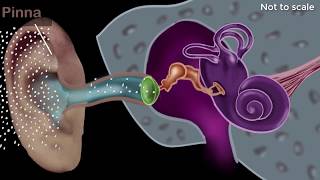
Middle Ear
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Middle Ear
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about the middle ear. Can anyone tell me what they think the middle ear does?

I think it helps us hear better?

That’s correct! The middle ear amplifies sound. It's located between the outer ear and the inner ear. Can anyone name the three bones found in the middle ear?

Are they the malleus, incus, and stapes?

Exactly! We can remember them by the acronym M.I.S. - Malleus, Incus, Stapes. These ossicles help amplify the vibrations from the eardrum. Why do you think amplification is necessary?

I guess because sound needs to be strong enough to be heard clearly?

Absolutely! The ossicles act like a lever to boost the strength of sound waves. To recap, the middle ear is crucial for transmitting sound to the inner ear.
Structure of the Middle Ear
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into the structure of the middle ear. What can you tell me about the ossicles and their roles?

The ossicles transmit sound vibrations, but how do they do it?

Great question! The malleus attaches to the eardrum and when it vibrates, it moves the incus, which then moves the stapes. Can anyone guess what the stapes connects to?

The inner ear?

Yes! The stapes connects to the oval window of the cochlea in the inner ear, transmitting the amplified vibrations. Remember, M.I.S. is key to understanding this system!
Eustachian Tube and Pressure Equalization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about the Eustachian tube. Who knows its function?

Does it help with balance?

Good guess! The Eustachian tube actually helps equalize pressure in the middle ear with the outside environment. Why is this pressure equalization important?

If there's too much pressure, it could affect our hearing?

Exactly! Unequal pressure can make hearing difficult and can even cause pain. So it's really important for our ears to maintain balance. Let's summarize: the middle ear not only amplifies sound through the ossicles but also manages pressure with the Eustachian tube.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The middle ear plays a crucial role in hearing by using the ossicles to amplify sound vibrations received from the eardrum, transmitting them to the inner ear, where they are converted into electrical signals for the brain to process.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The middle ear is a vital part of the human auditory system, situated between the outer ear and the inner ear. Its primary function is to amplify sound vibrations that the eardrum receives. The middle ear contains three small bones known as the ossicles: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). These bones work in a lever-like manner to increase the amplitude of sound vibrations before they are transferred to the inner ear. Furthermore, the Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the throat and helps equalize pressure on both sides of the eardrum. Understanding the function of the middle ear is essential for grasping how we perceive sound and the importance of hearing health.
Youtube Videos









Key Concepts
-
Middle Ear: The area through which sound vibrations travel from the outer ear to the inner ear.
-
Ossicles: The three bones (malleus, incus, stapes) that amplify sound in the middle ear.
-
Eustachian Tube: A passage that helps maintain air pressure on either side of the eardrum.
Examples & Applications
When you hear someone speak across the room, the sound is captured by the outer ear and amplified by the ossicles in the middle ear.
If you dive underwater, the Eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure so you don’t experience discomfort in your ears.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Middle ear, listen here, ossicles help sound appear!
Stories
Once upon a time, there were three little bones named Mal, Incus, and Stapes, who worked together to carry the sound to the land of Cochlea.
Memory Tools
M.I.S. - Remember Malleus, Incus, Stapes for the middle ear.
Acronyms
O.E.E. - Outer ear, Eustachian tube, Ear canal.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Middle Ear
The part of the ear between the outer ear and inner ear that amplifies sound vibrations.
- Ossicles
Three tiny bones in the middle ear (malleus, incus, and stapes) that convey sound vibrations to the inner ear.
- Eustachian Tube
A canal that connects the middle ear to the throat, helping equalize air pressure.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
