Auditory Nerve
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Auditory Nerve
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to discuss the auditory nerve, which is essential for our sense of hearing. Can anyone tell me what happens in our ears when we hear a sound?

I think sound waves enter the ear and make the eardrum vibrate.

Exactly! The eardrum vibrations are transmitted to the inner ear through tiny bones. But after that, how do these vibrations become something we can understand?

Do we need the auditory nerve for that?

Yes! The auditory nerve carries the electrical signals from the cochlea, where those vibrations are converted into electrical impulses, directly to the brain.

So, without the auditory nerve, we wouldn't hear anything?

That's correct! Let’s remember this with the acronym 'SOUND' - 'Signals Of Unbelievably New Data' to think about how sound is transformed into signals.

That’s a great way to remember it!
Functionality of the Auditory Nerve
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Great participation! Let's delve deeper into how the auditory nerve works. Once the cochlea converts sound into electrical impulses, what do you think happens next?

The impulses travel through the auditory nerve to the brain?

Exactly! The auditory nerve acts like a communication cable between the cochlea and the brain. How do you think this impacts people with hearing loss?

They might need hearing aids to help send those signals?

Right! Hearing aids amplify sound, making it easier for the auditory nerve to detect and transmit those signals to the brain. Remember, only a fully functioning auditory nerve makes hearing possible.

Can we learn more about how technology helps those who have issues with their auditory nerves?

Definitely! We will touch on that in our next class. For now, let’s recap. The auditory nerve transmits signals from the cochlea to the brain; without it, sound perception is impossible.
Importance of Auditory Nerve
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the functionality of the auditory nerve, let’s discuss its broader importance. Why do you think it’s important to study the auditory nerve?

To understand how we hear and what can go wrong?

Exactly! By studying the auditory nerve, we can develop interventions for those with hearing loss. What are some impacts of hearing loss?

It might affect communication and social interactions.

Yes, it can significantly impact one's quality of life. How might technology help here?

With implantable devices or hearing aids to support the auditory nerve function!

Exactly! Technologies serve to assist and enhance the functionality of the auditory nerve. Let's summarize today's discussion: The auditory nerve is essential for conveying sound signals to the brain, and understanding it allows us to innovate technology for those with hearing impairments.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the structure and function of the auditory nerve, detailing its role in the hearing process by sending electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain. Understanding this process is essential for grasping how sound perception occurs.
Detailed
Auditory Nerve
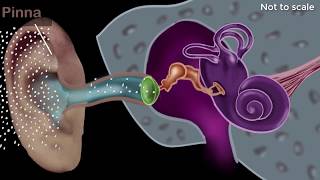
The auditory nerve, also known as the cochlear nerve, is pivotal in the auditory system. It plays a vital role in our ability to hear by transmitting sound information converted into electrical signals from the cochlea. The cochlea of the inner ear contains specialized sensory cells that respond to sound vibrations. When sound waves cause the hair cells in the cochlea to move, they generate electrical impulses. These impulses travel through the auditory nerve to the auditory cortex in the brain, where they are interpreted as sound.
Understanding the auditory nerve's function is crucial not only in the context of biology but also in addressing hearing impairments and tailoring auditory devices, such as hearing aids, to support those with hearing loss.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Function of the Auditory Nerve
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Auditory Nerve: Sends signals to the brain.
Detailed Explanation
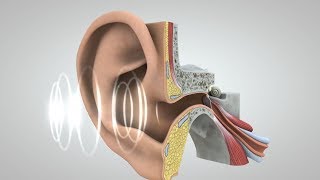
The Auditory Nerve is a crucial part of the hearing process. It is responsible for transmitting the electrical signals converted from sound waves by the cochlea (inner ear) to the brain. Once sound waves enter the ear, they cause vibrations in the eardrum, which are transmitted through the ossicles (small bones in the middle ear) to the cochlea. The cochlea transforms these vibrations into electrical signals. The Auditory Nerve then carries these signals to the brain, where they are interpreted as sound.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Auditory Nerve like a delivery service. When you order something online (the sound waves), the package arrives at a warehouse (the cochlea), where it is sorted and prepared for delivery (converted to electrical signals). The delivery truck (the Auditory Nerve) then takes the package to your house (the brain), where you can finally unpack and enjoy your order (hear the sound).
Key Concepts
-
Auditory Nerve: Transmits electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain.
-
Cochlea: Converts sound vibrations into electrical impulses that the auditory nerve carries.
-
Hearing Impairment: Issues with the auditory nerve can lead to difficulties in hearing, impacting communication.
Examples & Applications
When someone speaks, sound waves vibrate the eardrum; the ossicles amplify this vibration, and the cochlea converts it to electrical signals via the auditory nerve.
Hearing aids work by amplifying sound to help the auditory nerve send stronger signals to the brain, improving hearing for individuals with hearing loss.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
The auditory nerve, so fine and bright, sends sound to the brain, it's our hearing's light.
Stories
Imagine a messenger (the auditory nerve) that travels from a market (cochlea), carrying all the sounds to the king (the brain). Without the messenger, the king cannot hear the market news.
Memory Tools
Remember A-C-T: 1. Auditory nerve 2. Connects 3. Transmits sounds.
Acronyms
C.N.S - Cochlea, Nerve, Sound (the process of hearing).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Auditory Nerve
A bundle of nerve fibers that transmits sound information from the inner ear to the brain.
- Cochlea
A spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear that converts sound vibrations into electrical signals.
- Electrical Signals
Nerve impulses that are transmitted along the auditory nerve to convey sound information to the brain.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
