Separation of Mixtures
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Basics of Mixture Separation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will dive into how we can separate mixtures. First, can anyone tell me what a mixture is?

A mixture is made up of two or more substances that can be separated.

Exactly! Now, what are the two types of mixtures we often come across?

Homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures!

Well done! Now that we know about mixtures, let’s talk about how we can separate them. Can anyone suggest any separation techniques?

Filtration is one technique, right?

Yes! Filtration is used to separate insoluble solids from liquids. Remember the acronym 'FIND' - Filtration Is Not Difficult! It will help you remember this process.

What about evaporation?

Exactly! Evaporation removes a liquid from a solution. It’s like leaving a puddle to dry; what’s left behind?

The solid!

Correct!
Advanced Separation Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at more advanced separation techniques. Who can explain how distillation works?

It separates liquids based on their boiling points.

Correct! It’s very useful when dealing with liquid mixtures. Always remember 'Distillation is Dramatic!' to recall that higher boiling points separate first.

And what about chromatography?

Great question! Chromatography separates substances based on how they move through a medium—think of it like a race!

Is that related to colors spreading in ink?

Absolutely! The different colors travel different distances. That’s why we can see a rainbow in a drop of ink!
Practical Applications of Separation Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s connect what we’ve learned to real-world applications. Can anyone think of where filtration might be used?

In water purification!

Exactly! It's crucial for making safe drinking water. What about magnetic separation?

It can be used to separate metal from recycling waste.

Great point! The recycling process often uses this technique. Remember, 'Magnetic Magic for Metal!' What about evaporation?

In cooking, like when making syrup!

Correct! Evaporation concentrates the flavors. Excellent connections everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The separation of mixtures can be achieved through several techniques including filtration, evaporation, distillation, chromatography, and magnetic separation. Each method is suitable for specific types of mixtures based on their unique characteristics.
Detailed
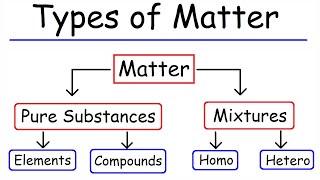
Separation of Mixtures
In this section, we explore the various techniques available for separating mixtures, which are combinations of two or more substances that retain their individual properties. Mixtures can be broadly classified into heterogeneous and homogeneous types, and the separation technique employed is often chosen based on the specific properties of the components involved. Here are the primary techniques:
- Filtration: This method is used to separate insoluble solids from liquids. It involves passing a mixture through a filter paper that allows the liquid to pass while retaining solid particles.
- Evaporation: Used to remove a liquid from a solution. When a solution is heated, the solvent evaporates, leaving behind a solid residue.
- Distillation: This technique separates components based on their differing boiling points. For example, when heating a mixture of liquids, the one with the lower boiling point vaporizes first, and can be condensed back into a liquid.
- Chromatography: This method separates substances based on their movement through a medium (like paper or gel). Different substances move at different rates, allowing for separation.
- Magnetic Separation: This technique employs magnets to separate magnetic materials from a mixture, especially useful in heterogeneous mixtures.
Understanding these methods is crucial for analyzing and utilizing mixtures in various scientific and industrial applications.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Filtration
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Filtration: Separates insoluble solids from liquids.
Detailed Explanation
Filtration is a process used to separate solid particles from a liquid by passing the mixture through a filter. The filter allows the liquid to pass while trapping the solid particles in the filter paper or mesh. This method is effective when dealing with mixtures where one component is a solid that does not dissolve in the liquid.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a coffee maker. When you brew coffee, hot water passes through the coffee grounds. The filter catches the solid coffee grounds, allowing the liquid coffee to pass through. This is just like filtration separating sand from water.
Evaporation
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Evaporation: Removes a liquid from a solution to leave a solid residue.
Detailed Explanation
Evaporation is the process of turning a liquid into vapor, often by heating. In the context of separating mixtures, it is used to remove a liquid in a solution, leaving behind the solid that's dissolved in it. For example, if you have saltwater and you heat it, the water will evaporate, and you'll be left with salt crystals.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a puddle of water on a hot day. You notice that it slowly disappears. The sun's heat causes the water to evaporate, turning it into vapor and leaving nothing behind. This is similar to how evaporation can be used to separate salt from water.
Distillation
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Distillation: Separates components based on boiling points.
Detailed Explanation
Distillation is a technique used to separate liquids based on their different boiling points. When a mixture is heated, the component with the lowest boiling point vaporizes first. This vapor is then cooled and condensed back into liquid form, effectively separating it from the rest of the mixture. This method is commonly used for purifying liquids.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how you can separate alcohol from a mixture. When you heat a solution that contains alcohol and water, the alcohol will boil off at a lower temperature than water. By collecting the vapor and allowing it to cool, you can obtain pure alcohol, much like how distillation works in the production of spirits.
Chromatography
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Chromatography: Separates substances based on their movement through a medium.
Detailed Explanation
Chromatography is a method used to separate different components of a mixture based on their movement through a stationary phase (like paper) or a mobile phase (like liquid or gas). As the mixture moves, different substances travel at different rates, allowing them to be separated and analyzed. This method is widely used in laboratories and industries.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a race where different runners (substances) are running through a muddy field (the medium). Some runners sprint quickly while others lag behind because of the mud. By the end of the race, the runners are spread out according to how fast they moved through the muddy field. This is similar to how chromatography separates substances.
Magnetic Separation
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Magnetic Separation: Uses magnets to separate magnetic materials from mixtures.
Detailed Explanation
Magnetic separation is a technique that utilizes magnets to attract and separate magnetic materials from non-magnetic ones in a mixture. This process is particularly useful in recycling and processing materials that include metals. By running a mixture past a magnet, you can effectively remove the iron filings or other magnetic components.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how a magnet can pick up paper clips from a pile of mixed office supplies. As you move the magnet through the clutter, only the magnetic paper clips stick to it, leaving the non-magnetic items behind. This is the principle behind magnetic separation in larger industrial applications.
Key Concepts
-
Mixtures: Combinations of two or more substances that maintain their individual properties.
-
Separation Techniques: Methods to isolate components of mixtures based on their physical properties.
-
Heterogeneous vs. Homogeneous: Types of mixtures differentiated by uniformity in composition.
Examples & Applications
Using a coffee filter to separate coffee grounds from liquid coffee.
Heating salt water to evaporate the water, leaving salt crystals behind.
Using a magnet to separate iron filings from sand.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Filtration’s a breeze, separates with ease; Evaporation heats, leaving solids like sweets.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a kitchen full of mixtures, a chef used filtration to brew coffee, evaporation to make syrup, and distillation to create flavored oils, each technique helping to separate and create delicious dishes.
Memory Tools
Remember 'F.E.D.C.M.' for the steps: Filtration, Evaporation, Distillation, Chromatography, Magnetic separation.
Acronyms
Use 'FECMD' to recall filtration, evaporation, chromatography, magnetic separation, and distillation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Filtration
A separation process that removes solids from liquids by using a medium that allows only the liquid to pass.
- Evaporation
The process of turning a liquid into vapor, leaving solid components behind.
- Distillation
A separation technique that uses boiling points to separate components of a liquid mixture.
- Chromatography
A method for separating substances based on their movement through a medium.
- Magnetic Separation
A process that uses magnets to separate magnetic materials from a mixture.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
