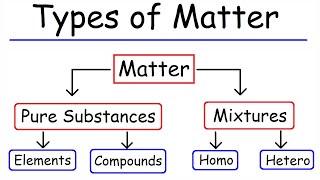
Introduction to Matter
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Matter
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're diving into the world of matter! Can anyone tell me what matter is?

Isn't matter something that has weight?

Exactly! Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. You could think of it like a filled balloon or a solid rock. Both are forms of matter!

So, does that mean everything around us is matter?

Good question! Yes, everything you can touch, see, or even smell generally qualifies as matter. Now, let’s talk about the states of matter. Can anyone name them?

Solid, liquid, and gas, right?

That's right! Let's break them down. A solid has a definite shape and volume. Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container. And gases have neither a definite shape nor a volume, expanding to fill any space available. Here's a mnemonic to help you remember: 'Some Lions Grow!'. Each initial stands for the three forms: Solid, Liquid, Gas.

That sounds helpful! But why is it necessary to understand matter?

Understanding matter is essential in chemistry. It helps us learn about substances, their properties, and interactions. Remember, it's the foundation for everything we will study in this chapter!

To wrap up, matter has mass and occupies space, existing in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Each state has unique properties that we’ll explore further as we move on.
States of Matter
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve deeper into the states of matter. What separates a solid from a liquid?

Solids keep their shape, right? Liquids don’t?

Correct! Solids have molecules that are tightly packed and vibrate in place. In liquids, the molecules are still close together but can move past one another, which allows them to take the shape of their container. What about gases?

Gases can spread out and fill any space!

Exactly! Gas particles are far apart and move freely. Let's visualize it: imagine a room filled with air. That air is gas, and it expands to occupy the space available. Remember the acronym we learned? 'Some Lions Grow!' helps us recall solids, liquids, and gases.

So, temperature can affect the state of matter too?

Absolutely! Increasing temperature can make solids melt into liquids and liquids evaporate into gases. That's an essential concept we’ll build on later.

To summarize, solids, liquids, and gases each have distinct properties based on how their molecules are arranged and move. Keeping these differences in mind is key to our study of matter.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space, existing in three primary states: solid, liquid, and gas. Each state has distinct characteristics that determine its behavior and properties.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of 'Introduction to Matter'
Matter is defined as anything that possesses mass and occupies space. It can exist in three primary states: solid, liquid, and gas. A solid has a definite shape and volume, meaning its structure is rigid, while a liquid has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container. In contrast, a gas has neither a defined shape nor volume, expanding to fill any available space. Understanding these states is fundamental to various scientific fields, particularly chemistry, as it lays the groundwork for studying the characteristics and behaviors of substances.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Matter
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
Detailed Explanation
Matter is defined as anything that possesses mass and takes up space. This means that all physical objects, whether they're solid, liquid, or gaseous, are classified as matter. For example, the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the table we sit at are all forms of matter because they have weight (mass) and they occupy physical space in our environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of matter as all the ingredients that make up a cake. Just as flour, sugar, eggs, and milk combine to create a cake, any substance in our world—like a rock, a drop of water, or the air around us—combines to form what we recognize as matter.
States of Matter
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● It exists in three primary states:
○ Solid: Definite shape and volume.
○ Liquid: Definite volume but no definite shape.
○ Gas: Neither definite shape nor volume.
Detailed Explanation
Matter exists in three main states: solids, liquids, and gases. In solids, the particles are closely packed together, giving them a definite shape and volume; for example, ice is a solid where the water molecules are tightly held together. In liquids, the particles are still close but can move past one another, which means they have a fixed volume but can take the shape of their container, like water in a glass. Gases have particles that are far apart and move freely, meaning they don't have a definite shape or volume, as seen with air filling a balloon.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a box of ice cubes (solid) placed in a bowl. If you let them sit out, they will melt into water (liquid), taking the shape of the bowl but keeping the same amount of water. If you leave that water out longer, it will evaporate and turn into steam (gas), which spreads into the air, filling the entire room. Each state represents a different way matter can exist.
Key Concepts
-
Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies space.
-
Solid: Definite shape and volume.
-
Liquid: Definite volume, no definite shape.
-
Gas: Neither definite shape nor volume.
Examples & Applications
A rock is a solid, as it has a definite shape and volume.
Water is a liquid; it takes the shape of its container but has a definite volume.
Air is a gas; it has neither a definite shape nor volume.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Matter has mass, and space it takes, Solid, liquid, gas, those are the stakes.
Stories
Once upon a time, three friends lived in a mysterious land. Solid was a rock, always still and sturdy. Liquid was water, flowing and free. Gas was air, invisible yet everywhere. Together, they showed how matter could be seen, felt, and understood.
Memory Tools
'Some Lions Grow' to remember Solid, Liquid, Gas.
Acronyms
SLG - stands for Solid, Liquid, Gas.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space.
- Solid
A state of matter with a definite shape and volume.
- Liquid
A state of matter with a definite volume but no definite shape.
- Gas
A state of matter with neither definite shape nor volume.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
