Ear Canal
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Function of the Ear Canal
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the ear canal's role in hearing. Can anyone tell me what happens when sound waves enter the ear?

The sound waves go into the ear canal!

That's correct! The ear canal is like a tunnel that carries sound waves to the eardrum. Can someone explain what happens to the sound waves when they reach the eardrum?

The eardrum vibrates in response to the sound waves.

Exactly! Those vibrations are then converted into electrical signals for the brain to process. How does the ear canal help improve our hearing?

It amplifies the sound waves, right?

Correct! Think of it as a megaphone. At the end of this lesson, remember: the ear canal helps us hear by channeling sounds to the eardrum.
Protective Role of the Ear Canal
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about how the ear canal protects the inner workings of our ear. Does anyone know what helps keep our ears clean?

Earwax!

Right! The ear canal produces earwax, or cerumen. What do you think its purpose is?

It traps dirt and dust so they don’t reach the inner ear.

Correct! It keeps harmful particles out and also helps to maintain moisture. Remember this protective role of the ear canal as we explore the hearing process further.
Sound Transmission through the Ear Canal
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s break down how sound travels through the ear canal. Can anyone describe the journey of a sound wave from the outside environment to our eardrum?

The sound wave first hits the ear canal, and then it travels to the eardrum.

Right! And once the sound reaches the eardrum, what happens next?

The eardrum vibrates, and those vibrations go to the middle ear.

Good job! This capture and transfer of sound energy is vital for how we hear. So, remember, the ear canal is essential not just for transport, but for protection too.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The ear canal serves as a passage for sound waves from the outer ear to the eardrum, allowing sound to be converted into mechanical vibrations. Understanding its structure helps to appreciate how we perceive sound.
Detailed
Ear Canal
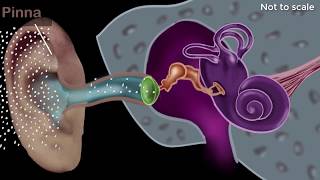
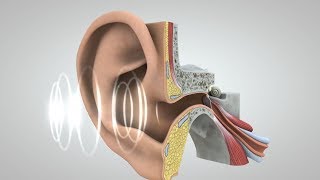
The ear canal, also known as the external auditory canal, is a crucial structure in the process of hearing. It functions as a tube that conveys sound waves from the outer ear (the pinna) to the eardrum. The sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate, initiating the transformation of sound energy into mechanical energy.
Significance
Its role is vital in amplifying sound. The ear canal also protects the inner structures of the ear by producing earwax, which helps trap dust and foreign particles. This section provides insight into how structures in the ear work together during the auditory process, underscoring the intricate design of human sensory systems.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Function of the Ear Canal
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The ear canal passes sound to the eardrum.
Detailed Explanation
The ear canal, also known as the external auditory canal, serves an essential role in the hearing process. It acts as a passageway, directing sound waves from the outer ear (the pinna) to the eardrum. When sound waves enter the ear canal, they cause the air molecules within it to vibrate, creating sound vibrations. These vibrations travel along the canal, culminating in the eardrum's movement.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the ear canal like a long tunnel leading into a cave. As someone shouts from outside the cave, the sound travels through the tunnel and reaches the cave’s entrance, where it reverberates and is amplified before echoing back. Similarly, the ear canal directs sound waves straight to the eardrum so that we can hear.
Structure of the Ear Canal
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The ear canal is a tube-like structure.
Detailed Explanation
The ear canal is approximately 2.5 centimeters long and is shaped like an 'S'. It is lined with skin and contains tiny hair follicles and glands that produce earwax, known as cerumen. This earwax plays a protective role by trapping dust, debris, and any foreign particles, preventing them from reaching the eardrum and potentially causing harm. Additionally, the hairs in the ear canal help to keep the canal clean by moving the earwax and trapped particles out of the ear.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the ear canal as a clean, well-maintained hallway in a museum where precious artifacts are displayed (the eardrum and inner ear). The floor (canal) is kept clean by janitors (earwax and hairs) that remove any dirt (dust and debris) that might otherwise damage the exhibits. This ensures that the valuable artwork—our ability to hear—is protected.
Importance of the Ear Canal
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The ear canal amplifies and directs sound waves to the eardrum.
Detailed Explanation
One of the primary functions of the ear canal is to amplify sound waves as they travel towards the eardrum. The canal also prevents high-frequency sounds from being overly intense and causing damage to the ear. By funneling sound waves effectively, it enhances sound quality and helps us perceive sounds more clearly. This amplification process is vital for understanding speech and enjoying music.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a funnel used for pouring water into a bottle. The wider opening gathers more water, which then flows down to the narrower end, directing all the water into the bottle without spilling. Similarly, the ear canal acts like a funnel, gathering sound waves and directing them toward the eardrum so that we can interpret them accurately and effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Function of the Ear Canal: Transmits sound waves to the eardrum.
-
Protective Role: Produces earwax to trap dust and dirt.
-
Sound Transmission: Converts sound into mechanical vibrations for hearing.
Examples & Applications
The ear canal directs sound waves from the environment to the eardrum.
Earwax plays a critical role in protecting the ear canal and maintaining ear health.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Sound waves travel through a lane, the ear canal's the name; to the eardrum they'll soar, then hearing you will explore.
Stories
Once upon a time, sound waves traveled like little cars through the ear canal highway, racing to the eardrum to create the magic of hearing.
Memory Tools
EAR: E for Entry of sound, A for Amplification and R for Relay to the brain.
Acronyms
CANAL
for Carrying sound
for Amplifying
for Nourishing with earwax
for Assuring clean passage
for Leading to the eardrum.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ear Canal
A tube that connects the outer ear to the eardrum, facilitating the transmission of sound waves.
- Eardrum
A membrane that vibrates in response to sound waves, playing a key role in the hearing process.
- Cerumen
Also known as earwax; a substance produced in the ear canal that protects the inner ear.
- Vibrations
Oscillations or movements that occur in sound waves, causing the eardrum to move.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
