Objectives of Hydrographic Surveying
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Depth Measurement (Bathymetric Surveys)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into our first objective—depth measurement through bathymetric surveys. Why do we need to measure the depth of water bodies?

To know how deep the water is for navigation, right?

Exactly! It's crucial for safe navigation and understanding underwater topography. Remember, 'Depth is Life' for mariners. What instruments do we use for this?

I think we use echo sounders?

And sonar systems, right?

Spot on! Echo sounders and sonar help us map underwater features and depths accurately. Let's recap: measuring depth helps us navigate safely. Next question—how can changes in depth affect navigation?

If the depth changes unexpectedly, it could lead to grounding of vessels.

Correct! Always keep the phrase 'Check Depth Before You Step' in mind for safe navigation. Let's move to our next objective.
Mapping Underwater Topography
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Our second objective is to map underwater topography and locate submerged objects. Why is this mapping important?

Is it for avoiding underwater hazards while navigating?

Absolutely! Identifying submerged hazards helps ensure sailor safety. What tools do we use to accomplish this mapping?

We can use side-scan sonar to create images of the seabed.

And multi-beam echo sounders to get a 3D view of the underwater landscape!

Great examples! So, remember: 'Map to Navigate, Inspect before you Direct.' This is crucial for any maritime operation.
Coastline Monitoring and Environmental Studies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore our objective related to coastline monitoring. Why must we observe changes in shorelines?

To manage coastal erosion and sedimentation!

Precisely! Monitoring helps in eco-management and understanding human impact. What kind of studies do we conduct for sedimentation?

We look at how sediments deposit and how that affects marine ecosystems.

Wonderful! The phrase 'Erosion Action, Ocean Reaction' highlights this interconnectivity. Finally, why might this be significant for our future development?

It helps with planning construction projects like coastal defenses.

Exactly! Knowledge is essential for sustainable coastal development. Let's summarize: monitoring coastlines informs future planning.
Support in Navigational Chart Preparation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Another crucial objective is assisting in navigational chart preparation. Why is accurate charting vital for navigators?

So they can avoid hazards and follow safe routes!

Correct! 'Chart Smart to Navigate Safe' should be our motto. How often should these charts be updated?

Regularly, especially after significant geological or environmental changes!

Exactly! Maintaining up-to-date charts prevents accidents. What other applications might benefit from this data?

Marine construction projects like docks and bridges.

Indeed! Correct charts are vital for safe and effective marine structures. Let's recap: navigating and constructing rely heavily on accurate charts!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The objectives of hydrographic surveying encompass depth determination, underwater mapping, coastal monitoring, navigational support, and marine infrastructure development. This section outlines how hydrographic surveys are essential for safe navigation, environmental studies, and scientific research in marine contexts.
Detailed
Objectives of Hydrographic Surveying
Hydrographic surveying plays a pivotal role in understanding aquatic environments. The primary objectives include:
- Depth Measurement: Conducting bathymetric surveys to ascertain water body depths, which is essential for safe navigation and construction.
- Mapping Underwater Topography: Identifying and mapping submerged objects and underwater features, facilitating navigation and environmental assessments.
- Coastline Monitoring: Tracking changes in shorelines and river banks over time, which is important for coastal management and erosion studies.
- Navigational Support: Aiding in the preparation and updating of navigational charts, ensuring maritime safety by informing seafarers about potential hazards.
- Infrastructure Development: Supporting dredging operations and the construction of marine structures, including ports and bridges, contributing to coastal development.
- Environmental Studies: Assisting in studying sedimentation and erosion impacts on marine environments, contributing to ecological research and oceanography.
- Scientific Research: Providing valuable data for marine geology and oceanographic studies, supporting a broader understanding of oceanic processes.
Understanding these objectives is vital for professionals involved in maritime navigation, environmental science, and civil engineering.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
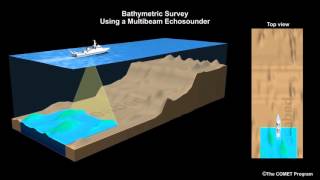
Determining Depth of Water Bodies
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• To determine depth of water bodies (bathymetric surveys).
Detailed Explanation
Hydrographic surveys primarily aim to measure how deep various bodies of water are. This measurement is essential for numerous applications, including navigation and construction. By using techniques like echo sounding, surveyors collect data that indicate the depth at various points in a water body. This information is crucial for creating accurate maps and ensuring safety in maritime activities.
Examples & Analogies
Think of using a long ruler to check the depth of a swimming pool. Just like how you measure the depth at different points to get a complete picture of the pool, hydrographic surveyors do the same in oceans or rivers to map out the underwater landscape.
Mapping Underwater Topography
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• To map the underwater topography and locate submerged objects.
Detailed Explanation
Another objective of hydrographic surveying is to create detailed maps of the underwater landscape, including terrains such as valleys, hills, and boulders. This mapping includes identifying submerged objects like shipwrecks or obstacles that could pose navigational hazards. By understanding the underwater topography, mariners can navigate more safely and efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to navigate through a dense forest where you can’t see the ground. Mapping the forest to know where trees, streams, or rocks are is similar to what hydrographic surveyors do underwater, creating a clear map that helps in safe navigation.
Monitoring Changes in Coastlines or River Banks
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• To monitor changes in coastline or river banks.
Detailed Explanation
Hydrographic surveying also plays a critical role in monitoring the changes in shorelines and riverbanks. This is increasingly important in light of climate change and erosion, which can alter landforms significantly over time. Regular surveys can help identify these changes, allowing for better planning in coastal development and environmental protection efforts.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a gardener regularly checks the growth of plants and adjusts their care based on changes in the garden's layout. Similarly, hydrographic surveys help scientists and planners see how coastlines evolve so they can protect them from erosion or plan new developments.
Assisting in Navigational Chart Preparation
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• To assist in navigational chart preparation.
Detailed Explanation
One of the vital goals of hydrographic surveying is to provide the data needed to create navigational charts. These charts are essential tools for mariners, offering detailed information about water depths, hazards, and safe routes. Accurate charts contribute significantly to maritime safety, preventing accidents and enabling efficient navigation.
Examples & Analogies
It's akin to how a travel guidebook helps tourists navigate a new city, highlighting safe paths, attractions, and potential hazards. Navigational charts serve a similar purpose for sailors, ensuring they have all the necessary information to navigate safely.
Supporting Dredging Operations and Marine Infrastructure Construction
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• To support dredging operations and construction of marine infrastructure (ports, docks, bridges).
Detailed Explanation
Hydrographic surveying is essential for dredging operations, which involve removing sediment from the bottom of water bodies to maintain or increase depth for navigation and construction. Surveys provide crucial data about the underwater environment, which is necessary when planning the construction of marine infrastructure such as ports, docks, and bridges.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how builders need to know the foundation of a building site before construction. Similarly, hydrographic surveys inform engineers about what's below the water's surface before they can safely build docks or piers.
Studying Sedimentation and Erosion Impact
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• To study the impact of sedimentation and erosion.
Detailed Explanation
Another important goal of hydrographic surveys is to study how sedimentation (the accumulation of sediments) and erosion (the wearing away of land) affect various ecosystems. Understanding these processes helps in managing waterways and protecting habitats from degradation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a beach where storms wash away sand and deposits new materials—hydrographic surveys help track these changes, much like how a scientist might study soil erosion on land to understand its impact on agriculture.
Supporting Scientific Research in Marine Geology and Oceanography
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• To support scientific research in marine geology and oceanography.
Detailed Explanation
Finally, hydrographic surveying provides essential data that supports scientific research in fields such as marine geology and oceanography. By gathering information about seafloor structures and water characteristics, researchers can better understand marine environments and the processes that govern them.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a scientist collecting samples of soil to study how different elements interact. In a similar way, hydrographic surveys gather critical information that helps scientists explore and understand the vast and complex ocean ecosystem.
Key Concepts
-
Depth Measurement: Essential for navigation and construction; conducted through bathymetric surveys.
-
Underwater Mapping: Involves locating submerged features vital for safe navigation and marine studies.
-
Coastline Monitoring: Tracks changes to aid in coastal management and environmental protection.
-
Navigational Chart Support: Facilitates safe maritime navigation by providing updated navigational aids.
Examples & Applications
Mapping the underwater terrain of a harbor to prevent ship grounding.
Using sonar technology to locate wrecks or underwater hazards.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To map the depth and gauge the sea, for safe navigation, that’s the key.
Stories
Imagine a sailor named Sam, who always checked the depths with his echo sounder, avoiding hazards like submerged rocks and wrecks, ensuring his safe passage through the vast ocean.
Memory Tools
DUMES: Depth, Underwater, Monitoring, Environmental Studies, Support - remember these objectives of hydrographic surveying.
Acronyms
HIDES
Hydrographic
Instumentation
Depth
Erosion
Safety - key components in hydrographic surveying.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bathymetry
The study of underwater depth of ocean floors or river beds.
- Echo Sounder
A device used to measure water depth by sending sound waves and measuring their return time.
- Sedimentation
The process of sediment settling out of transport and accumulating in a new location.
- Erosion
The process by which soil and rock are removed from the Earth's surface by wind or water flow.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
