Water Vapor
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Water Vapor
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to discuss water vapor, an important component of our atmosphere. Can anyone explain what water vapor is?

Isn't it just water in the form of gas?

Exactly! Water vapor is indeed water in a gaseous state. It plays a significant role in weather and climate. Does anyone know how water vapor affects weather patterns?

Does it help in making clouds?

Yes! In fact, water vapor is crucial for cloud formation. When it cools, it condenses to form clouds and can lead to precipitation. Remember this key phrase: ‘water vapor creates waves of weather’ as a memory aid!

So, without water vapor, there wouldn't be any clouds or rain?

That's correct! Water vapor is indispensable for precipitation. Let's summarize: water vapor is vital for cloud formation and affects our weather patterns.
Impact of Water Vapor on Temperature
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss the greenhouse effect. How does water vapor fit into this important process?

I think water vapor helps keep the Earth's temperature warm, right?

Precisely! Water vapor, along with other greenhouse gases, traps heat in the atmosphere. This is essential for keeping our planet warm enough to support life. Can anyone think of a disadvantage to having too much water vapor?

Maybe that would cause warming?

Exactly! An excess of water vapor can enhance the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming. Let's use the mnemonic 'HVAC' to remember: Heat, Vapor, Atmosphere, Climate – key concepts in understanding this process.

So water vapor can actually contribute to climate change?

Yes, and that's why understanding water vapor is crucial in climate studies. To recap, water vapor is essential for temperature regulation and can influence climate change.
The Water Cycle and Its Relationship with Water Vapor
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's connect water vapor to the water cycle. Who can explain how water vapor participates in this cycle?

Water vapor forms clouds and then falls as precipitation, right?

Absolutely! Water vapor rises, cools, and condenses to form clouds. This cycle is vital for replenishing our water sources. What happens after precipitation?

It goes back into the bodies of water or the ground?

Right! It's an ongoing cycle. We can remember this with the acronym ‘WEEP’ for Water, Evaporation, Excess, Precipitation. This summarizes the water vapor's journey!

So, if there’s more water vapor, does that mean it can also increase rainfall?

Yes! More water vapor can lead to heavier rainfall, which ties back to our earlier discussions on climate. To summarize, water vapor is central to the water cycle and greatly influences weather patterns.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
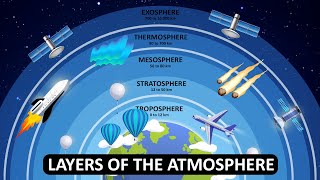
In the atmosphere, water vapor varies in concentration based on location and time, playing a key role in climate and weather phenomena. It is integral to processes like cloud formation and precipitation, while also contributing to the greenhouse effect that helps regulate Earth's temperature.
Detailed
Water Vapor
Water vapor is an essential component of the Earth's atmosphere, significantly impacting both weather and climate. It exists in varying concentrations that depend on geographic location and temporal factors, such as time of day. The presence of water vapor is vital for cloud formation, which leads to precipitation in the form of rain, snow, or hail.
Additionally, water vapor contributes to the greenhouse effect, where it traps heat in the atmosphere, thereby playing a critical role in maintaining the Earth's temperature at a level suitable for life. This section explores how water vapor behaves within the atmosphere and its critical functions in various atmospheric processes.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Water Vapor as a Component of the Atmosphere
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Water vapor is another crucial component of the atmosphere. It varies in concentration depending on the location and time of day, affecting weather patterns and climate.
Detailed Explanation
Water vapor is essentially water in its gaseous state and plays a significant role in the atmosphere. Its concentration can change based on various factors such as geography (e.g., coastal vs. desert areas) and time (e.g., daytime heating vs. nighttime cooling). These variations influence not only local weather conditions but also broader climate patterns across the planet.
Examples & Analogies
Think of water vapor like the different levels of humidity you feel on a summer day. When the air is thick and moist, it often leads to more clouds and possibly rain, much like a sponge that can soak up water until it's full and starts to drip.
Water Vapor and Weather Patterns
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Water vapor is responsible for cloud formation, precipitation, and influencing the Earth's temperature through the greenhouse effect.
Detailed Explanation
Water vapor contributes to the formation of clouds as it rises, cools, and condenses into tiny droplets. This process is essential for precipitation. Additionally, water vapor acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heat in the atmosphere, which helps to keep Earth's temperature at a level that supports life. Without sufficient water vapor, the Earth would be much colder, making it less hospitable for living beings.
Examples & Analogies
You can imagine how a warm, steamy bathroom quickly becomes humid after a hot shower. The warm water vapor in the air not only creates a comfortable feeling but also can cause the mirrors to fog up, similar to how clouds form in the sky when water vapor cools and condenses.
Key Concepts
-
Water Vapor: The gaseous form of water that is essential for weather and climate.
-
Greenhouse Effect: The process by which certain gases trap heat in the atmosphere, including water vapor.
-
Cloud Formation: Water vapor condenses to form clouds, crucial for precipitation.
-
Water Cycle: The continuous cycle of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation involving water vapor.
Examples & Applications
An example of water vapor's effect can be seen when humid weather leads to an increase in cloud formation and increased likelihood of rain.
When temperatures rise, water vapor in the atmosphere increases, which can enhance the greenhouse effect and lead to warmer temperatures.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Vapor up high, clouds in the sky, makes rain fall, oh my!
Stories
Once in a land, a cloud named Wavy always danced in the sky, cooling down like it should, to rain on the ground, ensuring life thrived with its gentle touch.
Memory Tools
Remember 'HVAC' for Heat, Vapor, Atmosphere, Climate to understand water vapor’s importance.
Acronyms
WEEP – Water, Evaporation, Excess, Precipitation summarizes the water cycle.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Water Vapor
Water in a gaseous state, which plays a crucial role in weather and climate.
- Greenhouse Effect
The warming of the Earth's surface due to the trapping of heat by greenhouse gases, including water vapor.
- Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds to the Earth's surface, such as rain, snow, or hail.
- Humidity
The amount of water vapor present in the air, influencing comfort and weather conditions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
