Classification of Matter
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Pure Substances
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the classification of matter, starting with pure substances. What do you think a pure substance is?

Is it something that is made up of one kind of particle?

Exactly! A pure substance consists of only one type of atom or molecule. Can anyone give me examples of pure substances?

Oxygen is one, and also gold!

What about water? It's made of different elements?

Great point! Water is actually a compound, which is a type of pure substance consisting of two or more elements chemically combined. Remember: compounds are pure substances too!

So, compounds are different from elements, right?

Correct! Elements are the simplest form of matter, while compounds are combinations of multiple elements.

To sum up, pure substances include elements like oxygen and compounds like water. Remember the acronym 'E-C' for Elements and Compounds. Next, let's look at mixtures!
Understanding Mixtures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift our focus to mixtures. Can anyone describe what a mixture is?

Is it when two or more substances are combined?

Exactly! Mixtures involve two or more substances that are physically combined, not chemically. Mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. Who can explain the difference?

Homogeneous mixtures look the same throughout, like a saltwater solution.

Heterogeneous mixtures can be picked apart, like a salad, where you can see and separate the ingredients.

Perfect! Homogeneous mixtures are uniform, while heterogeneous mixtures have distinct components. Remember: 'Homo is Whole' for homogeneous and 'Hetero has Hiccups' for heterogeneous. Now, let’s discuss how these classifications are important!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
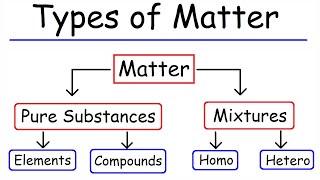
In the classification of matter, substances are categorized as pure substances—which include elements and compounds—or mixtures. Pure substances have a uniform composition, while mixtures can either be homogeneous with a consistent composition throughout or heterogeneous with a non-uniform composition.
Detailed
Classification of Matter
In this section, we explore the classification of matter, which is fundamental to understanding chemistry and its principles. Matter is broadly categorized into pure substances and mixtures:
- Pure Substances:
- Elements: These consist solely of one type of atom. Examples include oxygen (O) and gold (Au).
- Compounds: Compounds are composed of two or more elements chemically combined in a specific ratio. A classic example is water (H₂O), which consists of hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
- Mixtures:
- Homogeneous Mixtures: These have a uniform composition throughout, meaning that the individual components are thoroughly mixed. An example is a salt solution where the salt is completely dissolved.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: These do not have a uniform composition, and the individual components can often be distinguished. An example includes a mixture of sand and iron filings, where each component retains its properties.
Understanding these classifications is essential for further studies in chemistry as they lay the groundwork for topics such as chemical reactions and material properties.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Pure Substances
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Pure Substances:
○ Elements: Consist of only one type of atom (e.g., Oxygen, Gold).
○ Compounds: Consist of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio (e.g., Water - H₂O).
Detailed Explanation
A pure substance is a material that has a uniform and definite composition. There are two main types of pure substances: elements and compounds. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom; for example, Oxygen (O) and Gold (Au) are elements because they cannot be broken down into simpler substances. On the other hand, compounds are made when two or more elements chemically combine in a specific ratio. For instance, water (H₂O) is a compound formed from the elements hydrogen and oxygen in a 2:1 ratio.
Examples & Analogies
Think of elements as unique building blocks like individual Lego pieces. Each piece is distinct (like how gold or oxygen is unique), while compounds are like a completed Lego creation, such as a car or a house, which combines multiple blocks to create something new.
Mixtures
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Mixtures:
○ Homogeneous Mixtures: Uniform composition throughout (e.g., Salt solution).
○ Heterogeneous Mixtures: Non-uniform composition (e.g., Sand and iron filings).
Detailed Explanation
Mixtures consist of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. They can be classified as homogeneous or heterogeneous. Homogeneous mixtures, like a salt solution, have a uniform composition throughout. This means that if you take a sample from any part of the mixture, it will have the same proportions of salt and water. In contrast, heterogeneous mixtures, such as a mix of sand and iron filings, have a non-uniform composition. If you take samples from different parts of this mixture, the amounts of sand and iron filings will vary.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a fruit salad. Each bite might contain varying amounts of different fruits, illustrating a heterogeneous mixture. Now contrast that with a smoothie made from those same fruits—the smoothie is smooth, and every sip contains a uniform mix of fruits, exemplifying a homogeneous mixture.
Key Concepts
-
Pure Substances: Uniform composition consisting of either elements or compounds.
-
Elements: Simple substances that consist of only one type of atom.
-
Compounds: Substances formed from two or more elements in a fixed ratio.
-
Mixtures: Combinations of substances that retain their identity and properties.
-
Homogeneous Mixtures: Mixtures with a uniform composition throughout.
-
Heterogeneous Mixtures: Mixtures where the different components are easily identifiable.
Examples & Applications
Oxygen (O) is an element and a pure substance.
Water (H₂O) is a compound and a pure substance.
A saltwater solution is a homogeneous mixture.
A salad is an example of a heterogeneous mixture.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a pure substance, atoms are tight; mixed with others, that feels just right.
Stories
Imagine a wizard who combines elements—like water from a magic potion—making compounds that create powerful spells, while mixtures are just the chaos of ingredients mixing together in a cauldron!
Memory Tools
E-C for Easy Classification: Elements and Compounds are the pure part, Mixtures come in two types, so play your part!
Acronyms
P-M for Pure and Mixtures
for Pure Substances
for Mixtures—remember the difference!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pure Substance
Matter that has a uniform and definite composition, including elements and compounds.
- Element
A substance that consists of only one type of atom.
- Compound
A substance formed from two or more different elements that are chemically bonded together.
- Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that retain their individual properties.
- Homogeneous Mixture
A mixture that has a constant composition throughout, and components are indistinguishable.
- Heterogeneous Mixture
A mixture where the individual components are easily visible and can be separated.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
