Eardrum
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Eardrum
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll learn about an important component of our hearing system—the eardrum. Can anyone tell me where the eardrum is located?

Isn't it in the middle ear?

Correct! The eardrum, also known as the tympanic membrane, is indeed located in the middle ear. It acts as a barrier between the outer ear and the middle ear. Why do you think it’s important for hearing?

Because it vibrates when sound waves hit it?

Exactly! The eardrum vibrates in response to sound waves, which is step one in converting sound into something we can hear.
Function of the Eardrum
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve a bit deeper. Once the eardrum vibrates, it transfers these vibrations to the ossicles. Who can remind us what ossicles are?

They are the small bones in the middle ear, right?

That's right! The ossicles are made up of the malleus, incus, and stapes. Can anyone tell me why these bones are important?

They amplify the sound vibrations?

Exactly! The ossicles amplify the vibrations from the eardrum before sending them to the inner ear, where they are converted into electrical signals.
Significance of the Eardrum
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone explain why understanding the eardrum's function is crucial?

It helps us know how sound is processed, which is important for hearing health.

That's a great point! Our eardrum allows us to hear sounds, and protecting it from damage is vital for maintaining our hearing ability.

What can damage the eardrum?

Great question! Loud noises, infections, and injuries can all affect the eardrum. It’s crucial we protect our ears to ensure our eardrum remains healthy.
Recap and Review
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let's summarize what we’ve learned about the eardrum. What is its main function?

It vibrates in response to sound waves, allowing us to hear.

Exactly! And what happens after the eardrum vibrates?

The ossicles amplify the vibrations before they reach the inner ear.

Great job! Understanding the eardrum's role helps illustrate the entire hearing process.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The eardrum, located in the middle ear, vibrates when sound waves reach it, transmitting these vibrations to the ossicles for amplification. This process is essential for converting sound waves into signals that the brain can interpret.
Detailed
Eardrum
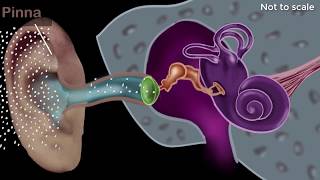
The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is an essential part of the human auditory system. Located in the middle ear, it serves as a barrier between the outer ear and the middle ear. When sound waves travel through the ear canal, they strike the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. These vibrations then pass to the three tiny bones in the middle ear known as the ossicles (the malleus, incus, and stapes), which amplify the sound before it advances to the inner ear.
The ability of the eardrum to vibrate with sound is crucial for the conversion of sound waves into electrical signals processed by the brain, thus enabling human hearing. Understanding the eardrum's role assists in comprehending how sound is perceived and processed, highlighting its significance within the broader context of sound.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Eardrum Function
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Eardrum: Vibrates with sound waves.
Detailed Explanation
The eardrum, also known as the tympanic membrane, plays a crucial role in hearing. It is a thin membrane located at the end of the ear canal. When sound waves enter the ear, they hit the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. These vibrations are essential for converting sound waves into signals that our brain can interpret. The movement of the eardrum is directly influenced by the sound pressure of the waves, which determines how intensely it vibrates.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the eardrum as a drum. Just like a drummer taps on a drum skin to create sound, when sound waves hit the eardrum, they make it vibrate. This vibration is similar to the way the drum produces music. The harder the sound wave hits the eardrum, the more it vibrates, just like hitting a drum harder produces a louder sound.
Importance of Eardrum in Hearing
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The eardrum is vital for converting sound waves into mechanical vibrations.
Detailed Explanation
The vibration of the eardrum is not just about moving back and forth; it is the first step in a series of processes that lead to hearing. Once the eardrum vibrates, these vibrations are transmitted to three tiny bones in the middle ear, known as ossicles. These bones amplify the vibrations and pass them along to the inner ear, where they are transformed into electrical signals that the brain can understand.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the eardrum as the first link in a relay race. When one runner (the eardrum) receives the baton (sound waves), they don't just hold onto it; they pass it quickly to the next runner (ossicles). This teamwork ensures that the sound information travels quickly and effectively to the finish line, which is the brain.
Key Concepts
-
Eardrum: The tympanic membrane that vibrates when hit by sound waves.
-
Ossicles: Three small bones in the middle ear that amplify sound vibrations.
-
Vibrations: The oscillating movements caused by sound waves.
Examples & Applications
When a singer hits a high note, the eardrum vibrates rapidly, sending amplified sound signals to the brain.
In a concert, loud music causes the eardrum to vibrate more intensely, which can lead to temporary hearing loss if exposure is too long.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
The eardrum's where sounds hit, making vibrations fit!
Stories
Imagine a drum in a band; when struck, it vibrates and sends signals to the audience, just like the eardrum sends sound signals to the brain.
Memory Tools
Ears Help Us (E-H-U) - Eardrum, Hear, Understand.
Acronyms
E-M-S (Eardrum, Middle Ear, Sound) - key parts in the hearing process.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Eardrum
The tympanic membrane that vibrates in response to sound waves.
- Ossicles
The three small bones in the middle ear that amplify sound vibrations.
- Tympanic Membrane
Another name for the eardrum.
- Vibration
An oscillating movement that sound waves induce in the eardrum.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
