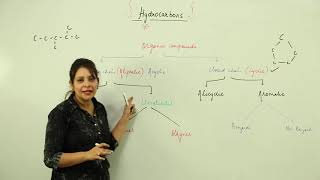
Introduction to Hydrocarbons
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Hydrocarbons
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will begin our journey into hydrocarbons. Can anyone tell me what hydrocarbons are?

Are they compounds made only of carbon and hydrogen?

Exactly! Hydrocarbons consist solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They're the simplest organic compounds. Why do you think that is important in chemistry?

Maybe because they form the basis for more complex compounds?

Correct! And hydrocarbons are crucial in our everyday lives as they are major sources of fuel and raw materials. Can anyone name some major sources of hydrocarbons?

Petroleum and natural gas?

Yes, great job! Petroleum and natural gas are two of the primary sources, along with coal. Now, remember, hydrocarbons are not just basic building blocks; they're significant for various applications, including fuels. Let's summarize: hydrocarbons are simple organic compounds, and they primarily come from petroleum, natural gas, and coal.
Sources and Importance of Hydrocarbons
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's focus on the sources of hydrocarbons. Can anyone explain how petroleum and natural gas come into play?

They are formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals, right?

Exactly! They are formed over millions of years under heat and pressure. Why do we consider hydrocarbons as important in society?

Because they are used in fuels like gasoline and diesel and also as raw materials in manufacturing?

Right on! Hydrocarbons are pivotal for energy and industry. To remember, think of H.E.L.P: Hydrocarbons Energy, Linked to industries, and Powerful!
Significance of Hydrocarbons
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've discussed hydrocarbons as organic compounds. Why do we study hydrocarbons in chemistry?

To understand how they react and how we can use them?

Correct! The reactions of hydrocarbons lay the groundwork for organic chemistry. They're involved in combustion, synthesis of various substances, and even environmental studies. Let’s summarize: hydrocarbons are crucial in energy and industry, and understanding them enables us to explore more advanced chemistry.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces hydrocarbons, outlining their composition as organic compounds made from carbon and hydrogen. Hydrocarbons are foundational to organic chemistry and are predominantly sourced from natural resources like petroleum and coal. Understanding these compounds sets the stage for exploring their various types, properties, and applications in subsequent sections.
Detailed
Introduction to Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are the essential building blocks of organic chemistry, comprising only carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms. As the simplest organic compounds, they serve as foundations for more complex structures and reactions. Major natural sources of hydrocarbons include petroleum, natural gas, and coal, all crucial to various industrial applications. In this section, we will explore what hydrocarbons are, their significance in organic chemistry, and the sources from which they originate. The knowledge of hydrocarbons is vital for understanding different chemical reactions in subsequent chapters.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Hydrocarbons
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made up of only carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms.
Detailed Explanation
Hydrocarbons are a class of organic compounds that consist solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Understanding hydrocarbons is essential because they are among the simplest forms of organic chemistry. In simpler terms, if you imagine a compound as a recipe, hydrocarbons are a basic recipe that only includes the ingredients carbon and hydrogen in various arrangements. This simplicity makes them foundational in the study of organic chemistry.
Examples & Analogies
Think of hydrocarbons like LEGO blocks. Just as you can create different structures using the same blocks, hydrocarbons can be structured in different ways by combining carbon and hydrogen atoms. Depending on how you connect these blocks (or atoms), you create different hydrocarbons that can behave differently, just like different LEGO structures have different functions.
Importance of Hydrocarbons
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● They are the simplest organic compounds and serve as the foundation of organic chemistry.
Detailed Explanation
Hydrocarbons are not just basic; they are fundamental. As the simplest forms of organic molecules, they help scientists and students understand more complex organic compounds. They represent the building blocks for constructing various other chemical structures in organic chemistry. You can consider them as the ‘ABC’s of organic chemistry, where once you learn these basic letters (hydrocarbons), you can begin to understand as you build up to more complex words and sentences (more complex organic molecules).
Examples & Analogies
Imagine learning to read and write. At first, you focus on the alphabet and simple words—like learning to say 'cat' or 'dog.' These fundamental elements prepare you for more advanced concepts. Similarly, hydrocarbons lay the groundwork for diving into more intricate organic compounds like alcohols, acids, and more complex synthetic materials.
Major Sources of Hydrocarbons
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Major sources: Petroleum, natural gas, and coal.
Detailed Explanation
Hydrocarbons come from a few primary natural sources: petroleum, natural gas, and coal. Petroleum and natural gas are particularly noteworthy because they are widely used as fuel and energy sources. Coal, while mainly recognized as a fuel, is also composed of hydrocarbons. Understanding these sources is important for realizing where hydrocarbons are found and their significance in energy production and everyday life.
Examples & Analogies
Consider looking for ingredients in your kitchen. If you want to bake a cake, the main ingredient could be flour, which you need in large quantity. Similarly, just like flour is essential for baking, hydrocarbons are essential for energy creation, and they predominantly come from 'kitchen ingredients' found in nature: petroleum, natural gas, and coal.
Key Concepts
-
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting only of carbon and hydrogen.
-
Major sources of hydrocarbons include petroleum, natural gas, and coal.
-
Hydrocarbons serve as foundational elements in organic chemistry.
Examples & Applications
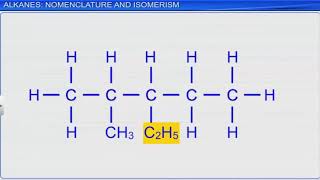
Methane (CH₄) is a simple hydrocarbon used as a fuel.
Ethane (C₂H₆) is derived from natural gas and used in various chemical products.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Hydrocarbons we see, pure Carbon and H, that's the key!
Stories
In a kingdom deep underground, clever hydrocarbons were found — in wells and mines, they serve mankind, powers and materials intertwined.
Memory Tools
Remember H.E.L.P for hydrocarbons: H for Hydrocarbon, E for Energy, L for Linked to industries, P for Powerful!
Acronyms
The acronym 'CH' can help to remember Carbon and Hydrogen as the main elements of hydrocarbons.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hydrocarbon
An organic compound made up solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Petroleum
A natural liquid found in geological formations, consisting of hydrocarbon deposits.
- Natural Gas
A fossil fuel consisting primarily of methane and found in association with other fossil fuels.
- Coal
A combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock formed from vegetation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
