Advanced Applications of GNSS in Civil Projects
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Deformation Monitoring
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing deformation monitoring using GNSS. Can anyone explain what deformation monitoring entails?

Is it about tracking movements in buildings or structures?

Exactly! GNSS continuously measures small movements, which can be crucial for monitoring structures like dams and bridges. Can anyone give me an example of where this might be particularly important?

It sounds vital for places prone to landslides.

Yes, monitoring landslide-prone regions can save lives! Remember, we use GNSS data to detect millimeter-level changes, which helps in timely maintenance and interventions.

Why is millimeter-level detection significant?

Great question! Even minor movements can indicate potential structural issues. If we can detect these changes early through GNSS, we can prevent catastrophic failures.

So, the precision of GNSS helps maintain safety overall?

Right! GNSS ensures safety through precise monitoring. Now, to summarize, we discussed how GNSS helps in deformation monitoring to track vital structural movements, essential for maintaining safety standards.
Machine Control in Construction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about how GNSS is integrated into construction machinery for machine control. What changes does this bring to construction?

It helps with tasks like grading and paving, right?

Exactly! GNSS helps machines work accurately on tasks like grading and excavation. This means they can operate more efficiently. Can someone explain how this might reduce manual errors?

If the machine controls itself, there are fewer chances of human mistakes.

Great answer! Automated control reduces reliance on manual input, which can lead to errors. Would anyone like to elaborate on how this might be beneficial for project timelines?

Machines are much faster than humans, so that would save time, right?

Correct! Speed and efficiency can significantly shorten project durations, allowing for faster project completion.

Does that also mean less labor is required?

Indeed! Fewer personnel are needed on site for specific tasks. To summarize, we've learned how the integration of GNSS in machine control improves efficiency in construction by automating processes and reducing error margins.
GNSS in Hydrology and Flood Mapping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's explore GNSS applications in hydrology and flood mapping. Why is this integration important?

It can help track water levels and manage flooding better?

Exactly! GNSS provides real-time data on water levels, which is crucial during flooding. Can anyone give an example of how real-time data could enhance disaster management?

Emergency services could respond more quickly if they know the water levels.

Perfect! Timely data allows for informed decision-making and quicker response times. What impact does this have on infrastructure planning?

It helps to build infrastructure in safer areas.

Yes! By analyzing data from GNSS, we can plan infrastructure to stay clear of flood-prone areas. To summarize, GNSS in hydrology is vital for immediate response and better infrastructure planning in the times of crisis.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
GNSS technology has a wide range of advanced applications in civil projects, including deformation monitoring for structures, machine control for construction efficiency, and supporting hydrological studies for disaster management. Each application enhances precision, safety, and operational effectiveness in various civil engineering fields.
Detailed
Advanced Applications of GNSS in Civil Projects
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) play a significant role in enhancing various civil engineering practices. This section highlights three critical advanced applications:
1. Deformation Monitoring
Continuous GNSS measurements enable the detection of millimeter-level movements vital for assessing the stability and safety of civil structures.
- Applications include:
- Monitoring dam safety to prevent structural failures.
- Tracking bridge displacements to ensure public safety.
- Assessing landslide-prone zones for risk management.
2. Machine Control in Construction
Integration of GNSS with construction machinery automates control processes in construction sites.
- Applications include:
- Grading and excavation tasks are made more accurate and efficient.
- Road paving activities enhance speed and reduce errors.
- Canal alignments benefit from improved precision and integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM) systems.
3. GNSS in Hydrology and Flood Mapping
GNSS enables real-time monitoring of water levels and station positions, supporting emergency functions and planning activities such as:
- Hydrologic modeling to prepare for floods.
- Infrastructure planning to mitigate disaster risks.
These applications illustrate the significant impact and growing reliance on GNSS in civil engineering, emphasizing improvements in monitoring, operational efficiency, and overall project effectiveness.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Deformation Monitoring
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Continuous GNSS measurements detect millimeter-level movements.
Applied in:
– Dam safety monitoring
– Bridge displacement tracking
– Landslide-prone zone assessment
Detailed Explanation
Deformation monitoring using GNSS involves measuring tiny movements in structures over time. This is critical for ensuring safety, particularly in large structures like dams and bridges. By continually monitoring, engineers can identify even the smallest shifts in position, which could indicate potential safety issues. For example, if a dam shows unexpected movement, engineers can investigate further to prevent a possible failure.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a tall building swaying slightly in the wind. Each small sway is being measured by sensors. If the swaying increases, engineers can take steps before it leads to damage, much like how GNSS can help monitor a dam for minute movements that could signal a problem.
Machine Control in Construction
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
GNSS integrated with construction machinery for automated control.
Used in:
– Grading and excavation
– Road paving
– Canal alignment
Increases speed, reduces manual error, and enables BIM integration.
Detailed Explanation
In construction, integrating GNSS with machinery allows for precise automation. This means that machines can be guided automatically without the need for constant human oversight. For example, when grading land for a new road, GNSS ensures that the machine levels the ground perfectly according to specifications. This automation speeds up the process and reduces mistakes, making construction more efficient and accurate.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a GPS-guided robot vacuum. Just as it navigates your home automatically and cleans your floors efficiently, GNSS-equipped machinery works on construction sites, following precise paths to ensure everything is built right without needing someone to control it manually.
GNSS in Hydrology and Flood Mapping
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
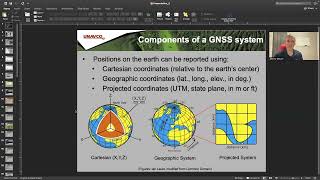
Provides real-time water level and station position.
Supports hydrologic modeling, disaster risk mitigation, and infrastructure planning.
Detailed Explanation
GNSS plays a crucial role in water management and flood response. By providing real-time data on water levels at various stations, it helps authorities anticipate flooding events. This information supports hydrologic models that predict how water behaves in different scenarios, thus helping to plan infrastructure accordingly. For instance, knowing where levels are rising can help in deploying resources effectively to mitigate flood risks.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how weather apps give updates about rainfall in your area. Similarly, GNSS provides continuous information about water levels, allowing emergency services to react swiftly, just like a parent running to grab an umbrella when rain is predicted.
Key Concepts
-
Deformation Monitoring: Continuous GNSS measurements to enhance structural safety.
-
Machine Control: GNSS integration with construction machines to automate and improve efficiency.
-
Hydrology: Use of GNSS for real-time water level monitoring and infrastructure planning.
Examples & Applications
Continuous monitoring of a dam to prevent structural failure.
Automation of road grading machinery using GNSS to enhance accuracy.
Real-time tracking of flood-prone areas for emergency response planning.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To monitor deformation, keep precision in creation.
Stories
Imagine a bridge that talks to the GNSS, sharing its heartbeats; this helps define when repairs are needed.
Memory Tools
DMM for Deformation Monitoring and Machine Control.
Acronyms
HWM for Hydrology, Water Management, and Mapping.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Deformation Monitoring
A system that utilizes GNSS to continuously measure structural movements to ensure safety and stability.
- Machine Control
The integration of GNSS with construction machinery to automate and enhance construction processes.
- Hydrology
The science concerning the properties and movement of water on the Earth, crucial for flood management and planning.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM)
A digital representation process that facilitates efficient planning, design, and construction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
