to accommodate high rainfall intensity.
A simple charcoal filter can be created at home to purify rainwater before it is stored.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Gutters channel the rain, let it flow, / Through conduits, to storage where it’ll grow.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a dry land, the rain was precious. The townsfolk built gutters to catch the falling rain, which flowed through conduits to a big tank where it was stored and safely used for crops.
Memory Tools
Remember G.C.F.S. - Gutters, Conduits, Filtration, and Storage for a complete rainwater system.
Acronyms
P.T.T. - for Recharge Methods
Pits
Trenches
and Tanks for effective water recharge.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Gutters
Channels around the edges of a roof that collect and transport rainwater.
- Conduits
Pipelines or drains that carry rainwater from the catchment area to the harvesting system.
- First Flushing
A mechanism that ensures runoff from the first rain is removed to avoid contamination.
- Filtration
The process of removing suspended pollutants from rainwater before it enters storage.
- Recharge Pits
Holes constructed to allow rainwater infiltration into the ground.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
