Inner Ear (Cochlea)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Cochlea
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to explore the cochlea, which is an essential part of our inner ear responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals.

How does the cochlea actually convert vibrations into signals?

Great question! The cochlea contains tiny hair cells. When sound waves vibrate the fluid inside the cochlea, these hair cells move, and that movement is what creates electrical signals.

So it's like converting sound into electricity?

Exactly! This process allows our brain to interpret different sounds based on the signals received from the cochlea.

Can the cochlea tell us different frequencies of sounds?

Yes, the cochlea has the ability to distinguish various frequencies, which helps us differentiate between sounds, such as music and speech.
Structure of the Cochlea
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive a bit deeper into the structure of the cochlea. It has three main sections named the scala vestibuli, scala tympani, and cochlear duct.

What do these sections do?

The scala vestibuli and scala tympani are filled with fluid, while the cochlear duct contains the hair cells that convert vibrations into electrical impulses.

Why is fluid important there?

The fluid movement is crucial because it transmits the vibrations. The hair cells only respond to the motion of the fluid.

Can you summarize the cochlea's role again?

Certainly! The cochlea converts sound vibrations into electrical signals through fluid movement and hair cell interaction, allowing us to hear.
Cochlea and Signal Transmission
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss how the electrical signals from the cochlea reach our brain.

Does the auditory nerve play a role in that?

Yes, the auditory nerve carries these electrical signals from the cochlea directly to the brain where they are interpreted as sound.

What happens if there's damage to the cochlea?

Damage to the cochlea can lead to hearing loss since it won't effectively convert vibrations into signals.

So the cochlea is vital for hearing?

Absolutely! It's essential for our ability to hear and enjoy different sounds.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The cochlea is essential for hearing, as it converts vibrations from sound waves into electrical impulses. This process allows the auditory nerve to transmit these signals to the brain for interpretation, enabling us to hear sounds of various frequencies and amplitudes.
Detailed
Inner Ear (Cochlea)
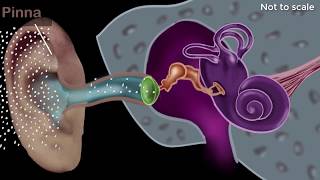
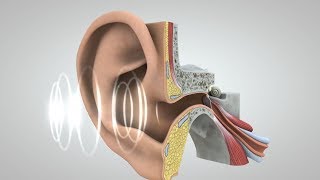
The cochlea is a spiral-shaped organ located in the inner ear that plays a vital role in hearing. Sound waves, after being collected by the outer and middle ear, reach the cochlea, where vibrations are transformed into electrical signals.
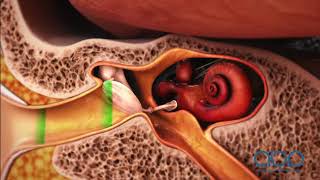
The cochlea consists of three main fluid-filled sections: the scala vestibuli, the scala tympani, and the cochlear duct. When sound waves enter the cochlea, they cause the fluid to move, triggering hair cells within the cochlear duct to flex. This mechanical movement is converted into electrical signals, which are then sent through the auditory nerve to the brain for interpretation. The ability of the cochlea to distinguish between different frequencies plays a critical role in our perception of sound, contributing to our ability to recognize speech and enjoy music.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Function of the Cochlea
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Inner Ear (Cochlea): Converts vibrations into electrical signals.
Detailed Explanation
The cochlea is a spiral-shaped organ located in the inner ear. Its primary function is to convert sound vibrations into electrical signals. When sound waves enter the ear, they cause the fluid inside the cochlea to move. This movement stimulates tiny hair cells lining the cochlea, which then convert the mechanical vibrations into electrical impulses.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the cochlea as a concert hall where sound waves are like music played. Just as the sound in a concert hall is converted into a beautiful melody that can be heard, the cochlea takes those sound vibrations and transforms them into signals that the brain can understand.
Structure of the Cochlea
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The cochlea is filled with fluid and has three main parts: the scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani.
Detailed Explanation
The cochlea consists of three fluid-filled sections: the scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani. The scala vestibuli and scala tympani are connected at the apex of the cochlea, and these channels are filled with perilymph fluid, while the scala media contains endolymph fluid. Each section plays a role in facilitating the movement of sound waves and the subsequent conversion into nerve impulses.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water park with different slides spreading out from a central hub. The slides represent the different parts of the cochlea, with the water (representing fluid) flowing through them to create excitement, similar to how sound vibrations travel through the cochlea to stimulate hearing.
Role of Hair Cells
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The tiny hair cells in the cochlea are responsible for converting mechanical vibrations into electrical signals.
Detailed Explanation
Hair cells are located within the cochlea and are essential for hearing. When the fluid within the cochlea moves due to sound vibrations, it causes the hair cells to sway. This movement generates an electrical signal, which is then sent to the brain via the auditory nerve. The brain interprets these signals as distinct sounds (like music, speech, or noise).
Examples & Analogies
Think of hair cells like tiny antennas picking up signals in a radio. Just as a radio antenna receives various radio waves and converts them into music or news you can hear, hair cells detect sound waves and convert them into signals that your brain can interpret as sound.
Connection to Auditory Nerve
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The auditory nerve carries the electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain.
Detailed Explanation
Once the hair cells generate electrical signals, these signals travel along the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve is responsible for transmitting sound information from the cochlea to the auditory cortex in the brain, where the sounds are processed, recognized, and interpreted.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the auditory nerve as a telephone line that connects the cochlea (the caller) to the brain (the receiver). Just like a telephone communication allows information to travel from one person to another, the auditory nerve conveys sound signals from the cochlea to the brain, enabling you to hear and understand what is happening around you.
Key Concepts
-
Cochlea: The organ that converts sound vibrations to electrical signals.
-
Hair Cells: Sensory receptors that detect vibrations.
-
Auditory Nerve: Pathway for sound signals to the brain.
-
Fluid Motion: Essential for signal transduction in the cochlea.
-
Frequency Discrimination: Ability of the cochlea to hear different pitches.
Examples & Applications
When you hear music, sound waves enter your ear, vibrate the eardrum, and are transmitted to the cochlea, where they are converted into electrical signals.
During a concert, the various instruments produce sounds at different frequencies; the cochlea enables you to differentiate between them.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cochlea's twist, a sound so fine, hair cells do dance, signals align.
Stories
Imagine a tiny spiral staircase within your ear, where each step represents a frequency. As sound waves climb the stairs, the tiny hair dancers sway, converting vibrations into electric whispers for your brain.
Memory Tools
C.H.A.S.E - Cochlea, Hair cells, Auditory nerve, Signals, Electrical - to remember key components of sound processing.
Acronyms
C.H.A.E. (Cochlea, Hair cells, Auditory Nerve, Electrical signals) to remember the steps of how sound is processed.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cochlea
A spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear that converts sound vibrations into electrical signals for the brain.
- Hair cells
Sensory cells within the cochlea that transduce mechanical sound vibrations into electrical signals.
- Auditory nerve
The nerve that carries auditory signals from the cochlea to the brain.
- Fluid movement
The motion of fluids within the cochlea that facilitates the bending of hair cells, leading to signal transduction.
- Frequency
The measure of how many sound waves occur in a second, affecting the pitch of the sound.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
