Human Impact on the Atmosphere
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Air Pollution
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about air pollution. Can anyone tell me what air pollution is?

Is it when harmful substances are released into the air?

Exactly! Air pollution results from various human activities, such as industrial emissions and vehicle exhaust. These activities release pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. Let’s remember it with the acronym 'CAPS': Carbon monoxide, Airborne particles, Pollutants, and Smog.

What kind of health problems can it cause?

Great question! Air pollution can lead to respiratory issues, cardiovascular diseases, and even developmental problems in children. Any examples of air pollution we can think of?

What about when we see a lot of haze in cities?

Yes! That haze is often smog, a result of pollutants. Let’s make a quick recap: air pollution harms health and environment, remember 'CAPS'!
Ozone Depletion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s dive into ozone depletion. What’s the ozone layer's function?

It protects us from UV radiation, right?

Correct! However, CFCs and other chemicals have weakened it. Does anyone know where we find CFCs?

In old refrigerators and aerosol sprays?

Exactly! And the depletion leads to health risks like skin cancer. A good mnemonic is 'UV Safe': U for Ultraviolet, V for Vulnerability, reminding us to protect our ozone layer.

So if ozone is depleted, we could get more sunburns?

Yes, and also cataracts. A quick recap: CFCs are harmful as they thin the ozone layer, and 'UV Safe' reminds us of the hazards!
Global Warming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s discuss global warming. What is causing it?

Is it because of too many greenhouse gases?

You’re right! The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases like CO2, which trap heat. Let’s use 'GIG'—Greenhouse, Increasing gas—to remember its implications.

What are some consequences?

Good thought! Consequences include melting ice caps and extreme weather. So 'GIG' helps us recall that greenhouse gases are a major factor in global warming.

How can we help?

By reducing emissions and supporting renewable energy. Remember, every small action counts!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Human actions, such as industrial emissions and the use of ozone-depleting substances, have drastically altered the atmosphere. Key concerns revolve around air pollution leading to respiratory health issues, the thinning of the ozone layer, and the escalating challenge of global warming due to increased greenhouse gas emissions. Addressing these issues necessitates collective international efforts for a sustainable future.
Detailed
Human Impact on the Atmosphere
Human activities have profoundly impacted the Earth's atmosphere, leading to various environmental challenges. This section highlights three major aspects of this impact:
Air Pollution
Air pollution stems mainly from industrial activities, vehicle exhaust, and the burning of fossil fuels. Common pollutants include:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas that can be harmful when inhaled in large amounts.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Gases that play a significant role in forming smog and acid rain.
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2): Often produced from burning fossil fuels, it contributes to acid rain.
- Particulate matter (PM): Tiny particles that can penetrate the lungs and cause respiratory issues.
The effects of air pollution include smog formation, respiratory diseases, and environmental degradation.
Ozone Depletion
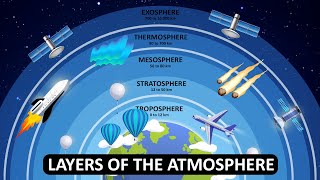
The release of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other ozone-depleting substances has resulted in the thinning of the ozone layer, particularly over polar regions. The ozone layer is crucial as it protects Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Its depletion can lead to:
- Increased risks of skin cancer and cataracts in humans.
- Harmful effects on animal and plant life.
Global Warming
The rise in greenhouse gases, primarily due to human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, has led to global warming. This phenomenon is characterized by:
- Rising global temperatures.
- Melting of polar ice caps.
- Alterations in weather patterns.
To mitigate these issues, global cooperation is essential to enforce stricter emissions regulations, promote renewable energy sources, and adopt sustainable practices.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Air Pollution
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Air Pollution
○ Human activities, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and the burning of fossil fuels, have led to the release of pollutants into the atmosphere.
○ Common air pollutants include carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, which contribute to smog, acid rain, and respiratory issues.
Detailed Explanation
Air pollution is the introduction of harmful substances into the atmosphere caused primarily by human activities. Industries emit pollutants, cars release exhaust fumes, and burning fossil fuels contributes significantly to poor air quality. Common air pollutants include:
1. Carbon monoxide (CO) - a colorless gas that can be harmful at high levels.
2. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) - gases that can lead to the formation of smog and respiratory problems.
3. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) - a gas that can cause acid rain, damaging ecosystems.
4. Particulate matter (PM) - tiny particles that can be inhaled, affecting health, especially in the lungs.
Overall, these pollutants can lead to serious health issues like asthma, lung cancer, and heart diseases, and contribute to environmental problems like smog and acid rain.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine living in a city with heavy traffic. Every time a car passes, it releases pollutants. Over time, these pollutants accumulate in the air, similar to how dust gathers in a corner of a room. Just as too much dust can make it hard to breathe or cause allergies, air pollution can make it hard for people to breathe properly and can even cause serious health problems.
Ozone Depletion
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Ozone Depletion
○ The use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other ozone-depleting substances has led to the thinning of the ozone layer, particularly in the polar regions.
○ The ozone layer protects life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation, and its depletion has increased the risks of skin cancer, cataracts, and other health issues.
Detailed Explanation
Ozone depletion refers to the thinning of the ozone layer caused by human-made chemicals, particularly chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which were once commonly used in refrigerants and aerosol sprays. The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, acts as a shield, absorbing the majority of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. As the ozone layer depletes, more UV rays reach the Earth's surface, increasing health risks for humans, such as skin cancer and eye cataracts, as well as negative effects on ecosystems and wildlife.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the ozone layer as a sunscreen for the Earth. When we use too much sunscreen and it gets thin or has holes, we become more susceptible to sunburn. Similarly, when the ozone layer thins out due to CFCs and other chemicals, it cannot protect us as effectively from the sun’s harmful rays, leading to increased health problems and environmental issues.
Global Warming
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Global Warming
○ The increase in greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, due to human activities, is contributing to global warming, which is causing rising global temperatures, melting polar ice, and changing weather patterns.
○ Addressing global warming requires international cooperation to reduce emissions, transition to renewable energy sources, and promote environmental sustainability.
Detailed Explanation
Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth's average temperature due to the buildup of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, in the atmosphere from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. This increase in temperature leads to consequences such as melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and shifts in weather patterns, resulting in extreme weather events. Tackling global warming requires a concerted global effort to reduce emissions, use renewable energy sources, and promote sustainable practices to protect the environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Earth’s atmosphere like a thick blanket that keeps you warm. If you add more blankets, you get too hot. Similarly, increasing amounts of greenhouse gases act like extra blankets for the Earth, trapping heat and leading to global warming. Just as we would want to remove some blankets to cool down, we need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impact of global warming.
Key Concepts
-
Air Pollution: Harmful substances released into the atmosphere through industrial activities and vehicles.
-
Ozone Depletion: Thinning of the ozone layer caused by CFCs and similar substances.
-
Global Warming: The rise in Earth’s temperatures due to increased greenhouse gases.
Examples & Applications
Example of Air Pollution: Smog in urban areas due to vehicle emissions.
Example of Ozone Depletion: The hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica.
Example of Global Warming: Increased frequency and intensity of hurricanes due to temperature rise.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Clean air for you and me, helps us breathe and live so free.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a land of clear skies, the people learned that pollutants contain harmful lies. They vowed to clean the air, to protect their health and fair, realizing their actions require care.
Memory Tools
UV Safe for ozone: U is for Ultraviolet and V for Vulnerability.
Acronyms
GIG
Greenhouse Increasing Gases remind us of global warming.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Air Pollution
The presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere resulting from human activities.
- Ozone Layer
A protective layer in the Earth's stratosphere that absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- Greenhouse Gases
Gases in the Earth's atmosphere that trap heat and contribute to global warming.
- CFCs
Chlorofluorocarbons, substances that deplete the ozone layer.
- Global Warming
The long-term rise in Earth's average temperature due to increased greenhouse gas concentrations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
