Introduction to GNSS
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of GNSS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will delve into the Global Navigation Satellite System, or GNSS. Can anyone tell me what GNSS enables?

It helps in finding positions based on satellite signals, right?

Exactly! GNSS allows users to determine their exact location – longitude, latitude, and height. This capability is critical in engineering tasks. Let’s remember it with the acronym 'NPD' for Navigation, Positioning, and Data.

What are some of the satellite systems included in GNSS?

Great question! GNSS encompasses several systems, including GPS from the USA, GLONASS from Russia, and Galileo from the EU. Together, they enhance the reliability of GNSS.

Is GNSS affected by the weather conditions?

No, GNSS works in all weather conditions, making it an excellent tool for surveying even under challenging scenarios. To summarize today’s discussion, GNSS is vital for accurate positioning and provides us signals and data from multiple satellite systems.
Applications of GNSS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's focus on the applications of GNSS in civil engineering. Can someone suggest how GNSS might be used?

Is it used for mapping and surveying?

Absolutely! GNSS is essential for topographic surveys and accurate mapping. Remember 'MAP' – Mapping, Alignment, and Precise positioning.

How precise can GNSS positioning be?

Depends on the method used! High-precision applications can achieve centimeter-level accuracy using RTK techniques. Who can tell me the importance of this in construction?

That would ensure that structures are built correctly and align with designed layouts.

Exactly! GNSS plays a crucial role in infrastructure development. Let’s close by highlighting that GNSS's reliability is pivotal across many civil engineering tasks.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
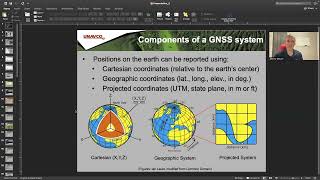
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) comprises several satellite constellations, including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and more, enabling users to determine their location in any weather condition. GNSS has critical applications in civil engineering, surveying, mapping, and infrastructure development.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of GNSS
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) refers to a collection of satellite systems that deliver signals from space to GNSS receivers on the ground. This allows users to ascertain precise positioning data, including longitude, latitude, and height, at any time, regardless of weather conditions.
Major Satellite Systems in GNSS
GNSS consists of various satellite systems:
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Operated by the USA
- GLONASS: Operated by Russia
- Galileo: A European Union initiative
- BeiDou: Operated by China
- NavIC: India's native system
- QZSS: Japan's system
Importance of GNSS
GNSS is vital in civil engineering due to its use in surveying, mapping, navigation, and infrastructure development. By utilizing over four satellites, users can achieve accurate three-dimensional positioning, contributing significantly to various engineering tasks.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of GNSS
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) refers to a constellation of satellites providing signals from space that transmit positioning and timing data to GNSS receivers. These systems enable users on the ground to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and height) at any time and in all weather conditions.
Detailed Explanation
GNSS is a system of satellites that orbit the Earth. These satellites send signals that contain important information about their positions and time. When these signals reach a receiver on Earth, it can calculate where it is located. This means that no matter where you are or what the weather is like, you can find out your precise location in terms of longitude, latitude, and height.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are lost in the woods, and you have a smartphone that uses GNSS. The phone connects with satellites overhead and determines your exact location, so you can find your way back to a trail or guide yourself home. Just like using a map and compass, but much more precise and quicker!
Satellite Systems Overview
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
GNSS includes multiple satellite systems:
• GPS (Global Positioning System) – USA
• GLONASS – Russia
• Galileo – European Union
• BeiDou – China
• NavIC – India
• QZSS – Japan
Detailed Explanation
There are several different satellite systems that make up GNSS. Each system is owned and operated by different countries or organizations. For example, the United States has GPS, while Russia has GLONASS, and the European Union has Galileo. Each of these systems provides similar services but may have different coverage and accuracy levels. This variety allows users to have multiple options for reliable positioning data.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a library that contains many different types of books. If one section is closed or books are checked out, you can still find information in another section. Similarly, if one GNSS system is unavailable, you can use another to find your location.
Importance of GNSS in Civil Engineering
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
GNSS plays a significant role in civil engineering, especially in surveying, mapping, navigation, and infrastructure development.
Detailed Explanation
In civil engineering, GNSS technology is crucial because it allows engineers and surveyors to perform precise measurements and mapping of construction sites. This technology helps in navigation for heavy machinery and planning infrastructure like roads and bridges. It ensures that everything is constructed according to the plans and specifications, contributing to the safety and effectiveness of civil projects.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a a large bridge. Engineers need to ensure that it is placed in the exact right location to be safe and functional. GNSS acts like an architect's blueprint that guides the builders in placing every concrete pillar and beam perfectly. Without GNSS, this process would be much more challenging and prone to errors.
Key Concepts
-
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS): A system of satellites that provide positioning and timing data.
-
Satellite Constellations: Includes GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, NavIC, and QZSS.
Examples & Applications
Using GNSS in urban planning to create accurate GIS base maps.
Employing GNSS for emergency response mapping in disaster-affected areas.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Acronyms
NPD
Navigation
Positioning
Data for understanding GNSS.
Rhymes
Satellites in the air, provide signals without a care.
Memory Tools
MAP - Mapping, Alignment, Precision for GNSS applications.
Stories
Imagine a surveyor on a vast land, using a magical tool from the sky that knows exactly where he is at all times.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- GNSS
Global Navigation Satellite System, a collection of satellite systems that provide positioning and timing data.
- GPS
Global Positioning System, the USA’s GNSS.
- GLONASS
Global Navigation Satellite System operated by Russia.
- Galileo
European Union's GNSS system.
- BeiDou
China's satellite navigation system.
- NavIC
Navigation with Indian Constellation, India’s GNSS.
- QZSS
Quasi-Zenith Satellite System, Japan's satellite navigation system.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
