Watershed Management
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Watersheds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today we’ll discuss watersheds. A watershed is a land area where water drains to a common outlet. Can anyone tell me why understanding watersheds is important?

It helps in managing water resources better!

Exactly! Effective watershed management ensures sustainable water supply, which is crucial for agriculture, urban areas, and ecosystems.

What happens if a watershed is not well-managed?

Great question! Poorly managed watersheds can lead to degradation, affecting water quality and increasing flood risks.

Let's remember the acronym 'SAFE' to highlight the significance of watershed management: Sustainability, Agriculture, Flood control, and Ecosystem health.

I’ll remember SAFE as important results of managing watersheds.

Perfect! Now, let’s move on to watershed degradation.
Watershed Degradation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What are the main reasons for watershed degradation?

Things like deforestation and mining, right?

Yes! These activities disturb the natural balance and can severely affect soil and water quality. Can anyone think of other activities contributing to this?

Urbanization!

Correct! Urban development often leads to more impervious surfaces, increasing runoff and reducing water absorption.

To remember the causes of degradation, we can use the mnemonic 'MDIES' - Mining, Deforestation, Infrastructure development, Erosion, and Soil contamination.

MDIES sounds easy to remember.

Great! Each element contributes to the overall degradation of the watershed.
Objectives of Watershed Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss the main objectives of watershed management. Can someone name one?

To rehabilitate degraded land?

Yes! Rehabilitation aims to restore land productivity. Another goal is minimizing risks of floods and droughts. Does anyone know why that is essential?

It helps to protect communities and agriculture!

Correct! For easier recall of the objectives, let’s use the acronym 'RMD': Rehabilitation, Management, and Development.

I’ll remember RMD next time I think about watershed goals.

Excellent! Let’s now explore the practices in watershed management.
Practices in Watershed Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone list some practices in watershed management?

Water harvesting is one!

Correct! Water harvesting captures and stores rainwater for later use. What’s another practice?

Afforestation, planting trees to prevent soil erosion!

Yes! Afforestation is vital. To remember these practices, we can use the mnemonic 'WARM': Water harvesting, Afforestation, Runoff management, and Mechanical soil protection.

WARM is easy! I’ll keep that in mind.

Wonderful! Finally, let’s summarize the key points of our discussions today.
Summary of Watershed Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we learned about watersheds, their importance, and the various practices for effective management. Can anyone summarize what we've covered?

We discussed what a watershed is and why it matters.

And the causes of watershed degradation like mining and deforestation!

Also, the objectives like rehabilitation and flood risk minimization.

And we talked about practices like water harvesting and afforestation!

Fantastic recap! Remember the key acronyms we’ve discussed: SAFE for significance, MDIES for degradation causes, RMD for objectives, and WARM for practices. You all did brilliantly!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the concept of watersheds, their significance, and the need for effective management practices to combat degradation. It covers objectives and practices like water harvesting, afforestation, and public participation, which contribute to sustainable watershed management.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Watershed Management
Watershed management refers to the strategic utilization and management of land and water resources in a watershed to improve productivity while minimizing damage to the environment.
Introduction to Watersheds
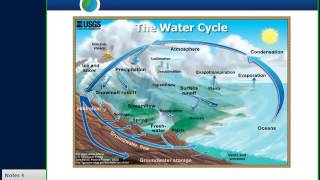
A watershed is defined as an area of land where all of the water that drains off of it goes into a common outlet, such as a river. The health of a watershed is essential for food production, water supply, and ecological balance.
Watershed Degradation
Watersheds often suffer degradation due to unplanned land use practices, deforestation, mining, and other human activities. This degradation can significantly impact biodiversity and the overall health of ecosystems.
Objectives of Watershed Management
The main objectives include:
1. Rehabilitation of degraded watersheds for better land productivity.
2. Sustainable management for domestic water supply, irrigation, and power generation.
3. Minimizing risks of natural disasters like floods and droughts.
4. Development of rural regions for economic upliftment.
Practices in Watershed Management
- Water Harvesting: Ensures that water is collected and stored for use during dry seasons.
- Afforestation and Agroforestry: Involves planting trees to reduce soil erosion and encourage moisture retention.
- Mechanical Erosion Control: Implements methods like terracing and bunding to minimize soil loss.
- Scientific Mining: Advocates for responsible mining operations to prevent ecological disturbances.
- Public Participation: Emphasizes the involvement of local communities, especially farmers and indigenous peoples, in management strategies to ensure success.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Watersheds
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The land area drained by a river is known as the river basin. The watershed is defined as the land area from which water drains under gravity to a common drainage channel. Thus watershed is a delineated area with a well defined topographic boundary and one water outlet. The watershed can range from a few square kilometers to few thousand square kilometers in size.
Detailed Explanation
A watershed is a specific geographical area that collects water that drains into a common place, like a river. It can be small, as little as a few square kilometers, or very large, spanning thousands of square kilometers. Understanding the boundaries of these areas is crucial for managing water resources effectively as they all funnel into one point.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a watershed like a bowl. When it rains, all the water that falls into the bowl collects in the bottom. The bowl's sides determine how much water can go in or out. Similarly, the boundaries of a watershed dictate how water flows and accumulates in a particular area.
Importance of Watersheds
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the watershed the hydrological conditions are such that water becomes concentrated within a particular location like a river or a reservoir, by which the watershed is drained. The watershed comprises complex interactions of soil, landform, vegetation, land use activities and water. People and animals are an integral part of a watershed having mutual impacts on each other.
Detailed Explanation
Watersheds are vital for water management because they help collect and process water that sustains ecosystems and human activities. Different factors, like soil type, terrain, and vegetation, interact in a watershed, influencing how water flows and is stored. This interconnectedness means that human choices and environmental health in one part of the watershed can affect the whole area.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a community garden where the arrangement of plants (vegetation), soil quality, and water distribution all contribute to the garden's success. If one plant absorbs too much water or if the soil is not well taken care of, it can affect all the other plants and the gardening community's yield, reflecting the interdependence found in a watershed.
Function of Watershed Management
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A watershed affects as it is directly involved in sustained food production, water supply for irrigation, power generation, and transportation as well as for influencing sedimentation and erosion, vegetation growth, floods and droughts. Thus management of watersheds treating them as a basic functional unit is extremely important.
Detailed Explanation
Watershed management is crucial because watersheds play a key role in various essential functions, including agriculture, providing water for crops, generating electricity from hydro power, and facilitating transport. Additionally, well-managed watersheds help reduce soil erosion and manage extremes like floods and droughts by stabilizing the environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of watershed management like maintaining a home. Just as fixing leaks and cleaning gutters prevent water damage in a house, proper management of watersheds helps prevent flooding, ensures clean water supply, and maintains healthy soil, which in turn supports the growth of crops and the overall ecosystem.
Challenges of Watershed Degradation
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The watersheds are very often found to be degraded due to uncontrolled, unplanned and unscientific land use activities. Organizing, deforestation, mining, construction activities, industrialization, shifting cultivation, natural and artificial fires, soil erosion and ignorance of local people have been responsible for degradation of various watersheds.
Detailed Explanation
Watersheds face many challenges that lead to their degradation, making it difficult for them to fulfill their essential functions. Activities like deforestation and unregulated development cause soil erosion, reduce vegetation, and disrupt the water cycle, which can have severe impacts on agriculture and local communities.
Examples & Analogies
It's like a school that keeps getting overcrowded and not maintained. If the classrooms get filled with trash, the teachers can't teach effectively, and the students can't learn. In a similar way, when a watershed is degraded, it can't provide clean water or support healthy ecosystems, affecting everyone who relies on it.
Objectives of Watershed Management
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Rational utilization of land and water sources for optimum production causing minimum damage to the natural resources is known as watershed management. The objectives of watershed management are as follows: 1. To rehabilitate the watershed through proper land use adopting conservation strategies for minimizing soil erosion and moisture retention so as to ensure good productivity of the land for the farmers. 2. To manage the watershed for beneficial developmental activities like domestic water supply, irrigation, hydropower generation etc. 3. To minimize the risks of floods, droughts and landslides. 4. To develop rural areas in the region with clear plans for improving the economy of the regions.
Detailed Explanation
Watershed management aims to utilize land and water resources wisely, ensuring they are available for farming, water supply, and energy generation, while minimizing environmental harm. The key objectives include rehabilitating degraded areas, providing water for domestic and agricultural uses, reducing risks associated with extreme weather events, and promoting economic development in rural areas.
Examples & Analogies
This is like a family budgeting for their home. They have to spend wisely on food, housing, and savings to ensure they don't run out of resources. Similarly, watershed management involves careful planning and usage of natural resources to support both the environment and local communities.
Watershed Management Practices
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the fifth year plan, watershed management approach was included with a number of programs for it and a national policy was developed. In watershed management the aspects of development are considered with regard to availability of the resources. The practices of conservation and development of land and water are taken up with respect to their suitability for people’s benefit as well as sustainability.
Detailed Explanation
The government has recognized the importance of watershed management by developing policies and programs that focus on sustainable practices. This includes conserving resources and promoting activities that benefit both people and the environment. These practices are tailored to meet local needs while ensuring the sustainability of resources for the future.
Examples & Analogies
Think of watershed management practices like community service projects that improve a neighborhood. People come together to clean parks, plant trees, and create gardens, improving their community while helping the local environment. In the same way, watershed management combines community efforts to improve and sustain the resources that everyone relies on.
Key Concepts
-
Watershed: A crucial area for managing water resources sustainably.
-
Degradation: A significant challenge affecting watershed health.
-
Sustainable Practices: Essential methods for maintaining watershed integrity.
-
Public Involvement: Vital for successful watershed management initiatives.
Examples & Applications
An example of effective watershed management is the use of rainwater harvesting systems to provide water during dry seasons.
Afforestation in areas like Dehradun helps prevent soil erosion and maintains ecological balance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a watershed, water flows, / For plants and crops, it surely grows.
Stories
Imagine a village that lives beside a river. They depend on the river for food, water, and energy. One day, they decided to plant trees and build dikes, and soon the river ran healthier, and their crops flourished. They learned how a little care for their watershed made a big difference.
Memory Tools
To remember watershed management objectives, think 'RMD' for Rehabilitation, Management, Development.
Acronyms
SAFE
Sustainability
Agriculture
Flood control
Ecosystem health.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Watershed
An area of land where all the water drains to a common outlet.
- Watershed Degradation
The deterioration of watershed health due to negative human activities.
- Water Harvesting
A process of collecting and storing rainwater for future use.
- Afforestation
The planting of trees in a previously bare or deforested area.
- Public Participation
Involvement of local populations in watershed management activities.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
