Range of Hearing in Humans
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Normal Human Hearing Range
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's talk about the range of hearing in humans. Who can tell me what the normal range is?

I think it's between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz?

Exactly! That's correct. We often refer to this range as the 'audible range.' It's essential because it helps us perceive many sounds around us.

But do we hear everything equally well in that range?

Great question! While 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz encompasses our hearing range, our sensitivity can change across different frequencies. We are generally more sensitive to frequencies between 1,000 and 4,000 Hz, where many important sounds like human voices fall.

Does the range change as we get older?

Yes, it does! As we age, the upper limit often decreases, making it harder to hear higher frequencies. This process is called presbycusis, which can affect communication and quality of life.

So, protecting our hearing is important?

Absolutely! Protecting our ears from loud noises is key to maintaining our hearing abilities. To recap: human hearing ranges from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz, and sensitivity varies by frequency while declining with age.
Animal Hearing Ranges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s expand our discussion to how different animals perceive sound. Can anyone name an animal that hears better than humans?

Dogs! They can hear high-pitched sounds?

Correct! Dogs can hear ultrasonic sounds above 20,000 Hz, which allows them to pick up sounds we cannot detect. Can anyone think of why this might be useful?

Maybe for training or in herding other animals?

Exactly! This ability aids them in various functions. Similarly, bats use echolocation, emitting ultrasonic sounds to navigate and find food in the dark.

That's fascinating! What about other animals? Do they hear different frequencies too?

Yes, many animals have adapted hearing ranges based on their environment. Understanding these differences helps us interact with and care for different species better. As a summary, humans hear from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz, but animals like dogs and bats can detect sounds beyond that range.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Humans can typically hear sounds between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz, though this range diminishes with age. Additionally, various animals, such as dogs and bats, can detect sounds beyond human hearing capabilities, including ultrasonic frequencies.
Detailed
Range of Hearing in Humans
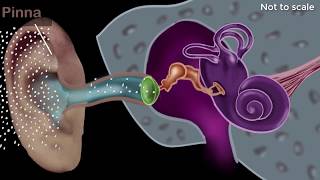
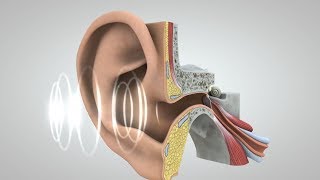
The human ear is designed to perceive sound waves within a specific frequency range, known as the audible range. Normal human hearing encompasses frequencies from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz (20 kHz). This range allows us to enjoy various sounds, including speech, music, and environmental noises.
As individuals age, the range of hearing often decreases, particularly for higher frequencies, which may lead to difficulties in hearing certain sounds. This phenomenon highlights the importance of protecting our hearing throughout life. Furthermore, it's notable that many animals possess different hearing capabilities: for instance, dogs can hear ultrasonic sounds beyond 20 kHz, while certain species of bats use echolocation to navigate through sounds well beyond human limits. Understanding the range of hearing is essential for various applications, including designing better hearing aids and ensuring the welfare of animals in various environments.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Normal Human Hearing Range
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Normal human hearing range: 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Detailed Explanation
Humans can hear sounds that fall within a specific frequency range. This range is from 20 Hertz (Hz) to 20,000 Hertz (20 kHz). Frequencies below 20 Hz are known as infrasonic sounds, while those above 20 kHz are ultrasonic sounds. This range is critical as it defines what sounds we can perceive and respond to.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a piano. The lowest note it can play is similar to 20 Hz, and the highest is akin to 20,000 Hz. Just as a musician can hit different keys to produce sounds of different pitches, humans can hear these various frequencies. If you were to play a note lower than the piano's lowest pitch or higher than its highest pitch, it would be like a sound that we cannot hear.
Decrease in Hearing Ability with Age
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Hearing range decreases with age.
Detailed Explanation
As people age, their ability to hear high frequencies diminishes. This often begins subtly and may not be noticed until someone finds themselves struggling to hear higher-pitched sounds. This natural degeneration can be attributed to changes in the ear structure and the auditory nerve, which affects how sound signals are transmitted to the brain.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a once-vibrant color painting that has faded over time. Just as the colors blend and lose their brightness, older adults may find that higher-pitched sounds, like birds chirping or a child’s laughter, become harder to detect. It’s as if certain vibrant frequencies are no longer part of their auditory palette.
Animal Hearing Ranges
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Animals have different hearing ranges – dogs and bats hear ultrasonic sounds.
Detailed Explanation
Different animals have varying ranges of hearing that allow them to interact with their environment in unique ways. For example, dogs can hear frequencies up to approximately 65,000 Hz, which is well above the human range; this ability helps them detect sounds like high-pitched whistles. Bats, on the other hand, use echolocation and can hear and emit sounds in the ultrasonic range, which helps them navigate and find food in the dark.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a superhero with super-hearing abilities. Just like how this superhero can hear sounds that are imperceptible to most people, dogs and bats possess their specialized hearing capabilities. When you call your dog and whistle, it can hear that high pitch you might not even notice, just like how a bat uses its special echo sounds to find its way home when it’s dark.
Key Concepts
-
Normal Human Hearing: Human hearing ranges from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz, though sensitivity varies across frequencies.
-
Aging Effects: Hearing typically decreases with age, particularly for higher frequencies.
-
Animal Hearing: Different species, like dogs and bats, can perceive ultrasonic sounds, which surpasses human hearing capabilities.
Examples & Applications
The sound of a whisper is around 20 Hz, while a jet engine can produce sounds over 100,000 Hz, an example of the upper limit of human hearing.
Dogs can hear sounds emitted from dog whistles that are above 20,000 Hz, showcasing their superior sensitivity to high-frequency sounds.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
From 20 Hz to 20k, lower sounds you may forsake; age may take the highest toll, but protect your ears for sound control.
Stories
Imagine a world where animals hear the whispers of the wind and the slightest rustle in the grass, while humans must keep their ears sharp as they age and silence starts to creep in.
Memory Tools
Hearing range: Remember '20-20 kHz Add Age Noise' to recall the standard range and effects of aging on hearing.
Acronyms
H.A.R.E. - Human Auditory Range Erodes as we age.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Audible Range
The range of frequencies that can be heard by the average human, typically 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
- Presbycusis
Age-related hearing loss that typically results in diminished ability to hear higher frequencies.
- Ultrasonic
Sound frequencies that are higher than the audible range for humans, typically above 20,000 Hz.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
