Definition of Atmosphere
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is the Atmosphere?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today we are going to discuss the atmosphere. Can anyone tell me what the atmosphere is?

Is it the air we breathe?

Exactly! The atmosphere is the layer of gases surrounding the Earth. It's crucial for our survival because it provides oxygen.

How does it protect us?

Great question! The atmosphere filters harmful radiation from the Sun. It regulates temperature, making Earth habitable. Remember the acronym 'O.P.R.' for Oxygen, Protection, and Regulation!

What happens if we didn't have it?

Without it, life as we know it couldn't exist. The Earth would be too harsh and cold.

In summary, the atmosphere is vital for oxygen, protection from radiation, and temperature regulation.
Composition of the Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into the gases that comprise our atmosphere. Can anyone name one?

Oxygen?

Correct! Oxygen makes up about 21% of the atmosphere. Can anyone tell me what the biggest gas is?

Is it nitrogen?

Right again! Nitrogen is about 78% of the atmosphere. It is important because it is inert and doesn't support combustion. Remember: 'N.O.N.' for Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Not active.

What about carbon dioxide?

That's a critical component too! Carbon dioxide is essential for plants during photosynthesis and makes up about 0.04% of the atmosphere.

To summarize, the key gases in our atmosphere are nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide, each playing vital roles.
Role of Water Vapor
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about water vapor. Who can tell me how it affects our weather?

Doesn't it create clouds?

Absolutely! Water vapor contributes to cloud formation and precipitation. It's also important in temperature regulation through the greenhouse effect.

How does that work?

The greenhouse effect is when certain gases trap heat in the atmosphere. Water vapor is one of those crucial gases. Keep in mind the phrase 'H.T.W.' for Heat Trapping Water!

What if there's too much water vapor?

Good point! Excess water vapor can lead to extreme weather, like heavy rains or storms. In summary, water vapor plays a vital role in cloud formation, precipitation, and regulating temperature.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The atmosphere consists of various gases, including nitrogen and oxygen, which are crucial for supporting life and regulating the environment. It protects the planet from harmful radiation and helps maintain a stable climate, making it indispensable for ecosystems.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The atmosphere is defined as the layer of gases that envelops the Earth, bound by gravitational forces. It plays a critical role in sustaining life by:
- Providing oxygen for organisms.
- Offering protection from harmful radiation from the Sun.
- Regulating Earth's temperature.
Composition of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is composed of a mixture of gases:
- Nitrogen (78%): The most abundant, inert gas that does not support combustion.
- Oxygen (21%): Essential for respiration and combustion.
- Argon (0.93%): An inert gas.
- Carbon Dioxide (0.04%): Important for photosynthesis and as a greenhouse gas.
Other trace gases, including neon, helium, and methane, also exist in small quantities.
Importance of Water Vapor
Water vapor varies widely, affecting weather patterns and climate. It is vital for processes such as:
- Cloud formation
- Precipitation
- Influencing the greenhouse effect, which helps to maintain the Earth's temperature.
Understanding the dynamics of the atmosphere is crucial for studying climate change, weather phenomena, and environmental protection.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is the Atmosphere?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the Earth, held in place by gravity.
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is essentially a vast dome of gases that envelopes our planet. It exists because gravity pulls these gases toward the Earth, keeping them from floating away into space. This layering of gases is crucial for all life on Earth, as it creates a stable environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the atmosphere like the skin of an apple. Just as the skin protects the flesh inside, the atmosphere protects all life on Earth by forming a barrier around the planet.
Importance of the Atmosphere for Life
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is essential for sustaining life, as it provides oxygen, protects us from harmful radiation, and regulates temperature.
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere plays several critical roles in sustaining life. First, it provides the oxygen that most living organisms need to breathe. Second, it acts as a shield, filtering out harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun, which can damage living tissues. Lastly, the atmosphere helps regulate the Earth's temperature, keeping it within a range that is suitable for life.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a greenhouse. Just like a greenhouse keeps plants warm and safe by trapping heat and blocking harsh weather, the atmosphere does the same for the Earth, allowing life to thrive.
Composition of the Atmosphere
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atmosphere is composed of a mixture of gases, water vapor, and dust particles that vary in composition at different altitudes.
Detailed Explanation
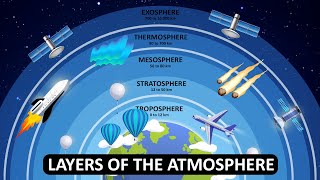
The atmosphere is not just a single type of gas; it consists of various gases that are mixed together. The primary components are nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide, along with trace amounts of other gases and varying levels of water vapor. The composition changes with altitude, which means that the higher you go, the less dense the atmosphere becomes, and the ratio of these gases can also change.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a fruit salad with different kinds of fruits. Just like each fruit contributes its unique taste and texture to the salad, each gas in the atmosphere plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall balance and functionality needed for life.
Key Concepts
-
Atmosphere: The layer of gases surrounding Earth.
-
Nitrogen: The most abundant gas in the atmosphere, accounting for 78%.
-
Oxygen: Essential for life and forms about 21% of the atmosphere.
-
Water Vapor: Crucial for weather and climate, responsible for cloud formation.
Examples & Applications
The atmosphere protects life by filtering UV radiation, enabling organisms to thrive under sunlight.
Water vapor contributes to rainfall, a key component of the water cycle, and ensures agricultural productivity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the air where we trot, nitrogen is the lot, oxygen's key, for you and me!
Stories
Once upon a time, there was a magical blanket around Earth called the atmosphere. It sheltered living creatures, gave them life with oxygen and shielded them from the sun's harsh rays.
Memory Tools
To remember the major gases, think 'Not Only A Cool Dragon,' for Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, and Carbon Dioxide.
Acronyms
Remember 'O.P.R.' - Oxygen, Protection, Regulation. This signifies the three key functions of the atmosphere.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding the Earth, essential for life and climate.
- Nitrogen
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere, making up 78%. It is inert.
- Oxygen
A gas essential for respiration in living organisms, comprising 21% of the atmosphere.
- Carbon Dioxide
A greenhouse gas vital for photosynthesis, existing at 0.04% in the atmosphere.
- Water Vapor
Water in its gaseous state, crucial for weather and climate, responsible for cloud formation and precipitation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
